|
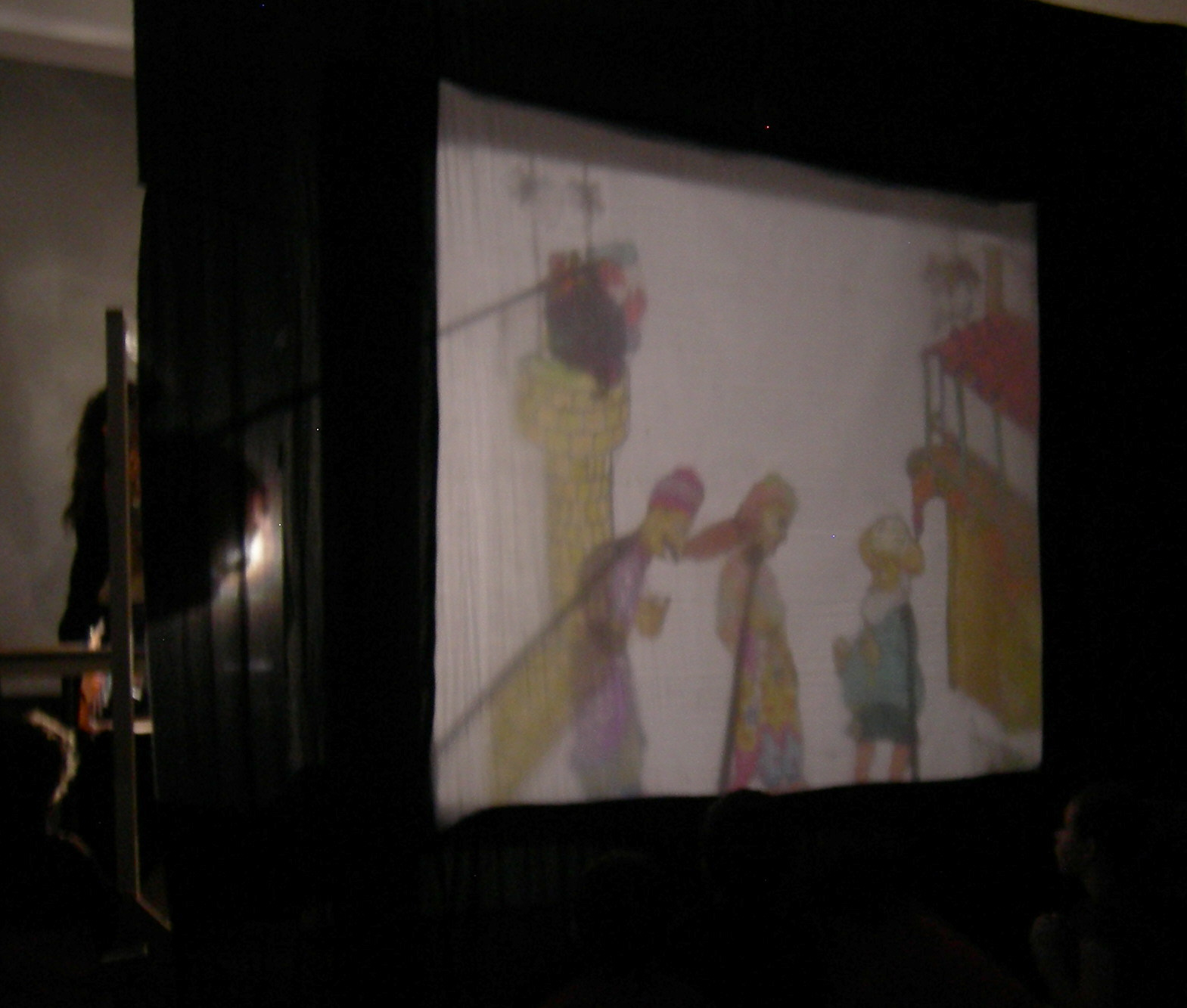
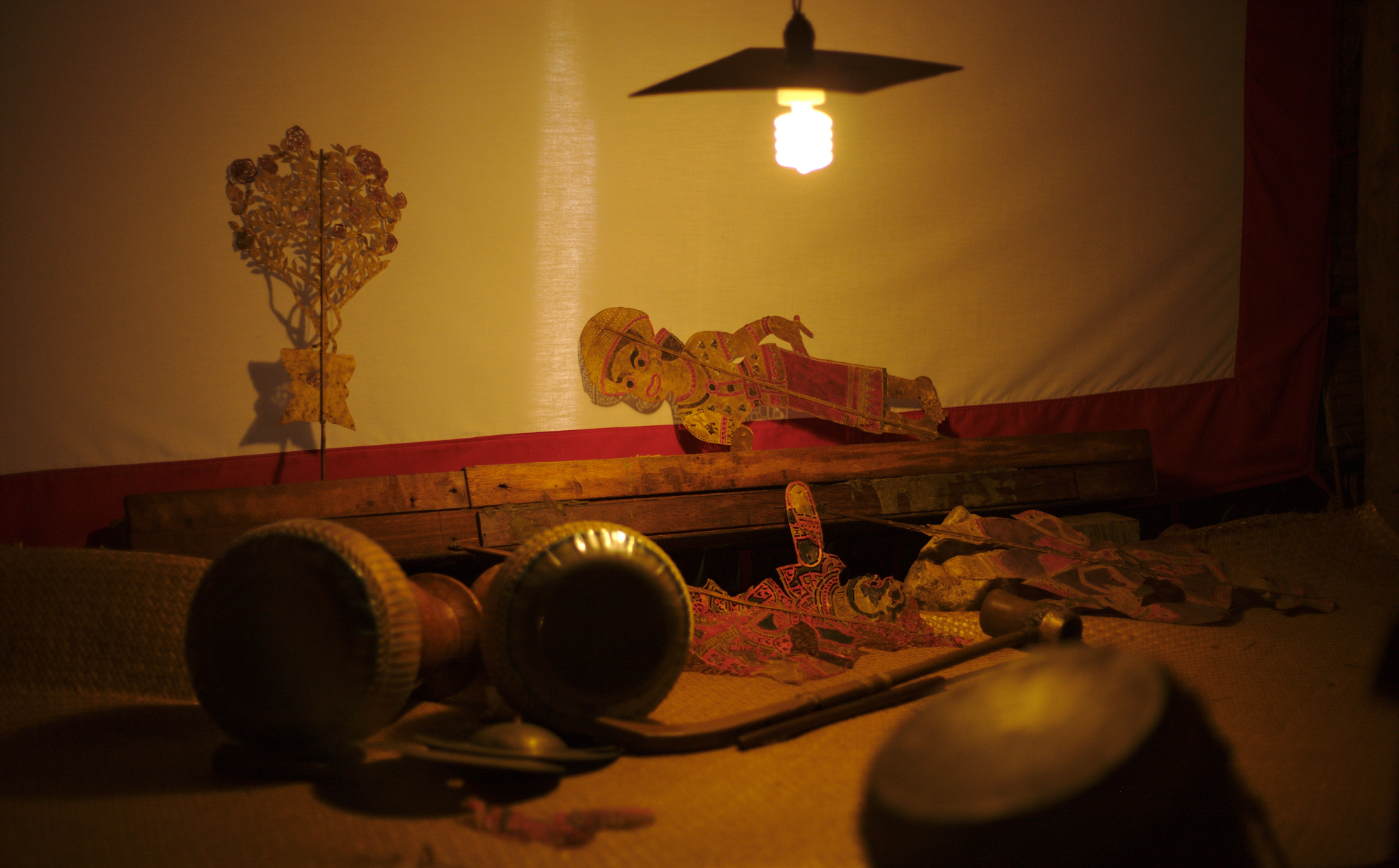
Nang Yai
''Nang yai'' (, ) is a form of shadow play found in Thailand. Puppets are made of painted buffalo hide, while the story is narrated by songs, chants and music. '' Nang'' means "leather" ("leather puppet" in this case), and in common usage refers to a dance-drama shadow puppet show. ''Nang yai'', whose name specifically means "large shadow puppet", features life-size puppets, while '' nang talung'' (a similar tradition of shadow puppetry whose name derives from Phattalung, a southern city where the tradition has long been popular) features much smaller puppets. Both are particularly popular in southern Thailand. According to James Brandon, most scholars believe that ''nang yai'' came to Thailand via Java and the Malay Peninsula from India. ''Nang yai'' and ''nang talung'' incorporate various episodes of the Indian epic ''Ramayana'' (known as the '' Ramakien'' in Thailand). The art form's traditions originated around the beginning of the 15th century. ''Nang yai'' performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nang Yai Puppet
Nang or nangs may refer to: * Nang County, Nyingchi, Tibet, China * Nang yai, a form of shadow play * '' Nang!'', a general interest magazine * Nang, a slang term for nitrous oxide (N2O), also known as laughing gas, when used as a recreational drug. Or less commonly for whipped-cream chargers. * Nang, Leh, a village in Ladakh, India * "Nangs", a Tame Impala song in the 2015 album ''Currents'' * Naan Naan () is a leavened, oven-baked or tawa-fried flatbread, that can also be baked in a tandoor. It is characterized by a light and fluffy texture and golden-brown spots from the baking process. Naan is found in the cuisines of Central Asia ... (Chinese:馕, pinyin:náng), a leavened, oven-baked or tawa-fried flatbread. People named Nang: * Che Nang (14th century), Annamese vassal king of Champa * Nang Keo Phimpha (14th century), Laotian ruler * Philibert Nang (born 1967), Gabonese mathematician {{disambig, given name, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. European travellers in the early 16th century called Ayutthaya one of the three great powers of Asia (alongside Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara and China). The Ayutthaya Kingdom is considered to be the precursor of modern Thailand, and its developments are an important part of the history of Thailand. The name Ayutthaya originates from Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya, a Sanskrit word. This connection stems from the Ramakien, Thailand's national epic. The Ayutthaya Kingdom emerged from the Mandala (political model), mandala or merger of three maritime city-states on the Lower Chao Phraya Valley in the late 13th and 14th centuries (Lopburi province, Lopburi, Suphan Buri province, Suphanburi, and Ayutthaya). The early kingdom was a maritime confedera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karagöz And Hacivat
Karagöz ( in Turkish) and Hacivat (shortened in time from "Hacı İvaz" meaning "İvaz the Pilgrim", and also sometimes written as Hacivad) are the lead characters of the traditional Turkish shadow play, popularized during the Ottoman period and then spread to most nation states of the Ottoman Empire. It is most prominent in Turkey, Syria, Egypt, Greece, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Adjara (autonomous republic of Georgia). In Greece, Karagöz is known by his local name Karagiozis; in Bosnia and Herzegovina, he is known by his local name Karađoz. Overview The central theme of the plays is the contrasting interaction between the two main characters. These are perfect foils of each other: in the Turkish version, Karagöz represents the illiterate but straightforward public, whereas Hacivat belongs to the educated class, speaking Ottoman Turkish and using a poetical and literary language. Although Karagöz is the more popular character with the Turkish peasantry, Hacivat is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholu Bommalata
''Tholu bommalata'' is the shadow puppet theatre tradition of the state of Andhra Pradesh in India with roots dating back to 3rd century BCE. Its performers are part of a group of wandering entertainers and peddlers who pass through villages during the course of a year and offer to sing ballads, tell fortunes, sell amulets, perform acrobatics, charm snakes, weave fishnets, tattoo local people and mend pots. ''Tholu bommalata'' has a history of consistent royal patronage. It is the ancestor of Wayang, the Indonesian puppet theatre play which has been a staple of Indonesian tourism and designated by UNESCO as Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. This ancient custom, which for centuries before radio, film, and television provided knowledge of Hindu epics and local folk tales, not to mention news, spread to the most remote corners of the Indian subcontinent. The puppeteers comprise some of the various entertainers who perform all night and usually reenact various stories from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayang
( , ) is a traditional form of puppet theatre play originating from the Indonesian island of Java. The term refers both to the show as a whole and the puppet in particular. Performances of wayang puppet theatre are accompanied by a ''gamelan'' orchestra in Java, and by '' gender wayang'' in Bali. The dramatic stories depict mythologies, such as episodes from the Hindu epics the ''Ramayana'' and the ''Mahabharata'', as well as local adaptations of cultural legends. Traditionally, a is played out in a ritualized midnight-to-dawn show by a , an artist and spiritual leader; people watch the show from both sides of the screen. performances are still very popular among Indonesians, especially in the islands of Java and Bali. performances are usually held at certain rituals, certain ceremonies, certain events, and even tourist attractions. In ritual contexts, puppet shows are used for prayer rituals (held in temples in Bali), ritual (cleansing children from bad luck), and ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hun Lakhon Lek
''Hun lakhon lek'' (, ) is a type of traditional small Thai puppet which uses three puppeteers working together to produce a character with more mobility and lifelike movement. History ''Hun la korn lek'' has been a form of entertainment for the Thai people and foreigners alike for more than a century. It was invented by Kru Krae Suppawanich in 1901 during the reign of King Mongkut (King Rama IV). He developed it while trying to construct a Hun Laung (Royal Thai puppet), which he found involved too many complicated structures and too many strings. He decreased the number of the strings inside the puppet, and thus invented ''hun la korn lek''. His first performance was in Varadis Palace. Kru Kare continued performing with his puppets, but after World War II he found he was growing older, and that ''hun la korn lek'' was beginning to decrease in popularity. He passed 30 of his puppets onto his daughter-in-law, and the rest of his puppets were "drowned" in the Chao Phraya Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nang Talung
''Nang talung'' (, ) is a traditional style of shadow puppetry from southern Thailand. Similar arts are found in Cambodia, Malaysia, and Indonesia. ''Nang'' means "leather" ("leather puppet" in this case), and ''talung'' is an abbreviation of Phattalung, a southern city where the shadow play tradition has long been popular. ''Nang yai'' features life-size puppets, while ''nang talung'' puppets are much smaller. ''Nang talung'' has been extremely popular for a long time. On the other hand, the art form is slowly disappearing because it is complicated. There is a campaign to preserve the traditions of ''nang talung'' for future generations. The Malaysian wayang kulit gedek has its origin from Nang Talung. History Many scholars believe that shadow play performances such as ''Nang Talung'' represent one of the oldest forms of theatrical art in human civilization. They were once widespread in Europe and Asia. Some evidence suggests that after Alexander the Great conquered Egypt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Thailand
Eastern Thailand is a region of Thailand, bordering Cambodia in the east, Northeastern Thailand in the north, and Central Thailand in the west. Geography Eastern Thailand lies between the Sankamphaeng Range, which forms a natural border with the Khorat Plateau to the north and the Gulf of Thailand to the south. The geography of the region is characterised by short mountain ranges (collectively grouped under the Chanthaburi Range) alternating with small basins of short rivers which drain into the Gulf of Thailand. Between the Chanthaburi and Sankamphaeng mountains lies the basin of the Bang Pakong River system. Fruit is a major component of agriculture in the area, and tourism plays a strong part in the economy. The region's coastal location has helped promote eastern seaboard industrial development, a major factor in the economy of the region. Islands off Eastern Thailand's coast include Ko Sichang, Ko Lan, Ko Samet, and Ko Chang. National parks Within the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi (, ) or Rajburi, Rat Buri) is a town ('' thesaban mueang'') in western Thailand, capital of Ratchaburi Province. Ratchaburi town covers the entire ''tambon'' Na Mueang (หน้าเมือง) of Mueang Ratchaburi District. As of 2017 it had an estimated population of 36,169, down from 38,149 in 2005. History The earliest evidence of settled habitation is that of the Dvaravati culture. At one time it was thought that the early town was founded on the coast of the Gulf of Thailand, and that over time the coast had moved 30 km (18 miles) away to the south, due to sedimentation coming down the Mae Klong River. However, geological and palynological investigation has shown that these early Dvaravati and proto-Dvaravati towns were all inland, at the edges of swamps when founded. Ratchaburi remains an important commercial centre, however. Archeological discoveries show that the area was already settled in the Bronze Age, and the town itself is known to have existed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Thailand
Central Thailand (Central Plain) (historically also known as Siam or Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun Mountains, Phetchabun mountain range. The Tenasserim Hills separate it from Myanmar to the west. In the north it is bounded by the Phi Pan Nam Range, one of the hilly systems of northern Thailand. The area was the heartland of the Ayutthaya Kingdom (at times referred to as Siam) and is still the dominant area of Thailand since it contains the world's most primate city#Examples, primate city, Bangkok. Definition The grouping of Thai provinces into regions follow two major systems in which Thailand is divided into either Regions of Thailand, four or six regions. In the six-region system, commonly used in geographical studies, central Thailand extends from Sukhothai Province, Sukhothai and Phitsanulok Province, Phitsanulok Provinces in the north t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khon
Khon (, ) is a dance drama genre from Thailand. Khon has been performed since the Ayutthaya Kingdom. It is traditionally performed solely in the royal court by men in masks accompanied by narrators and a traditional piphat ensemble. A variation of this genre with female performers is called ''khon phu ying'' (). History Khon is a Thai traditional dance which combines many arts like dance and drama. There was no exact evidence that dates its provenance, but it is mentioned in Thai literature's ''Lilit Phra Lo'' (c. 1529) which was written before the era of King Narai Maharaj.Sri Venkatesvara University, Oriental Research Institute. (2004). ''Sri Venkateswara University Oriental Journal Vol. 47''. p. 23. "In the reign of King Narai, Monsieur de La Loubere, French ambassador to Siam, wrote about the Khon performance in which performers wore masks." * Klamcharoen, A.. (1993). ''Sunthariyanattasin Thai'' ��ุนทรียนาฏศิลป์ไทย (2nd ed.). Bangkok: O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |