|
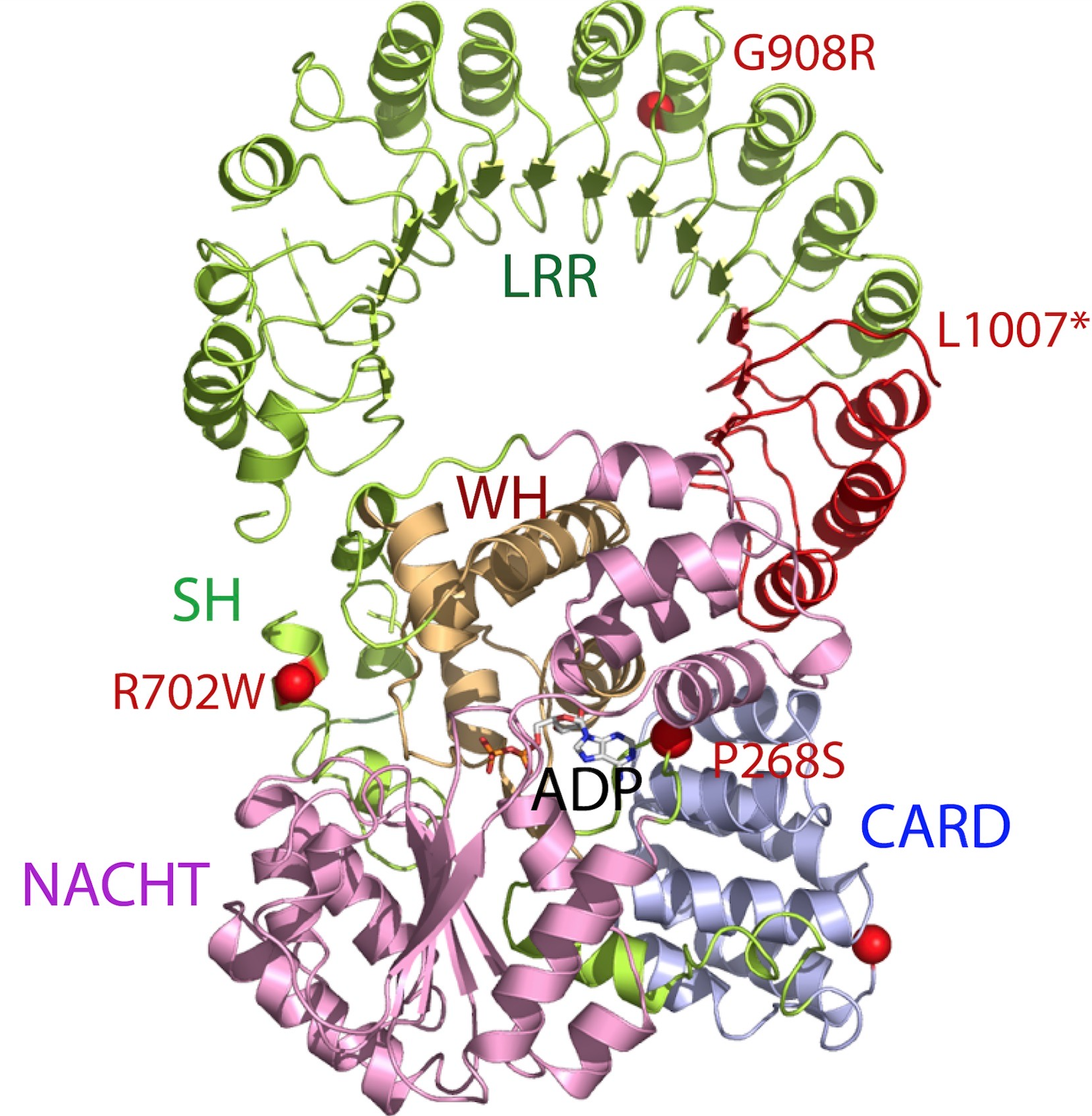
NLRP5
NLRP5, short for NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 5, is an intracellular protein that plays a role in early embryogenesis. NLRP5 is also known as NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 5 (NALP5), Mater protein homolog (MATER), PYPAF8, PAN11, and CLR19.8, and is one of 14 pyrin domain containing members of the NOD-like receptor family of cytoplasmic receptors known to mammals. In humans, the NLRP5 protein is encoded by the ''NLRP5'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... References Further reading * * * * LRR proteins NOD-like receptors {{Transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD-like Receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response. NLRs primarily recognize Gram-positive bacteria, whereas TLRs primarily recognize Gram-negative bacteria. They are found in lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species ( APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrin Domain
A pyrin domain (PYD, also known as PAAD/DAPIN) is a protein domain and a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold, the 4th and most recently discovered member of the death domain superfamily (DDF). It was initially discovered in the pyrin protein, also known as marenostrin, which is encoded by MEFV. The mutation of the MEFV gene is the cause of the disease known as Familial Mediterranean fever, Familial Mediterranean Fever. The domain is encoded in 23 human proteins and at least 31 mouse genes. Proteins containing a pyrin domain are frequently involved in programmed cell death processes, including pyroptosis and apoptosis. Proteins that possess a pyrin domain interact with the pyrin domains of other proteins to form multi-protein complexes called inflammasomes, triggering downstream immune responses. Structure Pyrin domains are a ~90 amino acid Protein motif, motif present only at the N-terminus of proteins. The core is composed of highly conserved hydrophobic residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of cell biology, Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, Glossary of environmental science and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in :Glossaries of biology. A B C D E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LRR Proteins
LRR may refer to: * Laminated root rot, a root disease in conifers *Leucine-rich repeat, a type of protein domain * LoadingReadyRun, a Canadian comedy troupe * Long Range Radar * '' Long River Review'', a literary magazine of the University of Connecticut *Low rolling resistance tires, a type of tires designed for fuel efficiency * Light Reaction Regiment The Light Reaction Regiment (LRR) is the special operations unit of the Philippine Army (PA), under the operational control of the Special Operations Command (Philippines), Armed Forces of the Philippines Special Operations Command (AFPSOCOM). ..., the Philippine Army counter-terrorist unit modeled after the U.S. Army Delta Force and British SAS * Loose Round Robin, Warp Scheduling See also * LR (other) * LRRR (other) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |