|
NGC 2547
NGC 2547 is a southern open cluster in Vela, discovered by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1751 from South Africa. The star cluster is young with an age of 20-30 million years. Observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope showed a shell around the B3 III/IV-type star HD 68478. This could be a sign of recent mass loss in this star. A study using Gaia DR2 data showed that NGC 2547 formed about 30 million years ago together with a new discovered star cluster, called BJ20186. The star cluster NGC 2547 has a similar age compared with Trumpler 10, NGC 2451B, Collinder 135 and Collinder 140. It was suggested that all these clusters formed in a single event of triggered star formation. NGC 2547 shows evidence for mass segregation down to 3 . Cluster members with debris disks Observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope have shown that ≤1% of the stars in NGC 2547 have infrared excess in 8.0 μm and 30-45% of the B- to F-type stars have infrared excess at 24 μm. The sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
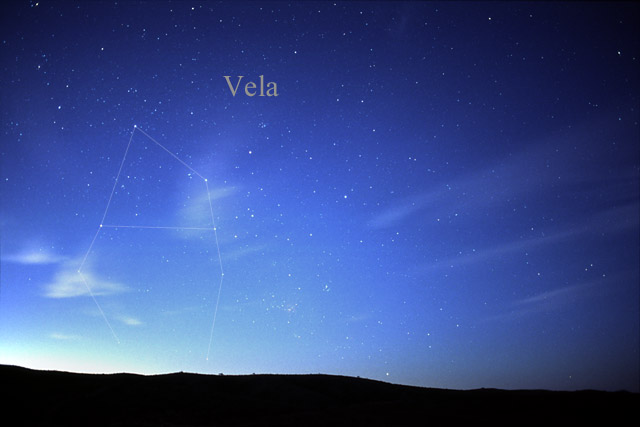
Vela (constellation)
Vela is a constellation in the southern sky, which contains the Vela Supercluster. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship ''Argo Navis'', which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis. With an apparent magnitude of 1.8, its brightest star is the hot blue multiple star Gamma Velorum, one component of which is the closest and brightest Wolf-Rayet star in the sky. Delta and Kappa Velorum, together with Epsilon and Iota Carinae, form the asterism known as the False Cross. 1.95-magnitude Delta is actually a triple or quintuple star system. History Argo Navis was one of the 48 classical constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and represented the ship ''Argo'', used by Jason and the Argonauts on their quest for the Golden Fleece in Greek mythology. German cartographer Johann Bayer depicted the constellation on his '' Uranometria'' of 1603, and gave the stars B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-type Star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Clusters
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of tens to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. Each one is loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and becomes disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the Galactic Center. This can result in a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters and a dispersion into the main body of the galaxy. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring. Young open clusters may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's '' General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitized Sky Survey
The Digitized Sky Survey (DSS) is a digital data, digitized version of several photography, photographic astronomical surveys of the night sky, produced by the Space Telescope Science Institute between 1983 and 2006. Versions and source material The term Digitized Sky Survey originally referred to the publication in 1994 of a digital version of an all-sky photographic atlas used to produce the first version of the Guide Star Catalog. For the northern sky, the National Geographic Society – Palomar Observatory Sky Survey E-band (red, named after the Eastman Kodak IIIa-E Photographic emulsion, emulsion used), provided almost all of the source data (plate code "XE" in the survey). For the southern sky, the J-band (blue, Eastman Kodak IIIa-J) of the European Southern Observatory, ESO/Science and Engineering Research Council, SERC Southern Sky Atlas (known as the SERC-J, code "S") and the "quick" V-band (blue or V in the UBV photometric system, Johnson–Kron–Cousins system, Eastm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
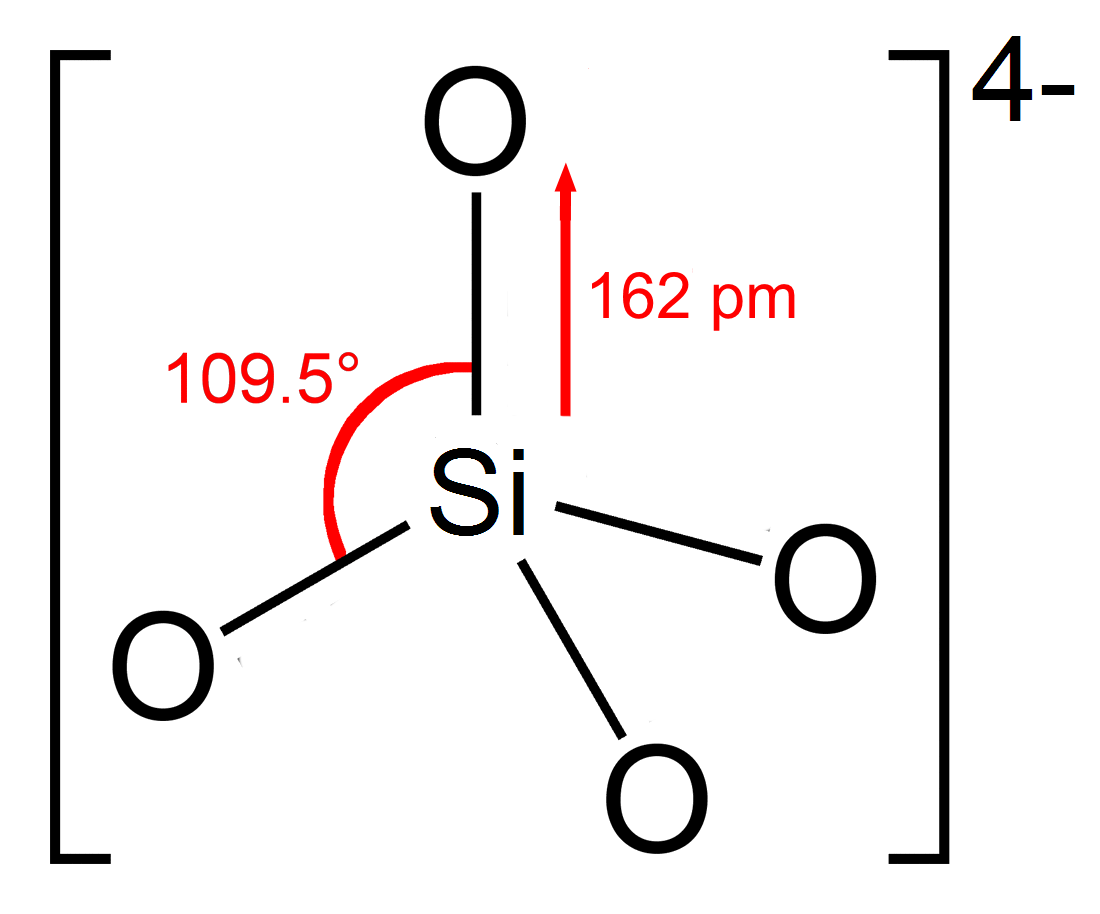
Silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate . Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In most silicates, a silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2MASS 08093547-4913033
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh less than it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Pan Disk
A Peter Pan disk is a circumstellar disk around a star or brown dwarf that appears to have retained enough gas to form a gas giant planet for much longer than the typically assumed gas dispersal timescale of approximately 5 million years. Several examples of such disks have been observed to orbit stars with spectral types of M or later. The presence of gas around these disks has generally been inferred from the total amount of radiation emitted from the disk at infrared wavelengths, and/or spectroscopic signatures of hydrogen accreting onto the star. To fit one specific definition of a Peter Pan disk, the source needs to have an infrared "color" of Ks-W4>2, an age of >20 Myr and spectroscopic evidence of accretion. In 2016 volunteers of the Disk Detective project discovered WISE J080822.18-644357.3 (or J0808). This low-mass star showed signs of youth, for example a strong infrared excess and active accretion of gaseous material. It is part of the 45 Myr old Carina young mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet Formation
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbiting the Sun which clumped up together to form the planets. The theory was developed by Immanuel Kant and published in his '' Universal Natural History and Theory of the Heavens'' (1755) and then modified in 1796 by Pierre Laplace. Originally applied to the Solar System, the process of planetary system formation is now thought to be at work throughout the universe. The widely accepted modern variant of the nebular theory is the solar nebular disk model (SNDM) or solar nebular model. It offered explanations for a variety of properties of the Solar System, including the nearly circular and coplanar orbits of the planets, and their motion in the same direction as the Sun's rotation. Some elements of the original nebular theory are echoed in modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Line (astronomy)
In astronomy or planetary science, the frost line, also known as the snow line or ice line, is the minimum distance from the central protostar of a solar nebula where the temperature is low enough for volatile compounds such as water, ammonia, methane, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide to condense into solid grains, which will allow their accretion into planetesimals. Beyond the line, otherwise gaseous compounds (which are much more abundant) can be quite easily condensed to allow formation of gas and ice giants; while within it, only heavier compounds can be accreted to form the typically much smaller rocky planets. The term itself is borrowed from the notion of " frost line" in soil science, which describes the maximum depth from the surface that groundwater can freeze. Each volatile substance has its own frost line (e.g. carbon monoxide, nitrogen, and argon), so it is important to always specify which material's frost line is referred to, though omission is common, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Dwarf
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun. However, due to their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs are not easily observed. Not one star that fits the stricter definitions of a red dwarf is visible to the naked eye. Proxima Centauri, the star nearest to the Sun, is a red dwarf, as are fifty of the sixty nearest stars. According to some estimates, red dwarfs make up three-quarters of the fusing stars in the Milky Way. The coolest red dwarfs near the Sun have a surface temperature of about and the smallest have radii about 9% that of the Sun, with masses about 7.5% that of the Sun. These red dwarfs have spectral types of L0 to L2. There is some overlap with the properties of brown dwarfs, since the most massive brown dwarfs at lower metallicity can be as hot as and have late M spectral types. Definitions and usage of the term "red d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Body
A planetary-mass object (PMO), planemo, or planetary body (sometimes referred to as a world) is, by geophysical definition of planet, geophysical definition of celestial objects, any celestial object massive enough to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium, but not enough to sustain core fusion like a star. The purpose of this term is to classify together a broader range of celestial objects than 'planet', since many objects similar in geophysical terms do not conform to conventional expectations for a planet. Planetary-mass objects can be quite diverse in origin and location. They include planets, dwarf planets, planetary-mass moon, planetary-mass satellites and free-floating planets, which may have been ejected from a system (rogue planets) or formed through cloud-collapse rather than accretion (sub-brown dwarfs). Usage in astronomy While the term technically includes exoplanets and other objects, it is often used for objects with an uncertain nature or objects that do not fit in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |