|
NGC 6755
NGC 6755 is an open cluster of stars in the celestial equator, equatorial constellation of Aquila (constellation), Aquila, positioned about 3° to the east of the star Delta Aquilae. It was discovered by the Anglo-German astronomer William Herschel on July 30, 1785 and is located at a distance of 8,060 light years from the Sun. NGC 6756 lies to the northeast of NGC 6755, with the pair forming a visual double cluster. However, they probably do not form a binary cluster system since they have different ages and are too distant from each other. This cluster has a Trumpler class of II2r with a visual magnitude of 7.5 and it spans an angular size . It has an estimated age of 250 million years, based on the main sequence turnoff. A total of 71 variable stars have been detected in the field of this cluster, of which 31 are Eclipsing binary, eclipsing binaries, seven are pulsating variables, and 28 are most likely irregular variable red giants. Gallery NGC 6755 map.png, Map s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to the brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a magnitude 2.0 star is 2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or lower. The appearance of the red giant is from yellow-white to reddish-orange, including the stellar classification, spectral types K and M, sometimes G, but also S-type star, class S stars and most carbon stars. Red giants vary in the way by which they generate energy: * most common red giants are stars on the red-giant branch (RGB) that are still stellar nucleosynthesis, fusing hydrogen into helium in a shell surrounding an inert helium core * red-clump stars in the cool half of the horizontal branch, fusing helium into carbon in their cores via the triple-alpha process * asymptotic-giant-branch (AGB) stars with a helium burning shell outside a degenerate carbon–oxygen core, and a hydrogen-burning shell just beyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Variable
An irregular variable is a type of variable star in which variations in brightness show no regular periodicity. There are two main sub-types of irregular variable: eruptive and pulsating. Eruptive irregular variables are divided into three categories: * Group I variables are split into subgroups IA (spectral types O to A) and IB (spectral types F through M). * Orion variables, GCVS type IN (irregular and nebulous), indigenous to star-forming regions, may vary by several magnitudes with rapid changes of up to 1 magnitude in 1 to 10 days, are similarly divided by spectral type into subgroups INA and INB, but with the addition of another subgroup, INT, for T Tauri stars, or INT(YY) for YY Orionis stars. * The third category of eruptive irregulars are the IS stars, which show rapid variations of 0.5 to 1 magnitude in a few hours or days; again, these come in subgroups ISA and ISB. Pulsating irregular giants or supergiants, called slow irregular variable A slow irregular variable (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsating Variable
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * ''Intrinsic variables'', whose luminosity actually changes periodically; for example, because the star swells and shrinks. * ''Extrinsic variables'', whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star Eclipsing binaries, has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars exhibit at least some oscillation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipsing Binary
A binary star or binary star system is a Star system, system of two stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars using a telescope, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit (astronomy), transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * ''Intrinsic variables'', whose luminosity actually changes periodically; for example, because the star swells and shrinks. * ''Extrinsic variables'', whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars exhibit at least some oscillation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
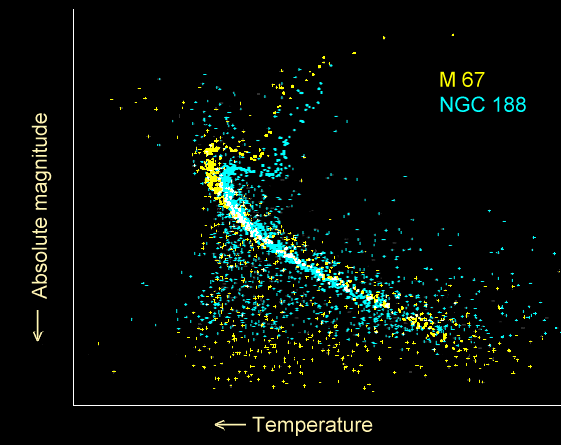
Main Sequence Turnoff
The turnoff point for a star refers to the point on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram where it leaves the main sequence after its main fuel is exhaustedthe main sequence turnoff. By plotting the turnoff points of individual stars in a star cluster one can Main sequence#Evolutionary_tracks, estimate the cluster's age. Stars with no turnoff point Red dwarfs, also referred to as classM stars, are stars of . They have sufficient mass to sustain hydrogen-to-helium Nuclear fusion, fusion via the proton–proton chain reaction, but they do not have sufficient mass to create the temperatures and pressures necessary to fuse helium into carbon, nitrogen or oxygen (see CNO cycle). However, all their hydrogen is available for fusion, and low temperature and pressure means a lifetime measured in trillions of years. For example, the lifespan of a star of 0.1 solar masses is six trillion years. This lifespan greatly exceeds the current age of the universe, therefore all red dwarfs are main sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Size
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the '' visual angle'', and in optics, it is the '' angular aperture'' (of a lens). The angular diameter can alternatively be thought of as the angular displacement through which an eye or camera must rotate to look from one side of an apparent circle to the opposite side. A person can resolve with their naked eyes diameters down to about 1 arcminute (approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians). This corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance, or to perceiving Venus as a disk under optimal conditions. Formulation The angular diameter of a circle whose plane is perpendicular to the displacement vector between the point of view and the center of said circle can be calculated using the formula :\delta = 2\arctan \left(\frac\right), in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trumpler Class
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of tens to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. Each one is loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and becomes disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the Galactic Center. This can result in a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters and a dispersion into the main body of the galaxy. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring. Young open clusters may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquila (constellation)
Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greco-Roman mythology, Greek-Roman mythology. Its brightest star, Altair, is one vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism (astronomy), asterism. The constellation is best seen in the northern summer, as it is located along the Milky Way. Because of this location, many clusters and planetary nebula, nebulae are found within its borders, but they are dim and galaxies are few. History Aquila was one of the 48 constellations described by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It had been earlier mentioned by Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus in the fourth century BC and Aratus in the third century BC. It is now one of the 88 constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. The constellation was also known as ''Vultur volans'' (the flying vulture) to the Ancient Rome, Romans, not to be confused with ''Vultur cadens'' which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |