|
NGC 3109
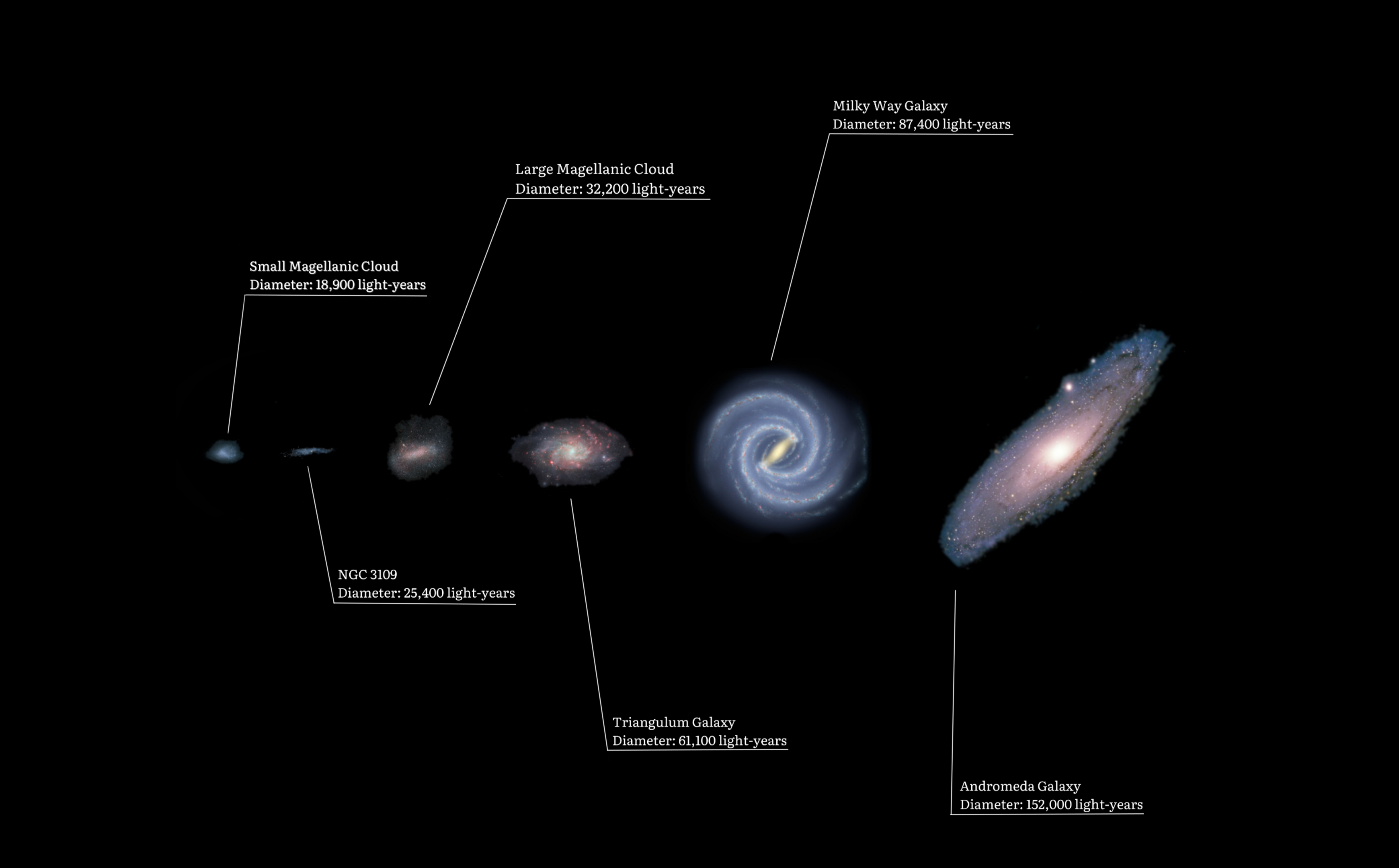
NGC 3109 is a small barred Magellanic type spiral or irregular galaxy around 4.35 Mly away in the direction of the constellation of Hydra. NGC 3109 is believed to be tidally interacting with the dwarf elliptical galaxy Antlia Dwarf. It was discovered by John Herschel on March 24, 1835 while he was in what is now South Africa.''Irregular Galaxy NGC 3109'' Size and morphology NGC 3109 is classified as a Magellanic type irregular galaxy, but it may in fact be a small spiral galaxy ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William Herschel, William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the Celestial sphere, celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy
Dwarf elliptical galaxies (dEs) are elliptical galaxies that are smaller than ordinary elliptical galaxies. They are quite common in galaxy groups and clusters, and are usually companions to other galaxies. Examples "Dwarf elliptical" galaxies should not be confused with the rare "compact elliptical" galaxy class, of which M32, a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy, is the prototype. In 1944 Walter Baade confirmed dwarf ellipticals NGC 147 and NGC 185 as members of the Local Group by resolving them into individual stars, thanks to their relatively little distance. In the 1950s, dEs were also discovered in the nearby Fornax and Virgo clusters. Relation to other elliptical galaxy types Dwarf elliptical galaxies have blue absolute magnitudes within the range fainter than ordinary elliptical galaxies. The surface brightness profiles of ordinary elliptical galaxies was formerly approximated using ''de Vaucouleur's model'', while dEs were approximated with an exponentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc (galaxy)
A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies like the Milky Way and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed of cool gas and dust). The stellar population of galactic discs tend to exhibit very little random motion with most of its stars undergoing nearly circular orbits about the galactic center. Discs can be fairly thin because the disc material's motion lies predominantly on the plane of the disc (very little vertical motion). The Milky Way's disc, for example, is approximately 1 kly thick, but thickness can vary for discs in other galaxies. Stellar component Exponential surface brightness profiles Galactic discs have surface brightness profiles that very closely follow exponential functions in both the radial and vertical directions. Radial profile The surface brightness radial profile of the galactic disc of a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kluwer Academic Publishers
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a " dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda and the Milky Way galaxies, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangulum Galaxy
The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy 2.73 million light-years (ly) from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC 598. With the D25 isophotal diameter of , the Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, behind the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way. The galaxy is the second-smallest spiral galaxy in the Local Group after the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is a Magellanic-type spiral galaxy. It is believed to be a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy or on its rebound into the latter due to their interactions, velocities, and proximity to one another in the night sky. It also has an H II nucleus. Etymology The galaxy gets its name from the constellation Triangulum, where it can be spotted. It is sometimes informally referred to as the " Pinwheel Galaxy" by some astronomy references, in some computerized telescope software, and in some public outreach websites. However, the SIMBAD Astronomical Databa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a dwarf galaxy and satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around , the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal ( away) and the possible dwarf irregular galaxy called the Canis Major Overdensity. Based on the D25 isophote at the B-band (445 nm wavelength of light), the Large Magellanic Cloud is about across. It is roughly one-hundredth the mass of the Milky Way and is the fourth-largest galaxy in the Local Group, after the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), the Milky Way, and the Triangulum Galaxy (M33). The LMC is classified as a Magellanic spiral. It contains a stellar bar that is geometrically off-center, suggesting that it was once a barred dwarf spiral galaxy before its spiral arms were disrupted, likely by tidal interactions from the nearby Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) and the Milky Way's gravity. The LMC is predicted to merge with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the ''visual angle'', and in optics, it is the ''angular aperture'' (of a lens (optics), lens). The angular diameter can alternatively be thought of as the angular displacement through which an eye or camera must rotate to look from one side of an apparent circle to the opposite side. A person can Angular resolution, resolve with their naked eyes diameters down to about 1 arcminute (approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians). This corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance, or to perceiving Venus as a disk under optimal conditions. Formulation The angular diameter of a circle whose plane is perpendicular to the displacement vector between the point of view and the center of said circle can be calculated using the formula :\delta = 2\arctan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, world's third-oldest university in continuous operation. The university's founding followed the arrival of scholars who left the University of Oxford for Cambridge after a dispute with local townspeople. The two ancient university, ancient English universities, although sometimes described as rivals, share many common features and are often jointly referred to as Oxbridge. In 1231, 22 years after its founding, the university was recognised with a royal charter, granted by Henry III of England, King Henry III. The University of Cambridge includes colleges of the University of Cambridge, 31 semi-autonomous constituent colleges and List of institutions of the University of Cambridge#Schools, Faculties, and Departments, over 150 academic departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are the following: * Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), about away * Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), about away The Magellanic Clouds are visible to the unaided eye from the Southern Hemisphere, but cannot be observed from the most northern latitudes. History They may be the objects mentioned by the polymath Ibn Qutaybah (d. 889 CE), in his book on ''Al-Anwā̵’'' (the stations of the Moon in pre-Islamic Arabian culture): وأسفل من سهيل قدما سهيل . وفى مجرى قدمى سهيل، من خلفهما كواكب زهر كبار، لا ترى بالعراق، يسميها أهل تهامة الأعبار And be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |