|
NR-40
The NR-40 (from , НР-40 ''nozh razvedchika'' meaning "scout's knife" or Finka) was a Soviet combat knife introduced in 1940 and used throughout World War II. History In the beginning of the 20th century, Finnish puukko knives started becoming popular with criminals in most cities of the Russian Empire. Local knife-makers then began modifying the Finnish woodsman's tool to make it more useful for fighting; for example, making the blade longer, changing from a flat back to a clip point, and adding a large guard. The resulting weapon, still called a "Finnish knife" or "finka" in Russian, looked rather different from a typical puukko. "Finnish knives" were ubiquitous in the criminal underworld of Russia and Soviet Union throughout the first half of the 20th century. Because of the criminal association, the "Finnish knife" was banned in the Soviet Union in the 1930s, much like the switchblade would later be banned in the West. The Winter War revealed a number of deficiencie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NRS-2
The NRS-2 (''Нож Разведчика Стреляющий'', "Scout Firing Knife") (official GRAU index 6P25U) is a gun hybrid with a combination of a knife blade and a built-in single-shot shooting mechanism designed to fire a 7.62×41mm SP-4 (СП-4) cartridge, originally designed for the PSS silent pistol. History It was manufactured by the Tula Arms Plant for Soviet ''Spetsnaz'' troops in the 1980s, and is still used as a personal weapon for modern ''Spetsnaz'' troops and special law enforcement groups. Design The NRS-2 is designed for either stabbing or throwing with the blade, or fired at distances of up to 25 metres. Shooting mechanism To load the shooting mechanism, the opening lever is pressed, and the barrel rotated out of the knife handle. Then the cartridge is inserted into the firing chamber and the barrel is reinserted back into the handle and rotated into place using two prongs that fit into the outer latch. The flip-up lever on the right side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puukko
A puukko () is a small traditional Finnish culture, Finnish general purpose belt knife with a single curved cutting edge, solid hidden tang (tools), tang, and usually, a flat spine. Design The basic components of a puukko are a handle and a blade along with a Scabbard, sheath, which can usually be attached to a Belt (clothing), belt, but sometimes to a shirt or coat button. The blade is usually short, typically no longer than the handle and can often be less than . The flat grind makes the puukko a natural choice for slicing, cutting and whittling, and the flat spine allows the user to use a thumb or the other hand to bring more force to bear on the task at hand. Puukkos are most often used as carving tools for decorative and fire-making purposes, and to clean fish and game. Some puukko designs have a slightly upwards-or downwards-curving point, depending on the knife's purpose. A hunting puukko's tip is often curved downwards, to make the skinning and gutting of an anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife Nr40 Ussr
A knife (: knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hikers carry a pocketknife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knife (butter knives and steak knives), weapons (daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing or juggling, and k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clip Point
The clip point is one of the three most common shapes for the blade of a knife (the others being the drop point and the spear point). Clip point blades have the appearance of having the forward third of the blade "clipped" off. The clip itself can be straight or concave. Description Traditionally, the spine or unsharpened edge of the knife begins at the hilt and continues to a point between one third to one fourth of the blade length. The blade spine then tapers in thickness in either a straight line or a recurve to the knife's point, which may be located above, below, or in line with the central axis of the blade. The thinned false edge of the clip may be sharpened to form a true second cutting edge. If the false edge is sharpened it increases the knife's effectiveness in piercing. History The clip point blade design dates back to at least Macedonian times, where examples of knapped flint clip point knives from the Eneolytic period have been unearthed at the estuary of Drim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Knives Of The Soviet Union
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily Weapon, armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Knife
A ballistic knife is a knife with a detachable blade that can be ejected to a distance of several meters/yards by pressing a trigger or operating a lever or switch on the handle.Crawford, Steve, ''Deadly fighting skills of the world'', New York: Thomas Dunne Books, St. Martin's Press, (1999), pp. 45-46: The minimum standard demanded of ''Spetsnaz'' recruits when throwing a knife from six feet is three consecutive hits on target; five hits is considered excellent. Spring-powered ballistic knives first appeared in books and press reports on Soviet and Eastern Bloc armed forces in the late 1970s. Commercially-produced ballistic knives gained notoriety in the United States in the mid-1980s after being marketed and sold in the United States and other Western countries. Since then, the marketing and sale of ballistic knives to civilians has been restricted or prohibited by law in several nations. Usage In its spring-propelled form, the blade of a ballistic knife is theoretically capa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampfmesser 42
The Seitengewehr 42 (bayonet model 1942), also called the ''Infanteriemesser 42'' or ''Kampfmesser 42,'' was a bayonet and multi-purpose knife used by the Wehrmacht. History The Seitengewehr 42 was developed in 1942 by Wilhelm Gustloff Werke and manufactured by Carl Eickhorn in Solingen. According to its description, the Gustloff Company and its chief designer, Carl Barnitzke, got a German patent 766198 in October 1942 for an ''Armeemesser'' (Army knife) according to its description. The SG 42 was intended to supplement and later replace the original S84/98 III bayonet of the Karabiner 98k service rifle. The ''Seitengewehr 42'' was designed as a multi-tool combat knife, but could also be mounted as a bayonet on the Karabiner 98k. The S84/98 III bayonet itself was a proven design, but there was a shortage of utility knives in the German military, which were usually procured privately. After the consistently positive reception of several hundred pieces in the 1943 troops trials, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairbairn–Sykes Fighting Knife
The Fairbairn–Sykes fighting knife is a double-edged fighting knife resembling a dagger or poignard with a brass or wooden foil grip. It was developed by William Ewart Fairbairn and Eric Anthony Sykes in Shanghai based on ideas that the two men had while serving on the Shanghai Municipal Police in China before World War II. The F-S fighting knife was made famous during World War II when issued to British Commandos, the Airborne Forces, the SAS and many other units, especially for the Normandy landings in June 1944. With its acutely tapered, sharply pointed blade, the F-S fighting knife is frequently described as a stiletto, a weapon optimised for thrusting, although the F-S knife can be used to inflict slash cuts upon an opponent when its cutting edges are sharpened according to specification.Cassidy, William L., A Brief History of the Fairbairn–Sykes Fighting Knife'' The Wilkinson Sword Company made the knife with minor pommel and grip design variations. History The F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
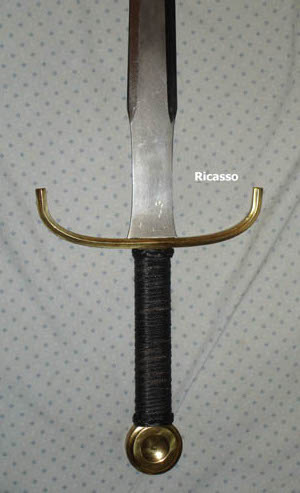
Ricasso
A ricasso is an unsharpened length of blade just above the guard or handle on a knife, dagger, sword, or bayonet. Blades designed this way appear at many periods in history in many parts of the world and date back to at least the Bronze Age—essentially, as long as humans have shaped cutting tools from metals. There were many reasons to make a blade with a ricasso, and in Europe, later longswords, claymores, rapiers, and other lengthy swords often had this feature. One very simple influence presently and historically is fashion, which often answers this question for blades where the presence or lack of a ricasso has no effect on how it is used. Leaving a ricasso can also save the blade maker's time—a section of blade that would not be used given the purpose of the piece does not have to be shaped and sharpened. In many cases, however, they are quite functional. Historically, ricassos were commonly present on medieval and early Renaissance swords. The basic function was to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Guards Uralsko-Lvovskaya Tank Division
The 10th Russian Guards, Guards ''Uralsko-Lvovskaya'' Volunteer Tank Division, also known as the Ural-Lvov Tank Division, is a armoured division, tank division of the Russian Ground Forces and part of the Moscow Military District's 20th Guards Army. The division traces its heritage back to 1943, during World War II. It is headquartered and based at Boguchar, 160 kilometres south of Voronezh, Voronezh Oblast. Its complete formal designation is: "The 10th Guards Tank Ural-L'vov the Order of October Revolution Red Banner, the Order of Suvorov and the Order of Kutuzov Military volunteer, Volunteer division in the name of Marshal of the Soviet Union Rodion Malinovsky, R.A. Malinovsky" (Russian: 10 гвардейская танковая Уральско-Львовская ордена Октябрьской революции Краснознаменная орденов Суворова и Кутузова добровольческая дивизия имени Маршала Со� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |