|
Namazga
Namazga-Tepe or ''Namazga-depe'', is a Bronze Age ( BMAC) archaeological site in Turkmenistan, at the foot of the Kopet-Dag, near the delta of the Tejen River, some 100 km east of Aşgabat, near the border to Iran. Excavated by Vadim Mikhailovich Masson, Viktor Sarianidi, and I. N. Khlopin from the 1950s, the site set the chronology for the Bronze Age sites in Turkmenistan (Namazga III-VI). Namazga culture was preceded in the area by the Jeitun culture. Chronology It is believed that the Anau culture of Turkmenistan considerably precedes the Namazga culture in the area. Namazga I period (c. 4000–3500 BC),Vidale, Massimo, (2017)Treasures from the Oxus. p. 9, Table 1. is considered contemporary with Anau IB2 period. Namazga III (c. 3200–2800) as a village settlement in Late Chalcolithic phase, and Namazga IV (c. 2800–2400 BC) as a proto-urban site, both belong to the Late Regionalization Era. Namazga V (c. 2400–2000 BC), is in the Integration Era or the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to –1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, –1700 BC.Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Turkmenistan Complex Archaeological Expedition
The South Turkmenistan Complex Archaeological Expedition (STACE), also called the South Turkmenistan Archaeological Inter-disciplinary Expedition of the Academy of Sciences of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic (YuTAKE) was endorsed by the Turkmenistan Academy of Sciences. It was initially organized by the Oriental studies, orientalist Mikhail Evgenievich Masson in 1946. The expedition had several excavations or "Brigades", based on sites and periods, and were spread over many years. The Chalcolithic settlements of southern Turkmenistan, according to Masson, date to the late 5th millennium – early 3rd millennium BC, as assessed by carbon dating and Paleomagnetism, paleomagnetic studies of the findings from the excavations carried out by STACE in the Altyndepe and Tekkendepe. The foothills of the Kopetdag mountains have revealed the earliest village cultures of Central Asia in the areas of Namazga-Tepe (more than 50 ha) and Altyndepe (26 ha), Ulug Depe (20 ha), Kara Depe (15 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anau Culture
The Anau culture was an ancient agricultural civilization of Central Asia centred in southern Turkmenistan. It started during the Chalcolithic period around 4000 BC, following the Neolithic Jeitun culture. It is named after its main site of Anau, Turkmenistan. The Namazga culture was contemporary to the Anau culture. Pottery similar to that of Anau (the earliest Anau IA phase) has been found as far as Shir Ashian Tepe in the Semnan Province of Iran. Site of Anau The settlement of Anau started around 4500 BC in the Neolithic period, before copper was used. Thus, it is earlier than Namazga-Tepe, the main site of the Namazga culture. Anau includes two mounds, north and south. Archaeological research here began in 1890. Raphael Pumpelly, Marushchenko, and Khurban Sokhatov were some of the researchers over the years. The lowest layers of the north mound in Anau provide some good evidence for the transition from the Neolithic to the Chalcolithic in the area. This archaeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaz Culture
The Yaz culture (named after the type site Yaz-Tappe, Yaz Tepe, or Yaz Depe, near Baýramaly, Turkmenistan) was an early Iron Age culture of Margiana, Bactria and Sogdia (–500 BC, or –330 BC). It emerges at the top of late Bronze Age sites ( BMAC), sometimes as mud-brick platforms and sizeable houses associated with irrigation systems. Ceramics were mostly hand-made, but there was increasing use of wheel-thrown ware. Bronze and iron arrowheads, also iron sickles and carpet knives among other artifacts have been found. With the farming citadels and absence of burials it has been regarded as a likely archaeological reflection of early East Iranian culture as described in the Avesta. So far, no burials related to the culture have been found, and this is taken as possible evidence of the Zoroastrian practice of exposure or sky burial. Overview Yaz I In the region of Southern Central Asia, the Bronze Age Oxus civilization (or BMAC) was characteristic for irrigation and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
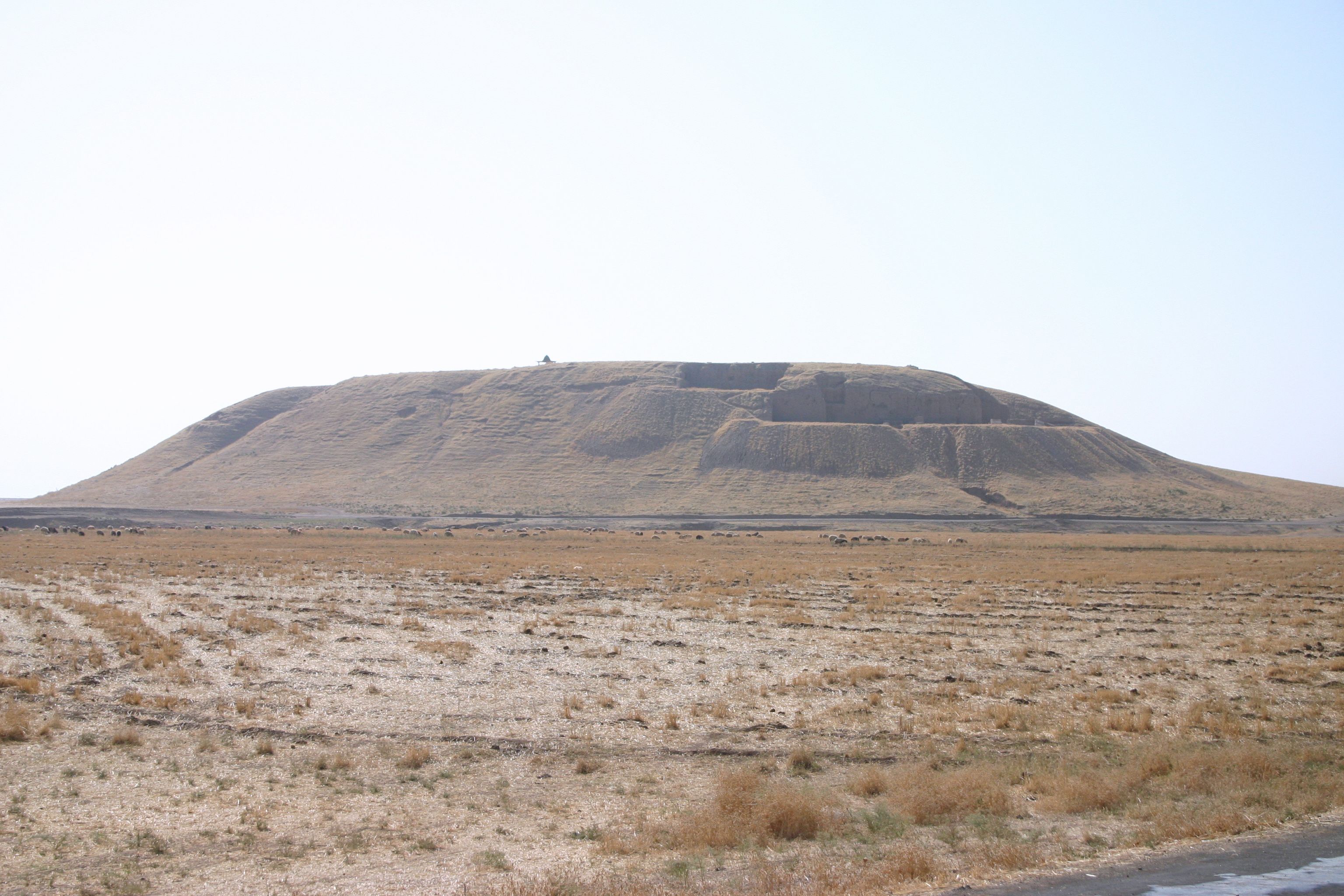
Altyndepe
(, sometimes Altyn Tepe, Turkmen "Golden Hill"), is a Bronze Age ( BMAC) archaeological site in Turkmenistan, near Aşgabat, inhabited first from c. 3200 to 2400 BCE in the Late Regionalization Era, and from c. 2400 to 2000 BCE in the Integration Era as a full urban site. Excavations Large-scale excavations at Altyn-depe started in 1965. During the late Chalcolithic period Altyn Depe became a large-scale center with an area of 25 hectares. It was surrounded by an adobe wall with rectangular watch towers. Several living quarters were uncovered. The area called ''Excavation 9'' was a living quarter with several houses, many of them perhaps belonging to wealthy people. The houses had courtyards and street were running between them. People were often buried within houses. At ''Excavation 5'' and ''Excavation 10'' two other larger parts of living quarters were found. Those belong more likely to craftsmen. The houses are smaller and not so well built. Ziggurat The site is notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
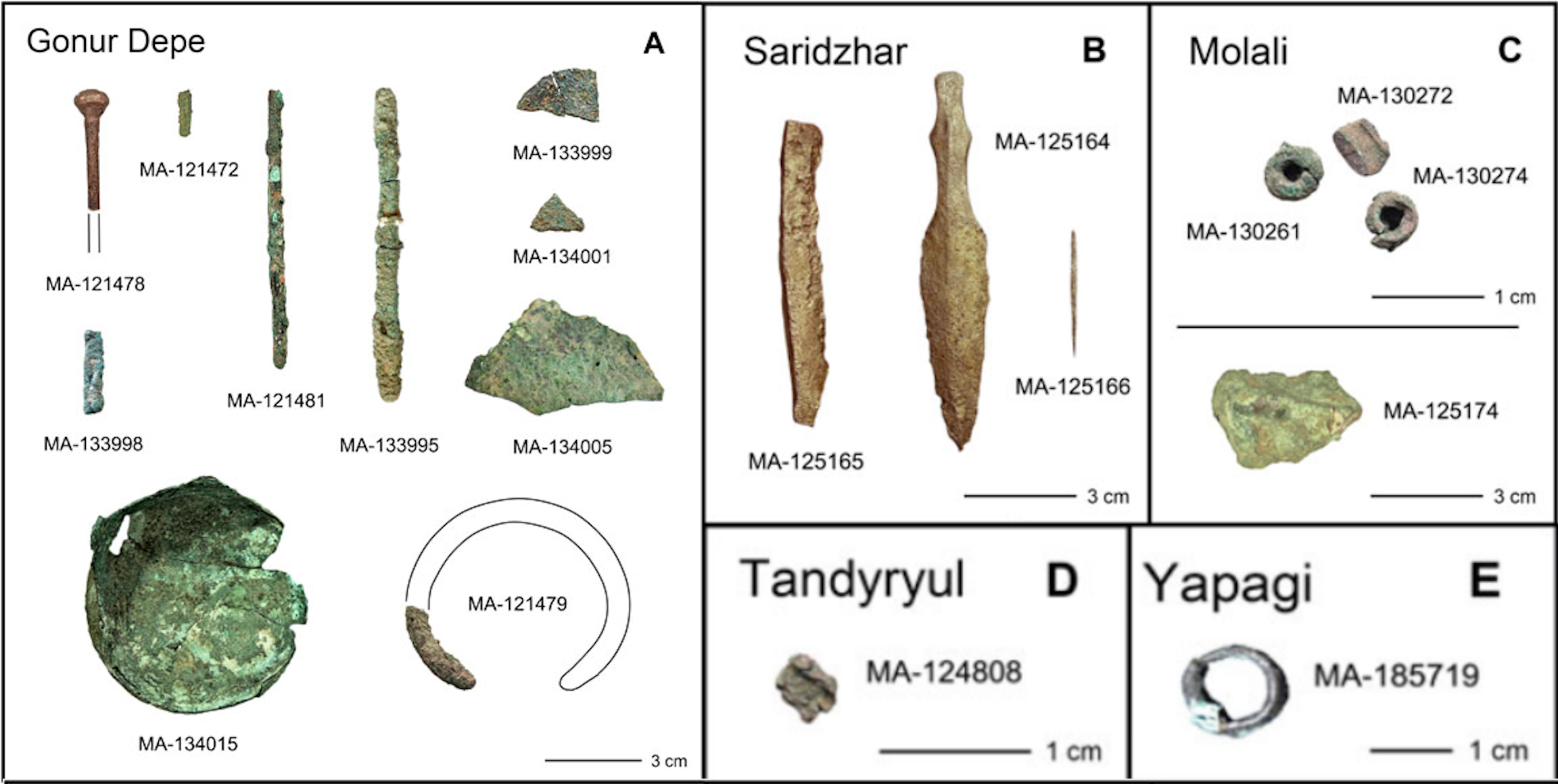
Gonur
Gonur Depe () is an archaeological site, dated from 2400 to 1600 BCE,Frenez, Dennys, (2018)"Manufacturing and trade of Asian elephant ivory in Bronze Age Middle Asia: Evidence from Gonur Depe (Margiana, Turkmenistan)"in Archaeological Research in Asia 15, p. 15. and located about 60 km north of Mary, Turkmenistan, Mary (ancient Merv), Turkmenistan consisting of a large early Bronze Age settlement. It is the "capital" or major settlement of the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC). Archaeology The site was discovered by Greek-Russian archaeologist Viktor Sarianidi. There he took first pottery shards from surface in 1972, and excavated the site since 1974 to 2013. Sarianidi uncovered a palace, a fortified mud-brick enclosure, and temples with Fire temple, fire altars which he associated with the Zoroastrian religion. Gonur Depe has a total area of about 55 hectares, and is divided by archaeologists in three main sectors: Gonur North, the Large Necropolis, and Gonu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alekseyevka Culture
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1150 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." spanning from the southern Urals to the upper Yenisei River in central Siberia and western Xinjiang in the east. In the south, the Andronovo sites reached Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It is agreed among scholars that the Andronovo culture was Indo-Iranian.: "Archaeologists are now generally agreed that the Andronovo culture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Turkmenistan
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tells (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell (from , ', 'mound' or 'small hill') is an artificial topographical feature, a mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them and natural sediment. Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East but are also found elsewhere, such as in Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and Spain,, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic, the Chalcolithic and the Bronze and Iron Ages. In the Southern Levant the time of the tells ended with the conquest by Alexander the Great, which ushered in the Hellenistic period with its own, different settlement-building patterns. Many tells across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex infrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |