|
Nanoelectronic Research Initiative
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical properties need to be studied extensively. Some of these candidates include: hybrid molecular/semiconductor electronics, one-dimensional nanotubes/nanowires (e.g. carbon nanotube or silicon nanowires) or advanced molecular electronics. Nanoelectronic devices have critical dimensions with a size range between 1 nm and 100 nm. Recent silicon MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) technology generations are already within this regime, including 22 nanometers CMOS (complementary MOS) nodes and succeeding 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) generations. Nanoelectronics is sometimes considered as disruptive technology because present candidates are significantly different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
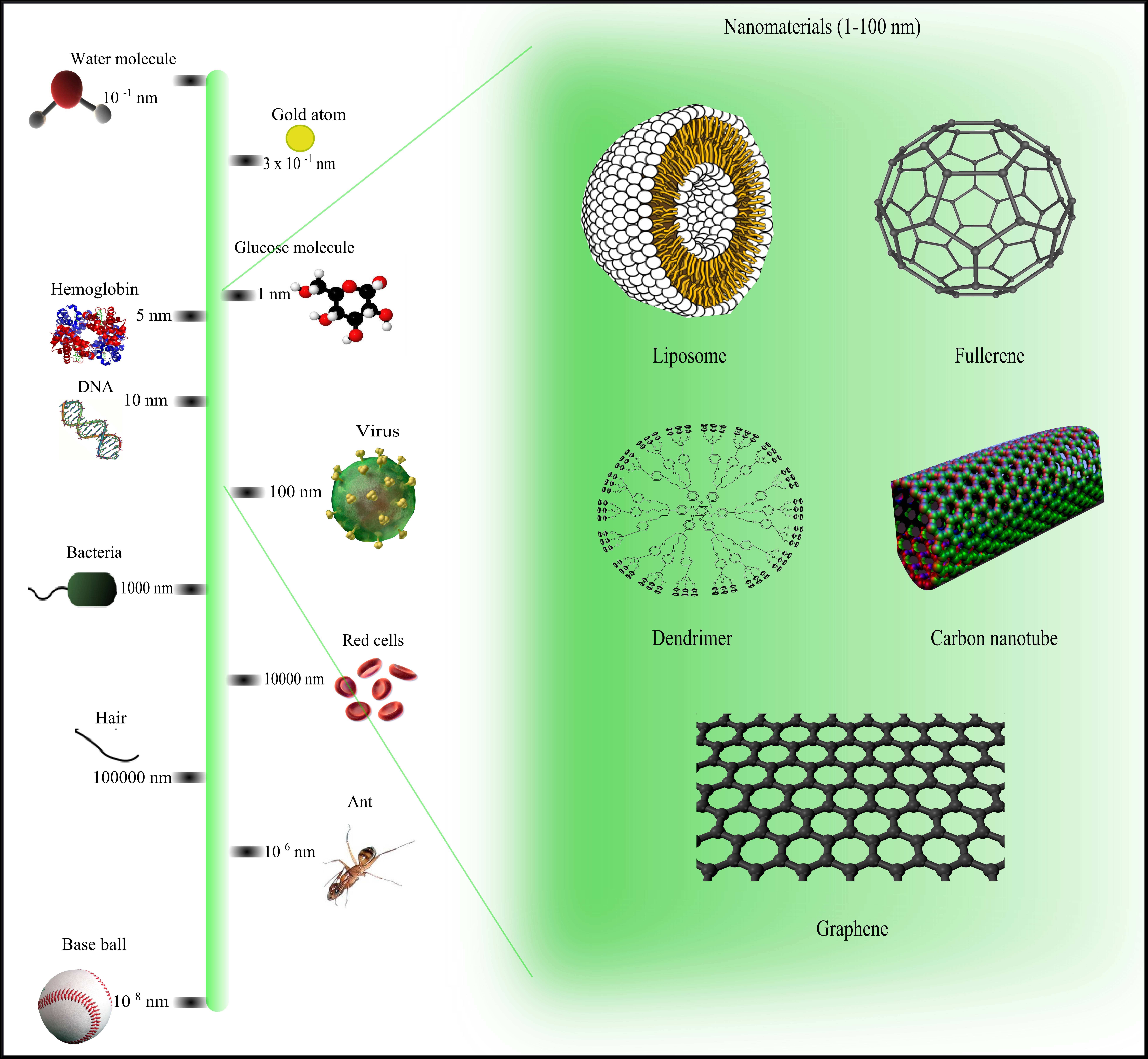
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 Nm Process
In semiconductor fabrication, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) defines the "10 nanometer process" as the MOSFET technology node following the "14 nm" node. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch on a "10nm" device is ten nanometers. For example, GlobalFoundries' " 7 nm" processes are dimensionally similar to Intel's "10 nm" process. TSMC and Samsung's "10 nm" processes are somewhere between Intel's "14 nm" and "10 nm" processes in transistor density. The transistor density (number of transistors per square millimetre) is more important than transistor size, since smaller transistors no longer necessarily mean improved performance, or an increase in the number of transistors. All production "10 nm" processes are based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless battery-powered drills are proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for surgery, dentistry, miniatures, and other applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power (physics)
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a Scalar (physics), scalar quantity. Specifying power in particular systems may require attention to other quantities; for example, the power involved in moving a ground vehicle is the product of the aerodynamic drag plus traction (engineering), traction force on the wheels, and the velocity of the vehicle. The output power of a Engine, motor is the product of the torque that the motor generates and the angular velocity of its output shaft. Likewise, the power dissipated in an electrical element of a electrical circuit, circuit is the product of the electric current, current flowing through the element and of the voltage across the element. Definition Power is the Rate (mathematics), rate with respect to time at which work is done or, more generally, the rate of change of total mechanical energy. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Area
The surface area (symbol ''A'') of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of one-dimensional curves, or of the surface area for polyhedra (i.e., objects with flat polygonal faces), for which the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces. Smooth surfaces, such as a sphere, are assigned surface area using their representation as parametric surfaces. This definition of surface area is based on methods of infinitesimal calculus and involves partial derivatives and double integration. A general definition of surface area was sought by Henri Lebesgue and Hermann Minkowski at the turn of the twentieth century. Their work led to the development of geometric measure theory, which studies various notions of surface area for irregular objects of any dimension. An important example is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid (gas or liquid) that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region (e.g., bounding volume). In ancient times, volume was measured using similar-shaped natural containers. Later on, standardized containers were used. Some simple three-dimensional shapes can have their volume easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of more complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscopic Scale
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Node
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as RAM and flash memory). It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physico-chemical process (with steps such as thermal oxidation, thin-film deposition, ion-implantation, etching) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. This article focuses on the manufacture of integrated circuits, however steps such as etching and photolithography can be used to manufacture other devices such as LCD and OLED displays. The fabrication process is performed in highly specialized semiconductor fabrication plants, also called foundries or "fabs", with the central part being the "clean room". In more advanced semicond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship. It is an experience-curve law, a type of law quantifying efficiency gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel and former CEO of the latter, who in 1965 noted that the number of components per integrated circuit had been exponential growth, doubling every year, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. Moore's empirical evidence did not directly imply that the historical trend would continue, nevertheless, his prediction has held si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Moore
Gordon Earle Moore (January 3, 1929 – March 24, 2023) was an American businessman, engineer, and the co-founder and emeritus chairman of Intel Corporation. He proposed Moore's law which makes the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Early life and education Gordon Moore was born in 1929 as the second son of Walter Harold Moore (a sheriff in San Mateo County) and Florence Almira "Mira" Williamson (a homemaker). When Moore started school in 1935, the faculty noted his introverted personality. His father accepted a promotion to deputy sheriff in 1938 and moved the family to Redwood City, California. In 1940, Moore received a chemistry set as a Christmas gift, which inspired him to become a chemist. From 1942 to 1946, Moore studied at Sequoia High School, where he was involved in athletic activities. From 1946 to 1947, Moore attended San José State College (now San José State University), studying chemistry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistors
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminal (electronics), terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or Electric current, current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits. Because transistors are the key active components in practically all modern electronics, many people consider them one of the 20th century's greatest inventions. Physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |