|
Nagqu
Nagqu (also Naqu, Nakchu, or Nagchu; ; ) is a prefecture-level city in the north of the Chinese autonomous region of Tibet. On May 7, 2018, the former Nagqu Prefecture was officially declared the sixth prefecture-level city in Tibet after Lhasa, Shigatse, Chamdo, Nyingchi and Shannan. The regional area, covering an area of , is bordered by Bayingolin and Hotan Prefectures of Xinjiang to the north, Haixi, Yushu Prefectures of Qinghai and Chamdo to the east, Nyingchi, Lhasa and Shigatse to the south, Ngari Prefecture to the west. As of the 2010 census, it had a population of 462,381. Since its official establishment in 2018, it is the largest prefecture-level city by area in the world, being slightly larger than Sweden. Nagqu contains 89 townships, 25 towns, and 1,283 villages. The main city of Nagqu is along the China National Highway 109, northeast of Lhasa. Amdo, Nyainrong and Xainza are other towns of note. Extremely rich in water resources, with 81% of Tibet's lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seni District
Seni District (; zh, s=色尼区) is a district within the Nagqu of the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Geography and climate Located in the northern part of the Tibet Autonomous Region, Seni ranges in latitude from 30° 31' to 31° 55' N and in longitude from 91° 12' to 93° 02' E. Bordering counties within Nagqu are Lhari County, Lhari to the southeast, Biru County, Biru to the east, Nyainrong County, Nyainrong to the northeast, Amdo County, Amdo to the northwest, and Baingoin County, Baingoin to the west, while Lhasa City, the regional capital, is to the south. With an elevation of around , Nagqu has a harsh, alpine climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen ''EH''), closely bordering on a subarctic climate (''Dwc''), with long, very cold and dry winters, and short, cool summers. In winter, temperatures frequently drop below at night and in summer typically rise to during the day. The monthly 24-hour average daily temperature ranges from in January to in July, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
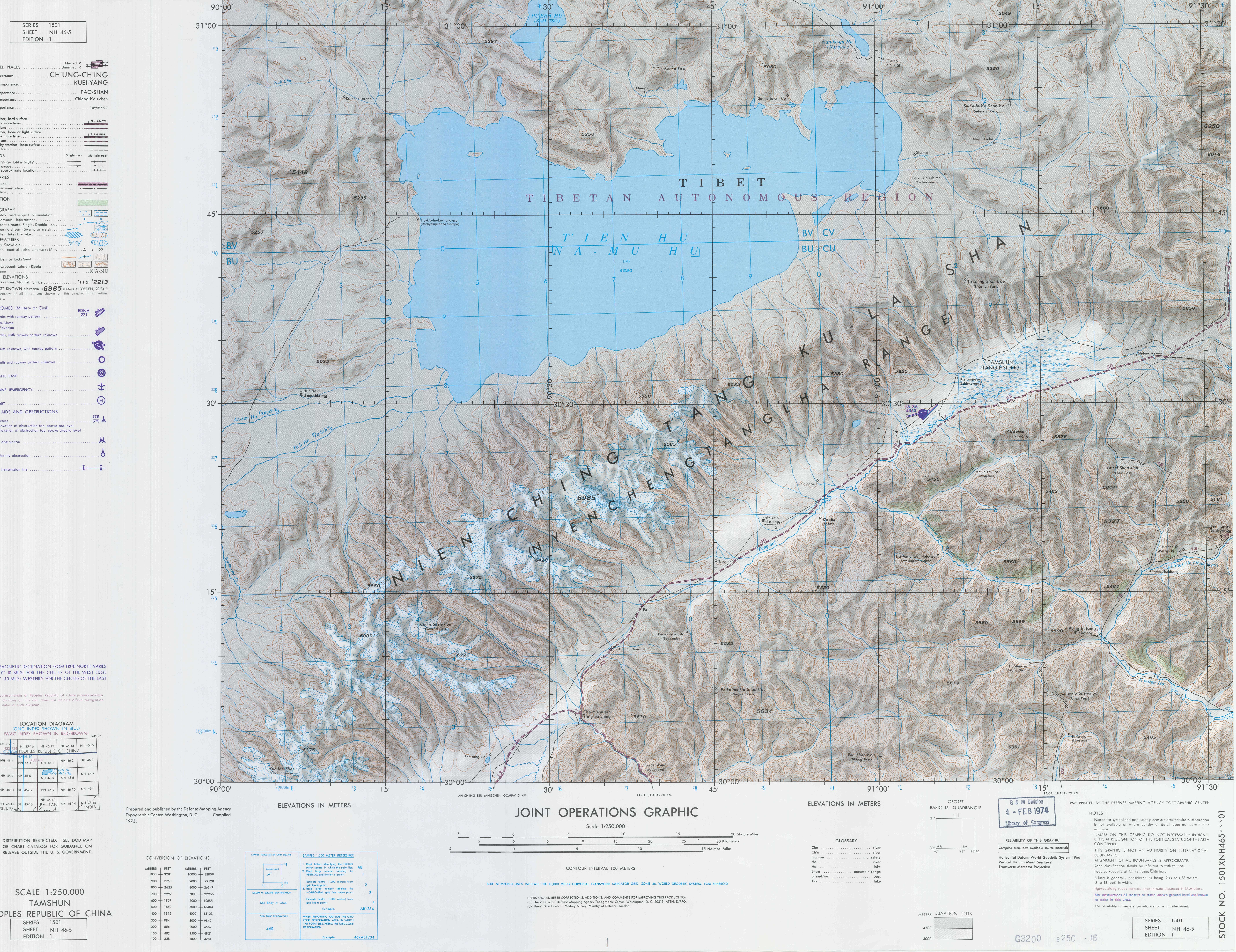
Nagqu Town
Nagqu, Nagchu in original Tibetan or Naqu (), also known as Nagchuka or Nagquka, is a town in northern Tibet, seat of the prefecture-level city of Nagqu, approximately by road north-east of the capital Lhasa, within the China, People's Republic of China. Nagqu railway station to the town's west sits on the Qingzang railway at . "Nagchu (...) is an important stop on both the road and railway line between Qīnghǎi and Tibet. In fact, this is where Hwy 317 ends as it joins the Qīnghǎi–Tibet Hwy (Hwy 109) on its way to Lhasa." At the time of the visit in 1950 of Thubten Jigme Norbu, the elder brother of Tenzin Gyatso the 14th Dalai Lama, Nagchukha was a small town with only a few clay huts but was also the headquarters of the District Officer, the Dzongpön. It was on the main caravan route coming from Amdo to Central Tibet. In 2010 China announced plans to build the highest airport in the world at Nagqu, at an altitude of , but construction of Nagqu Dagring Airport, the airpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the Tibet Area (administrative division), Tibet Area, a former administrative division of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. The current borders of the Tibet Autonomous Region were generally established in the 18th century and include about half of Tibet, cultural Tibet, which was at times independent and at times under Mongol or Chinese rule. The TAR spans more than and is the second-largest Administrative divisions of China, province-level division of China by area. Due to its harsh and rugged terrain, it has a total population of only 3.6 million people or approximately . Names and etymologies Tibet Autonomous Region is often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Hanyu Pinyin. The earliest official record of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdo Town
Pana, or Pagnag (), also known as Anduo, or Amdo, is a town and the seat of Amdo County in the Nagqu Prefecture of the Tibet Autonomous Region, in China. It lies 464 kilometres north of Lhasa and 138 km north of Nagchu Town, Nagqu. As of 2004 its jurisdiction had a population of about 2700, 683 of which were living in the town of Pana. The principal economic activity is animal husbandry, pastoral yak, goat, sheep, and so on. Blueschist outcrops are found in the area. The villagers in recent times organized a railway protecting committee to select locals to monitor the Qinghai-Tibet Railway. "Constructed on the southern side of the Dangla Mountains, Amdo is a Chinese-style town on the Qinghai-Tibet Highway. The road here leads off to the west, heading towards the Mount Kailash, Mt. Kailash area via the Changthang Plateau. Many of the buses from Golmud to Lhasa used to stay overnight here." At an elevation of , Amdo is one of the List_of_highest_cities_in_the_world, highest year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xainza
:''not to be confused with Naktsang Town in the Haa District of southwestern Bhutan'' Xainza (also Naktsang,Dorje (2009), p. 397. Xainza Town or Shantsa) is a town and township-level administrative unit and seat of Shentsa County or Xainza County, Nagqu Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It covers an area of 2146 square kilometres and in 2004 had a total population of about 17,000. The township was established by the Chinese in 1961. The main occupation is animal husbandry, mainly yak, goat and sheep rearing. Villages The township-level division contains the following settlements: *Gasangduo (neighborhood) (嘎桑多居委会) *Rongsaiduo (neighborhood) (融塞多居委会) *Nacha, Nagqu, Nacha (拿查村) *Luopu (罗普村 ) *Qiangrong (羌戎村) *Qubu (曲布村) *Yongzhu Woma (永珠沃玛村) *Rennaduo (仁那多村) Footnotes References * Dorje, Gyurme. ''Footprint Tibet Handbook''. 4th Edition. (2009) Bath, U.K. External linksPhoto of Xainza Town [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyainrong
Nyainrong is a small town and seat of Nyainrong County, Nagqu Prefecture, northern Tibet Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s .... {{Nagqu Prefecture Populated places in Nagqu Township-level divisions of Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siling Lake
Siling Lake (; ), (also known as Qilin or Selincuo) is a salt lake in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China to the north of Xainza. Doijiang is located near the lake. Administratively it belongs to Xainza County and Baingoin County of the Nagqu. Bangecuo is another nearby salt lake located east of Siling Lake, around four miles away. Overview The lake lies at an altitude of . It is a salt lake. It is fed by the rivers Za'gya Zangbo (or Tsagya Tsangpo) (扎加藏布) and the Boques Tsangpo (波曲藏布). With an area of , Siling Co is the second largest saltwater lake in the northern Tibetan Plateau and forms part of the Xainza Nature Reserve. The reserve was established in 1993 and contains significant populations of black-necked crane The black-necked crane (''Grus nigricollis'') is a medium-sized crane (bird), crane in Asia that breeds on the Tibetan Plateau and remote parts of India and Bhutan. It is long with a wingspan, and it weighs . It is whitish-gray, with a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa (prefecture-level City)
Lhasa is a prefecture-level city, one of the main administrative divisions of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It covers an area of of rugged and sparsely populated terrain. Its urban center is Lhasa, with around 300,000 residents, which mostly corresponds with the administrative Chengguan District, while its suburbs extend into Doilungdêqên District and Dagzê District. The consolidated prefecture-level city contains an additional five, mostly rural, counties. The city boundaries roughly correspond to the basin of the Lhasa River, a major tributary of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. It lies on the Lhasa terrane, the last unit of crust to accrete to the Eurasian plate before the continent of India collided with Asia about 50 million years ago and pushed up the Himalayas. The terrain is high, contains a complex pattern of faults and is tectonically active. The temperature is generally warm in summer and rises above freezing on sunny days in winter. Most of the rain falls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namtso
Namtso or Lake Nam (officially: Namco; ; ; ; “Heavenly Lake” in European literature: Tengri Nor, ) is a mountain lake on the border between Damxung County of Lhasa prefecture-level city and Baingoin County of Nagqu Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, approximately NNW of Lhasa. Geography Namtso (Namco) is a lake that first formed during the Paleogene age, as a result of Himalayan tectonic plate movements. The lake lies at an elevation of , and has a surface area of . This salt lake is the largest lake in the Tibet Autonomous Region. However, it is not the largest lake on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. That title belongs to Qinghai Lake (more than twice the size of Namtso); which lies more than to the north-east in Qinghai. Namtso has five uninhabited islands of reasonable size, in addition to one or two rocky outcrops. The islands have been used for spiritual retreat by pilgrims who walk over the lake's frozen surface at the end of winter, carrying their f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Highway 109
China National Highway 109 connects Beijing with Lhasa. It runs westwards from Beijing via Datong, Yinchuan and Xining to Golmud before turning southwest to Lhasa. The portion of the highway from Xining to Lhasa is known as the Qinghai-Tibet Highway. The total length of the route is 3,901 km. Fushi Road or Jinglan Road forms the stretch of G109 in Beijing, as it begins from Fuchengmen and traverses through Shijingshan. The majority of the Beijing section is in Mentougou District. The section of the highway within western Qinghai and Tibet, from Golmud to Lhasa, is paralleled by the Qinghai-Tibet Railway. The highway reaches its highest elevation of at Tanggula Pass. Construction of this section started on 11 May 1954. "Tasked with carrying upwards of 85 per cent of goods in and out of Tibet, the Qinghai-Tibet Highway has been dubbed the "Lifeline of Tibet." ... Since it was opened to traffic in 1954, the central government has spent nearly 3 billion yuan (US$362 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese language, Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat language, Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (, zh, s=玉树藏族自治州, p=Yùshù Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu, retranscribed into Tibetan as ), also transliterated as Yüxü or Yulshul, is an autonomous prefecture of Southwestern Qinghai Province, China. Largely inhabited by Tibetans, the prefecture has an area of and its seat is located in the town of Gyêgu in Yushu County, which is the place of the old Tibetan trade mart of Jyekundo. The official source of the Yellow River lies within the prefecture. Historically, the area belongs to the cultural realm of Kham in Eastern Tibet. On 14 April 2010, an earthquake struck the prefecture, registering a magnitude of 6.9 (USGS, EMSC) or 7.1About 400 dead, 10,000 injured in 7. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |