|
NMOSD
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) are a spectrum of autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis).Banerjee S, Butcher R. Rituximab for the Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder nternet Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2021 Feb. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK571350/ Episodes of ON and myelitis can be simultaneous or successive. A relapsing disease course is common, especially in untreated patients. * Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is a particular disease within the NMOSD spectrum. It is characterised by optic neuritis and longitudinally extensive myelitis. In more than 80% of NMO cases, the cause is immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to aquaporin 4 ( anti-AQP4), the most abundant water channel protein in the central nervous system. * Less common diseases with other manifestations are also part of the NMOSD spectrum. Signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satralizumab
Satralizumab, sold under the brand name Enspryng, is a humanized monoclonal antibody medication that is used for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), a rare autoimmune disease. The drug is being developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical, a subsidiary of Roche. The most common side effects include the common cold (nasopharyngitis), headache, upper respiratory tract infection, inflammation of the lining of the stomach, rash, joint pain, extremity pain, fatigue and nausea. Satralizumab regulates inflammation by inhibiting the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor, a key mediator of the immune response. Satralizumab was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2020, and in the European Union in June 2021. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Satralizumab is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adults with a particular antibody – people who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
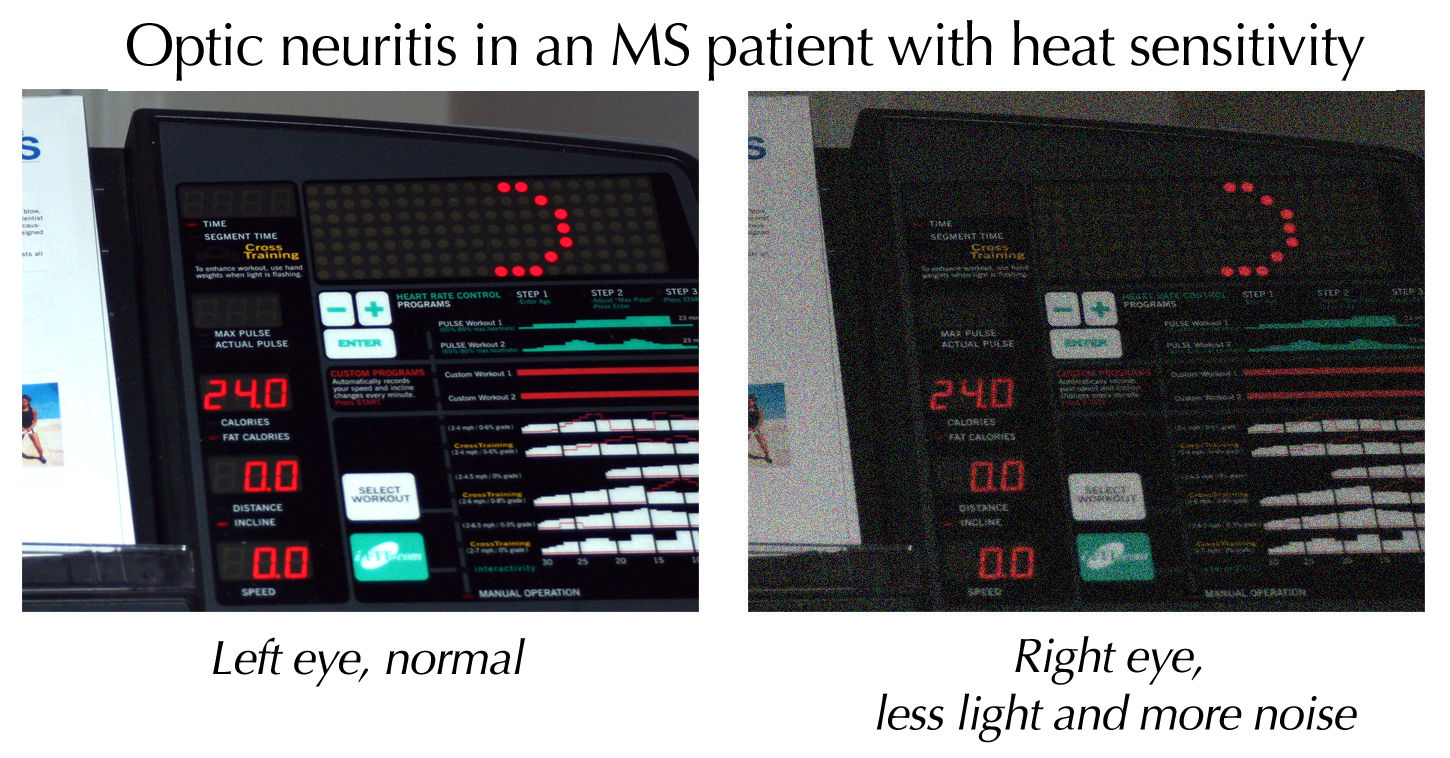
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis (ON) is a debilitating condition that is defined as inflammation of cranial nerve II which results in disruption of the neurologic pathways that allow visual sensory information received by the retina to be able to be transmitted to the visual cortex of the brain. This disorder of the optic nerve may arise through various pathophysiologic mechanisms, such as through Demyelinating disease, demyelination or inflammation, leading to partial or total loss of vision. Optic neuritis may be a result of standalone idiopathic disease, but is often a manifestation that occurs secondary to an underlying disease. Signs of ON classically present as sudden-onset visual impairment in one or both eyes that can range in severity from mild visual blurring to complete blindness in the affected eye(s). Although pain is typically considered a hallmark feature of optic neuritis, the absence of pain does not preclude a diagnosis or consideration of ON as some patients may report painlessne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inebilizumab
Inebilizumab, sold under the brand name Uplizna, is a medication for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adults and IgG4-RD. Inebilizumab is a humanized mAb that binds to and depletes CD19+ B cells including plasmablasts and plasma cells. The most common adverse reactions include urinary tract infection, headache, joint pain (arthralgia), nausea and back pain. Inebilizumab was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2020, in the European Union in April 2022, and in Canada in December 2023. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Inebilizumab is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adults with a particular antibody (patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 or AQP4 antibody positive). Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune system cells and autoantibodies attack and damage the optic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-MOG Associated Encephalomyelitis
MOG (myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein) antibody disease (MOGAD) or MOG antibody-associated encephalomyelitis (MOG-EM) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Serum anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies are present in up to half of patients with an acquired demyelinating syndrome and have been described in association with a range of phenotypic presentations, including acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, optic neuritis, transverse myelitis, and neuromyelitis optica. Presentation The clinical presentation is variable and largely dependent upon the overall clinical manifestation. The presence of anti-MOG autoantibodies has been described in association with the following conditions: * Seronegative neuromyelitis optica. * Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, especially in recurrent and fulminant cases. * Multiple sclerosis. * Optic neuritis(including cases of CRION ( chronic relapsing inflammatory optic neuropathy) * Transverse myeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) is a glycoprotein believed to be important in the myelination of nerves in the central nervous system (CNS). In humans this protein is encoded by the ''MOG'' gene. It is speculated to serve as a necessary "adhesion molecule" to provide structural integrity to the myelin sheath and is known to develop late on the oligodendrocyte. Molecular function While the primary molecular function of MOG is not yet known, its likely role with the myelin sheath is either in sheath "completion and/or maintenance". More specifically, MOG is speculated to be "necessary" as an "adhesion molecule" on the myelin sheath of the CNS to provide the structural integrity of the myelin sheath.Berger, T., Innsbruck Medical University Dept. of Neurology interviewed by S. Gillooly, Nov. 24, 2008." MOG's cDNA coding region in humans have been shown to be "highly homologous" to rats, mice, and bovine, and hence highly conserved. This suggests "an important biological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength. Its causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have either true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. Muscle weakness can also be caused by low levels of potassium and other electrolytes within muscle cells. It can be temporary or long-lasting (from seconds or minutes to months or years). The term myasthenia is from my- from Greek μυο meaning "muscle" + -asthenia ἀσθένεια meaning " weakness". Types Neuromuscular fatigue can be classified as either "central" or "peripheral" depending on its cause. Central muscle fatigue manifests as an overall sense of energy deprivation, while peripheral muscle fatigue manifests as a local, muscle-specific inability to do work. Neuromuscular fatigue Nerves control the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
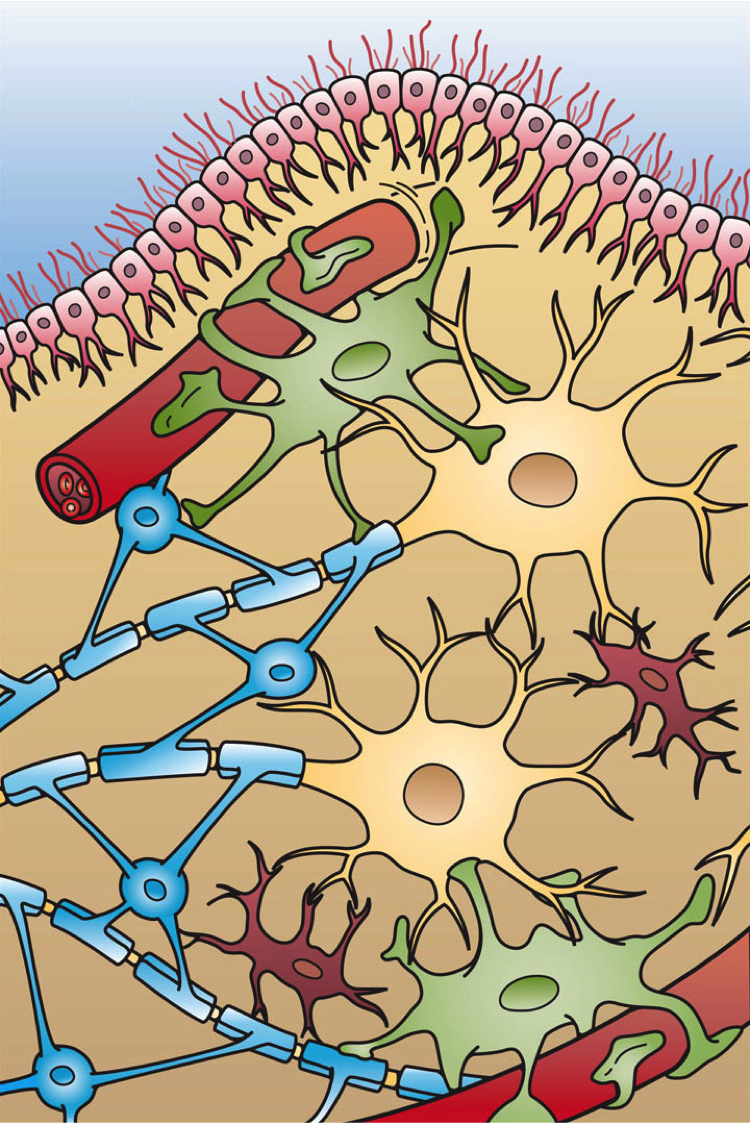
Optic Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, Pretectal area, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. Structure The optic nerve has been classified as the second of twelve paired cranial nerves, but it is technically a myelinated tract of the central nervous system, rather than a classical nerve of the peripheral nervous system because it is derived from an out-pouching of the diencephalon (optic stalks) during embryonic development. As a consequence, the fibers of the optic nerve are covered with myelin produced by oligodendrocytes, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaporin
Aquaporins, also called water channels, are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells, mainly facilitating transport of water between cells. The cell membranes of a variety of different bacteria, fungi, animal and plant cells contain aquaporins through which water can flow more rapidly into and out of the cell than by diffusing through the phospholipid bilayer. Aquaporins have six membrane-spanning alpha helical domains with both carboxylic and amino terminals on the cytoplasmic side. Two hydrophobic loops contain conserved asparagine– proline– alanine ("NPA motif") which form a barrel surrounding a central pore-like region that contains additional protein density. Because aquaporins are usually always open and are prevalent in just about every cell type, this leads to a misconception that water readily passes through the cell membrane down its concentration gradient. Water can pass through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-AQP4 Diseases
Anti-AQP4 diseases, are a group of diseases characterized by auto-antibodies against aquaporin 4. After the discovery of anti-AQP4 autoantibody in neuromyelitis optica, it was found that it was also present in some patients with other clinically defined diseases, including multiple sclerosis variants like optic-spinal MS. The collection of these condition has been named "anti-AQP4 disease" and "neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders" (NMSD) and they are expected to respond to the same treatments as standard NMO. Some authors propose to use the name "autoimmune aquaporin-4 channelopathy" for these diseases, while others prefer a more generic term "AQP4-astrocytopathy" that includes also problems in AQP4 with a non-autoimmune origin. Clinical Spectrum After finding the anti-AQP4 autoantibody in cases outside the standard Devic's disease course, the spectrum was expanded. The spectrum is now believed to consist of: * Standard Devic's disease, according to the diagnostic criteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
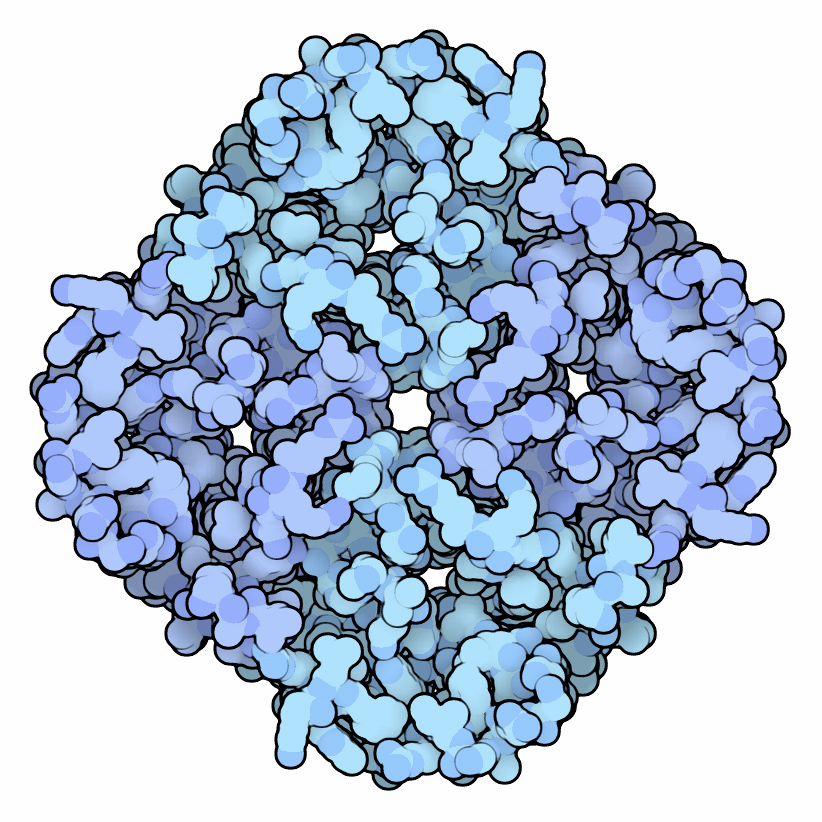
Aquaporin 4
Aquaporin-4, also known as AQP-4, is a water channel protein encoded by the ''AQP4'' gene in humans. AQP-4 belongs to the aquaporin family of integral membrane proteins that conduct water through the cell membrane. A limited number of aquaporins are found within the central nervous system (CNS): AQP1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, and 11, but more exclusive representation of AQP1, 4, and 9 are found in the brain and spinal cord. AQP4 shows the largest presence in the cerebellum and spinal cord grey matter. In the CNS, AQP4 is the most prevalent aquaporin channel, specifically located at the perimicrovessel astrocyte foot processes, glia limitans, and ependyma. In addition, this channel is commonly found facilitating water movement near cerebrospinal fluid and vasculature. Aquaporin-4 was first identified in 1986. It was the first evidence of the existence of water transport channels. The method that was used to discover the existence of the transport channels was through knockout experiments. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |