|
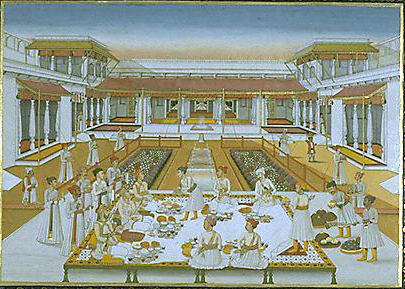
Najibabad
Najibabad is a town in the Bijnor district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, located near the city of Bijnor. It is a major industrial centre and has national transport links via rail and roadways such as NH 119 and NH 74. History Nawab Najib-ud-Daula, also known as Najib Khan Yousafzai, was a noted Rohilla Muslim warrior and serviceman of both the Mughal Empire and the Durrani Empire in 18th century Rohilkhand. In 1751, he founded the town of Najibabad in Bijnor district, India, after he received the title, "Najib-ud-Daula" from Mughal Emperor Alalmgir III. From 1757 to 1770 he was also the governor of Saharanpur, ruling over Dehradun. Many architectural relics of the period of Rohilla he oversaw remain in Najibabad, which he founded at the height of his career as a Mughal minister. He had succeeded Safdarjung as Grand Wazir of the Mughal Empire and was a devoted serviceman of the Mughal Emperor Alamgir II. According to George Foster ("A Journey from Bengal to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najibabad Fort
Najibabad Fort, also known as Sultana Daku Qila and Pathargarh Fort, is an 18th-century fort in Najibabad, Bijnor district, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was built in 1755 by the Mughal minister Najib ad-Dawlah. No longer in active military use, the former fort is a Monument of National Importance, administered by the Archaeological Survey of India. See also * Forts in India * List of forts in India * List of Monuments of National Importance in Agra circle The ASI has recognized 264 Monuments of National Importance in Agra circle of Uttar Pradesh. For technical reasons the Agra circle has to be split in two lists. The rest of Agra circle can be found in the list of Agra district. List of monumen ... References 18th-century forts in India Bijnor district Forts in Uttar Pradesh Monuments of National Importance in Uttar Pradesh {{Fort-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najib Ad-Dawlah
Najib ad-Dawlah (), also known as (), was an Afghan Yousafzai Rohilla who earlier served as a Mughal serviceman but later deserted the cause of the Mughals and joined Ahmad Shah Abdali in 1757 in his attack on Delhi. He was also a House Chief of Rohilkhand, and in the 1740s founded the city of Najibabad in Bijnor, India. He was instrumental in winning the Third Battle of Panipat and has been regarded as one of the greatest generals of India in the 18th century. He began his career in 1743 as an immigrant from Maneri, Swabi (of the Umarkhel subbranch of Mandanr Yousafzais) as a soldier. He was an employee of Imad-ul-Mulk but got alerte from going influence of Marhattas and by advise of Shah Waliullah, he invited Ahmad Shah Abdali in 1757 to attack on Delhi and secure the Muslims place in India. He was then appointed as '' Mir Bakhshi'' of the Mughal emperor by Abdali. Later in his career he was known as Najib ad-Dawlah, Amir al-Umra, Shuja ad-Dawlah. From 1757 to 1770, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najibabad Mosque
The Najibabad Mosque, also known as Jama Masjid Najibabad, is a Friday mosque, located in Najibabad, in the Bijnor district of the Moradabad division, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Najib ad-Dawlah built the Najibabad Fort in 1755, one of oldest Mughal Empire historic monuments in Bijnor district. It is believed that the mosque was completed in 1797. See also * Islam in India * List of mosques in India References 18th-century mosques in India Bijnor district Najibabad Najibabad is a town in the Bijnor district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, located near the city of Bijnor. It is a major industrial centre and has national transport links via rail and roadways such as NH 119 and NH 74. History Nawab ... Mosque buildings with minarets in India Mosques completed in the 1790s Mosques in Uttar Pradesh Mughal mosques Religious buildings and structures completed in 1797 {{India-mosque-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijnor District
Bijnor district () is one of the 75 districts in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. Bijnor city is the district headquarters. The government of Nagar Palika Parishad Bijnor Uttar Pradesh seeks its inclusion in National Capital Region (NCR) due to its close proximity to NCT of Delhi. Bijnor is notable for its sugarcane production and sugar mills, with two of the top five sugar mills situated in the district. History Bijnor district was created in 1817 out of part of Moradabad district, and it was originally called Nagina district after its headquarters at Nagina. The headquarters was relocated to Bijnor in 1824, although the district was still called "Nagina district" until 1837, when it officially became known as Bijnor district. Medieval history In 1399, the district was ravaged by Timur. Later, during the time of Akbar, Bijnor was part of his Mughal Empire. In the early 18th century, the Rohilla Pashtuns established their independence in the area called by the Rohilkh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamgir II
Mirza Aziz-ud-Din Muhammad (June 6, 1699 – November 29, 1759), better known by his regnal name Alamgir II, was the fifteenth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor from 1754 to 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah. Born Mirza Aziz-ud-Din, the second son of Jahandar Shah, was raised to the throne by Imad-ul-Mulk after he deposed Ahmad Shah Bahadur in 1754. On ascending the throne, he took the title of Alamgir and tried to follow the approach of Aurangzeb (Alamgir I). At the time of his accession to the throne he was 55 years old. He had no experience of administration and warfare as he had spent most of his life in jail. He was a weak ruler, with all powers vested in the hand of his vizier, Imad-ul-Mulk. In 1756, Ahmad Shah Abdali, Ahmad Shah Durrani invaded India once again and captured Delhi and plundered Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, Mathura. While the Marathas became more powerful because of their collaboration with Imad-ul-Mulk, and dominated the whole of northern India. This was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
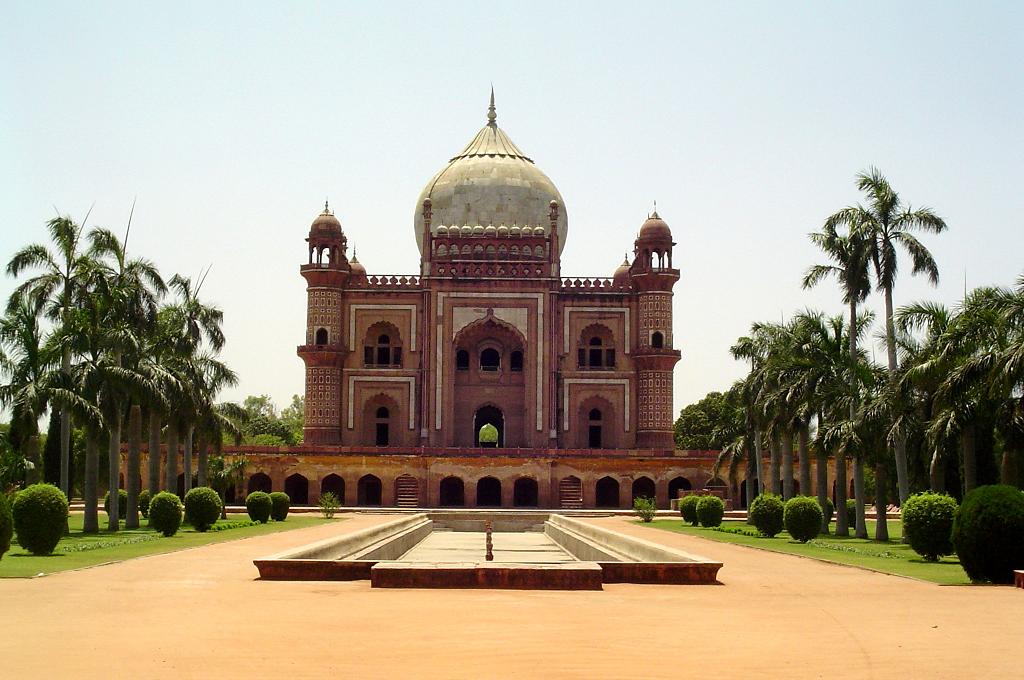
Tomb Of Najib-ud-Daula
The Tomb of Najib-ud-Daula is an 18th-century mausoleum built for Mughal commander and Afghan Rohilla Chieftain . The mausoleum dates from 1751, and is in Najibabad, Uttar Pradesh, India.Führer, Alois Anton (1891) The Monumental Antiquities and Inscriptions' North-Western Provinces and Oudh Volume II (''pg. 33'') Rohilkhand Division See also * Tomb of Mariam-uz-Zamani * Tomb of Akbar the Great * Tomb of Shuja-ud-Daula * Tomb of I'timād-ud-Daulah Tomb of I'timād-ud-Daulah (''I'timād-ud-Daulah Maqbara'') is a Mughal era, Mughal mausoleum in the city of Agra in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Often described as a "jewel box", sometimes called the "Bachcha Taj" or the "Baby Taj", th ... References Mausoleums in Uttar Pradesh Mughal tombs {{Bijnor-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohilla
Rohillas are a community of Pashtuns, Pashtun heritage, historically found in Rohilkhand, a region in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. It forms the largest Pashtun diaspora community in India, and has given its name to the Rohilkhand region. The Rohilla Chieftaincies, Rohilla military chiefs settled in this region of northern India in the 1720s, the first of whom was Ali Mohammed Khan. The Rohillas are found all over Uttar Pradesh, but are more concentrated in the Rohilkhand regions of Bareilly division, Bareilly and Moradabad division, Moradabad divisions. Between 1838 and 1916, some Rohillas migrated to British Guiana, Guyana, Surinam (Dutch colony), Suriname and History of Trinidad and Tobago#British period, Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbean region of the Americas in which they form a subset of the Muslim minority of the Indo-Caribbean ethnic group. After the 1947 Partition of India, many of the Rohillas migrated to Karachi, Pakistan as a part of the Muhajir (Pakistan) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohilkhand
Rohilkhand (today Bareilly, Moradabad, Badaun and Rampur; ) is a region in the northwestern part of Uttar Pradesh, India, that is centered on the Bareilly and Moradabad divisions. It is part of the upper Ganges Plain, and is named after the Rohilla. The region was called Madhyadesh and Panchala in the Sanskrit epics ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana''. During the colonial era in India, the region was governed by the Royal House of Rampur. Etymology ''Rohilkhand'' means "the land of the Rohilla". The term ''Rohilla'' first became common in the 17th century, with ''Rohilla'' used to refer to the people coming from the land of Roh which is a corruption of ''Koh'' meaning mountains (i.e. Kohistan in Persian), which was originally a geographical term that corresponded with the territory from Swat and Bajaur in the north to Sibi in the south, and from Hasan Abdal (Attock) in the east to Kabul and Kandahar in the west. A majority of the Rohillas migrated from Pashtunistan to Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Indian Cities
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safdar Jang
Wazir-ul-Mamalik-e-Hindustan Asaf Jah Jamat-ul-Mulk Shuja-ud-Daula Nawab Abul Mansur Khan Bahadur Safdar Jang Sipah Salar (c. 1708 – 5 October 1754), better known as Safdar Jang, was the second Nawab of Kingdom of Awadh succeeding Saadat Ali Khan I (his maternal uncle and father-in-law) in the year 1739. All future Nawabs of Awadh were patriarchal descendants of Safdar Jang. He was a major political figure at the imperial Mughal court during its declining years. Biography He was a descendant of Qara Yusuf of the Qara Qoyunlu confederation. In 1735, he was given the rank of sipahsalar. In 1739, he succeeded his father-in-law and maternal uncle, Burhan-ul-Mulk Saadat Ali Khan I to the throne of Awadh/Oudh and ruled from 19 March 1739 to 5 October 1754. The Mughal Emperor Muhammad Shah gave him the title of "Safdar Jang". Safdar Jang was an able administrator. He was not only effective in keeping control of Awadh, but also managed to render valuable assistance to the weakene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mughal Grand Viziers
The Grand Vizier of Hindustan (Hindustani language, Hindustani: ) was the highest ranking minister in the Mughal Empire and the chief adviser to the emperor himself. The position acted as the de facto head of government of the Mughal Empire and had responsibility for leading the ministers of the Empire. This is the list of grand viziers (''vazīr-e azam'') of the Mughal Empire. History The seniormost official under the Mughals, or the Prime Minister, held different titles such as ''Vakil, Vakil-us-Sultanat, Wazir, Diwan, Diwan-i-Ala and Diwan Wazir'' under different Mughal emperors. Under Babur and Humayun, the institution of the wazirat was not fully developed owing to a lack of an entrenched nobility and political upheaval. Nonetheless, individuals under both rulers did rise to positions equivalent to the position of prime minister and under Humayun reforms were first attempted to clarify the roles of Vakil and Wazir. In the early years of Akbar's reign, the position of prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |