|
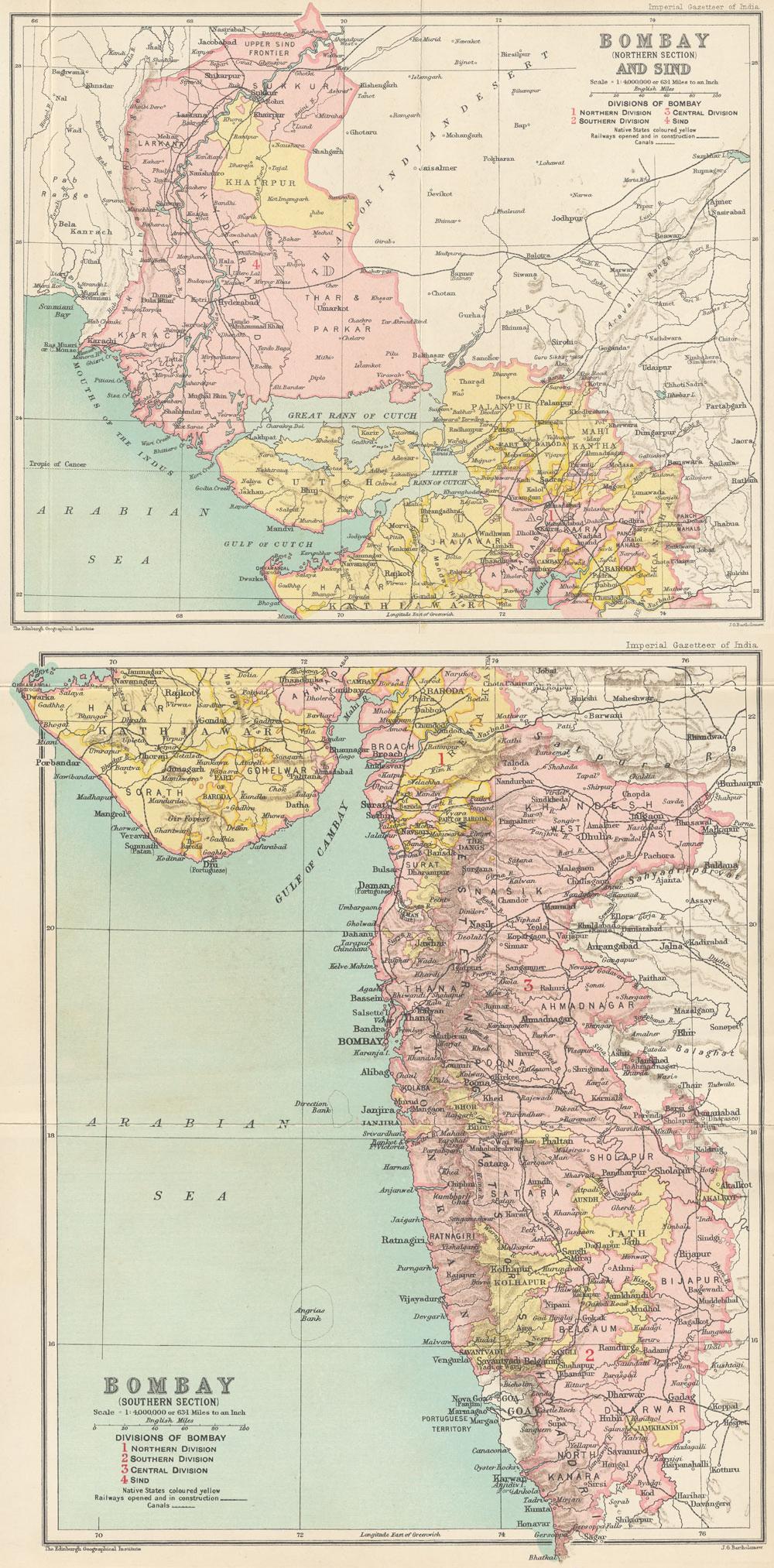
Nagarparkar
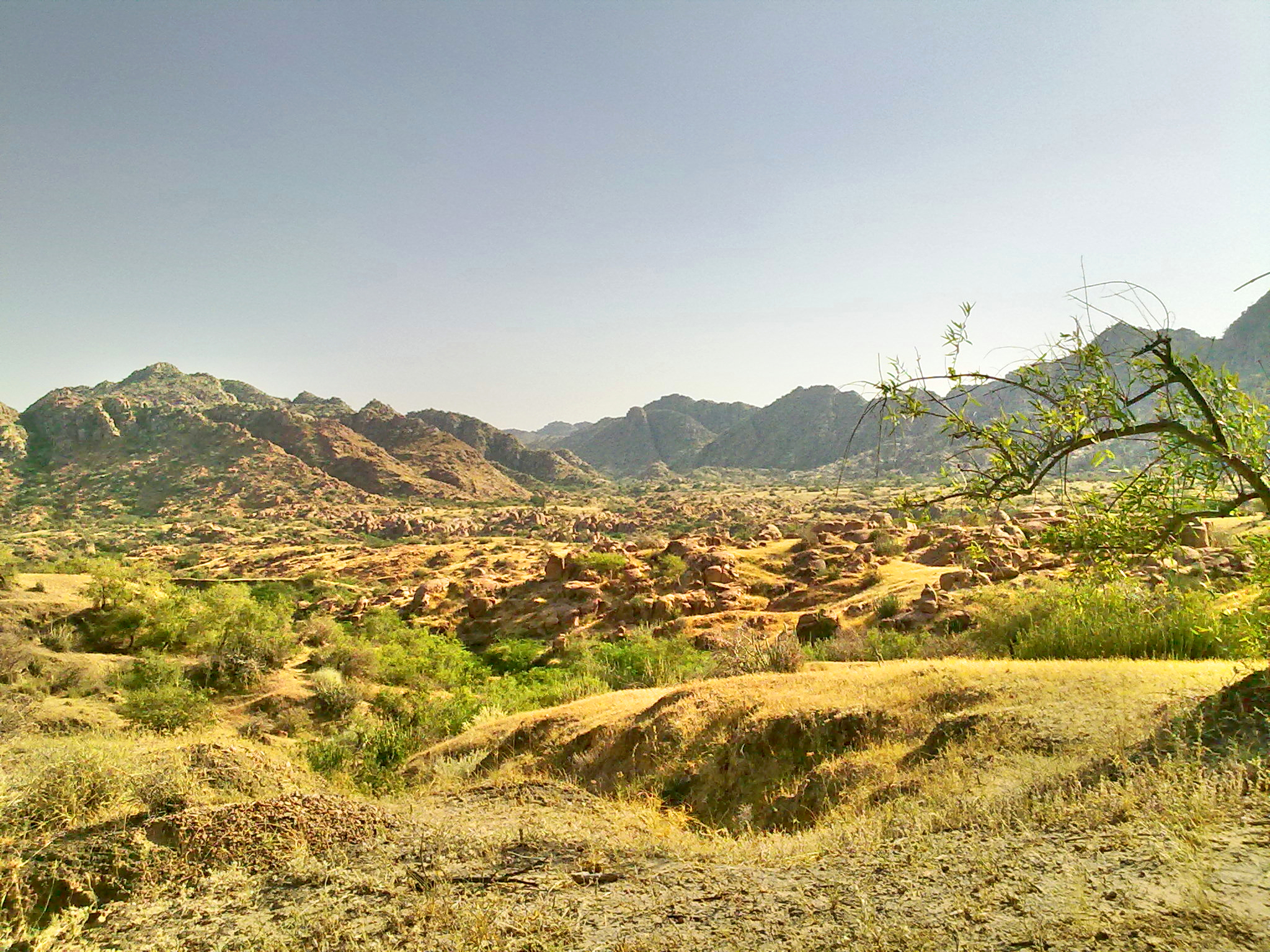
Nagarparkar (, ) is a tehsil in at the base of the Karoonjhar Mountains in Tharparkar District in Sindh province of Pakistan. The historic Churrio Jabal Durga Mata Temple is situated here. The taluka is located at a distance of 129 km from Mithi, in Sindh, Pakistan. It is the eastern-most part of Pakistan. Description The name comes from the original word ''Nangar Parkar''. It is at the foot of the Karoonjhar Hills. It is situated at a distance of about 16 km from south and about 23 from east from the Indian border. At one time the area was under the sea, which had to be crossed; the name "Parkar" means "to cross over". Nagarparkar has Chachro taluk on its north, and on its west is Islamkot taluk, while on east of it lies Barmer district of the Indian state of Rajasthan and on its south is Rann Kachchh and the Indian state of Gujarat. The surrounding area is a rocky belt called Parkar, and the remaining part is a sandy area. The Karoonjhar hills cover 16 miles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharparkar District
Tharparkar ( Dhatki/; , ), also known as Thar, is a district in Sindh province in Pakistan, headquartered at Mithi. Before Indian independence it was known as the Thar and Parkar (1901–1947) or Eastern Sindh Frontier District (1860–1901). The district is the largest in Sindh, and has the largest Hindu population in Pakistan. It has the lowest Human Development Index rating of all the districts in Sindh. Currently the Sindh government is planning to divide the Tharparkar district into Tharparkar and Chhachro district. History The name Tharparkar originates from a portmanteau of the words Thar (referring to the Thar Desert), and parkar (meaning "to cross over"). The Thar region was historically fertile, although it was mostly desertified between 2000 BCE and 1500 BCE. Before its desertification, a tributary of the Indus River was said to flow through the region; it is speculated by some historians that this river could be the ancient Sarasvati River mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoonjhar Mountains
Karoonjhar Mountains (, ) are located in south-eastern edge of the Tharparkar district in Sindh, Pakistan. The range is approximately long and reaches a height of , and contains vaste deposits of granite and Chinese clay. Geography Karoonjhar mountains are located in Nagarparkar near the district Tharparkar on the northern edge of the Rann of Kutch. They mostly consist of granite rock and are likely an extension of the Aravalli Range of India. The Aravalli range belongs to Archaen period, which makes it one of the oldest rock systems. Specialists have put the time period of the formation of these rocks at between 3.5 and 5 billion years ago. The Karoonjhar area is geographically different from the surrounding desert and is very limited in expanse. The mountain range is around 19 kilometers long and 305 meters high. To the east of the main range lie smaller hills which are covered with sparse vegetation. From these hills originate two perennial springs, Achleshwar and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the Demographics of Pakistan, second-largest province by population after Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the north. It shares an India-Pakistan border, International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert of Sindh, Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the India–Pakistan border, international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churrio Jabal Durga Mata Temple
Churrio Jabal Durga Mata Temple (چوڙيو جبل, pronunciation: choo-ryo ja-bal) is situated on a hill named Churrio, located in Nangarparkar in the Tharparkar District in the Sindh province of Pakistan. Hindus bring cremated ashes of their departed beloveds to immerse in the holy water in the temple. The valuable and multi-coloured hill supporting the temple is mined for its rare and expensive granite, which is posing a serious threat to the temple. Etymology The name Churrio (Choryo) is a word from Sindhi language, derived from a word (چوڙي), to be pronounced as (Choo-rree), which means 'a bangle'; thus the word Churrio—an adjective in Sindhi language—means "belonging to/related to bangles", because in the vicinity of the hill there are a number of small villages that have historically remained attached to the profession of manufacturing bangles for women. These locally manufactured bangles are then transported out of the villages to the nearby towns like Nangarpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkari Koli Language
The Parkari Koli language (sometimes called just ''Parkari'') is an Indo-Aryan language mainly spoken in the province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is spoken in the southeast tip bordering India, in the Tharparkar District, Nagarparkar. Most of the lower Thar Desert, west as far as Indus River, bordered north and west by Hyderabad, to south and west of Badin. Lexical similarity 77%–83% with Marwari, 83% with Wadiyara Koli. Orthography The orthography was standardized in 1983-84 and used from 1985 onward. It is based on the Sindhi alphabet which is itself based on modifications done on Persian alphabet, with three additional letters:Archive * , representing a voiced dental implosive /ɗ/ * , representing a retroflex lateral approximant /ɭ/ * , representing a voiced glottal fricative /ɦ/. These letters all use an inverted V (like the circumflex) as the diacritical mark. The decision to introduce this symbole was so that these letters would stand out more clearly in Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Pakistan
Hinduism is the second largest religion in Pakistan after Islam. Though Hinduism was the dominant faith in the region a few centuries back, its adherents accounted for just 2.17% of Pakistan's population (approximately 5.2 million people) according to the 2023 Pakistani census. With the largest population concentration in eastern Sindh province, Umerkot district has the highest percentage of Hindu residents in the country at 54.7%, while Tharparkar district has the most Hindus in absolute numbers at 811,507. Hindus are also found in southern Punjab and in areas of Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Prior to the partition of India, according to the 1941 census, Hindus constituted 14.6% of the population in West Pakistan (contemporary Pakistan) and 28% of the population in East Pakistan (contemporary Bangladesh). After Pakistan gained independence from the British Raj, 5 million (based on 1941 &1951 Census) of West Pakistan's Hindus and Sikhs moved to India as refuge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamkot Tehsil
Islamkot Tehsil (), () is a Tehsil in the Tharparkar District in Sindh, Pakistan. Hundreds of neem trees seen on Islamkot- Mithi, Islamkot- Chachro and Islamkot-Nagarparkar roads were planted during chairmanship of Rais Ahmed Khan Noon and under his care. For the same reason this region is also known as the Neem tree region. The Civil Aviation Authority of Pakistan is building the Islamkot International Airport here. Demographics As of the 2023 census, Islamkot tehsil had 52,509 households and a population of 265,643. 18.04% of the population is under 5 years of age. Islamkot had a sex ratio of 106.87 males per 100 females. The literacy rate is 36.01%: 48.29% for males and 22.97% for females. 7.18% of the population lives in urban areas. Sindhi is the predominant language, spoken by 98.91% of the population. Sant Nenuram Ashram The Hindu saint ''"Shri Sant Nenuram"'' was born here and Sant Nenuram Ashram located in this region was established by Nihalchand Pabani with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Sindh Province
Hinduism is the second-largest religion in Sindh, numbering 4.9 million people and comprising 8.8 percent of the province's population in the 2023 Pakistani census. Sindh has the largest population and the highest percentage of Hindus in Pakistan. Sindh has the Shri Ramapir Temple, whose annual festival is the country's second-largest Hindu festival (after the Hinglaj Yatra). History The region and its rulers play an important role in the Hindu epic, Mahabharata. Hinduism and Buddhism were the predominant religions in Sindh before the arrival of Islam, when a number of Hindu castes and communities occupied the region. Many ancient Hindu temples still exist; many Hindu dynasties, including the Gupta, Pala, Kushan and Hindu Shahis, ruled the region before Muhammad ibn Qasim led the Umayyad army in the Islamic conquest of Sindh. The region still had a Hindu majority, but repeated campaigns and persecution by the Delhi Sultanate led to a gradual decrease in the Hindu po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Community
The Jains in India are the last direct representatives of the ancient Shramana tradition. People who practice Jainism, an ancient religion of the Indian subcontinent, are collectively referred to as Jains. Sangha Jainism has a fourfold order of ''muni'' (male monastics), '' aryika'' (female monastics), ''Śrāvaka'' (layman) and ''sravika'' (laywoman). This order is known as a ''sangha''.. Many Jains are in general caste. Cultural influence The Jain have the highest literacy rate in India, 94.1.% compared with the national average of 65.38%. They have the highest female literacy rate, 90.6.% compared with the national average of 54.16%. As per national survey NFHS-4 conducted in 2018 Jains were declared wealthiest of any community with 70% of their population living in top quintiles of wealth. The sex ratio in the 0-6 age group is the second lowest for Jain (870 females per 1,000 males). Communities Jains are found in almost every part of India. There are about 100 diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kachi Koli Language
Kachi Koli is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in India. There is a small population of Koli who live across the border in eastern Sindh province in neighbouring Pakistan Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# .... Part of the Gujarati subfamily, Kachi Koli is closely related to Parkari Koli and Wadiyara Koli. References Languages of India Koli people Indo-Aryan languages Languages of Gujarat {{India-culture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadiyara Koli Language
Wadiyara Koli is an Indo-Aryan language of the Gujarati group. It is spoken by the Wadiyara people, who originate from Wadiyar in Gujarat; many of whom are thought to have migrated to Sindh in the early twentieth century, following the onset of famine. The Wadiyara people are affiliated with the Bhil people and Koli people The Koli is an Indian caste that is predominantly found in India, but also in Pakistan and Nepal. Koli is an agriculturist caste of Gujarat but in coastal areas they also work as fishermen along with agriculture. In the beginning of 20th ce ..., but are generally more inclined towards associating themselves with the Koli; they are often regarded as a subgroup of the latter. Phonology Vowels Wadiyari possesses eight distinct oral monophthongs coupled with five nasal monophthongs, in addition to five oral diphthongs and two contrastive nasal diphthongs. Oral vowels are also assimilated before nasal consonants. Monophthongs The word-initial occurrenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Language
Gujarati ( ; , ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Western Rājasthāni, Old Gujarati (). In India, it is one of the 22 Languages with official status in India, scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the List of languages by number of native speakers in India, 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the List of languages by number of native speakers, 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in ''Nationalencyklopedin''. Asteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |