|
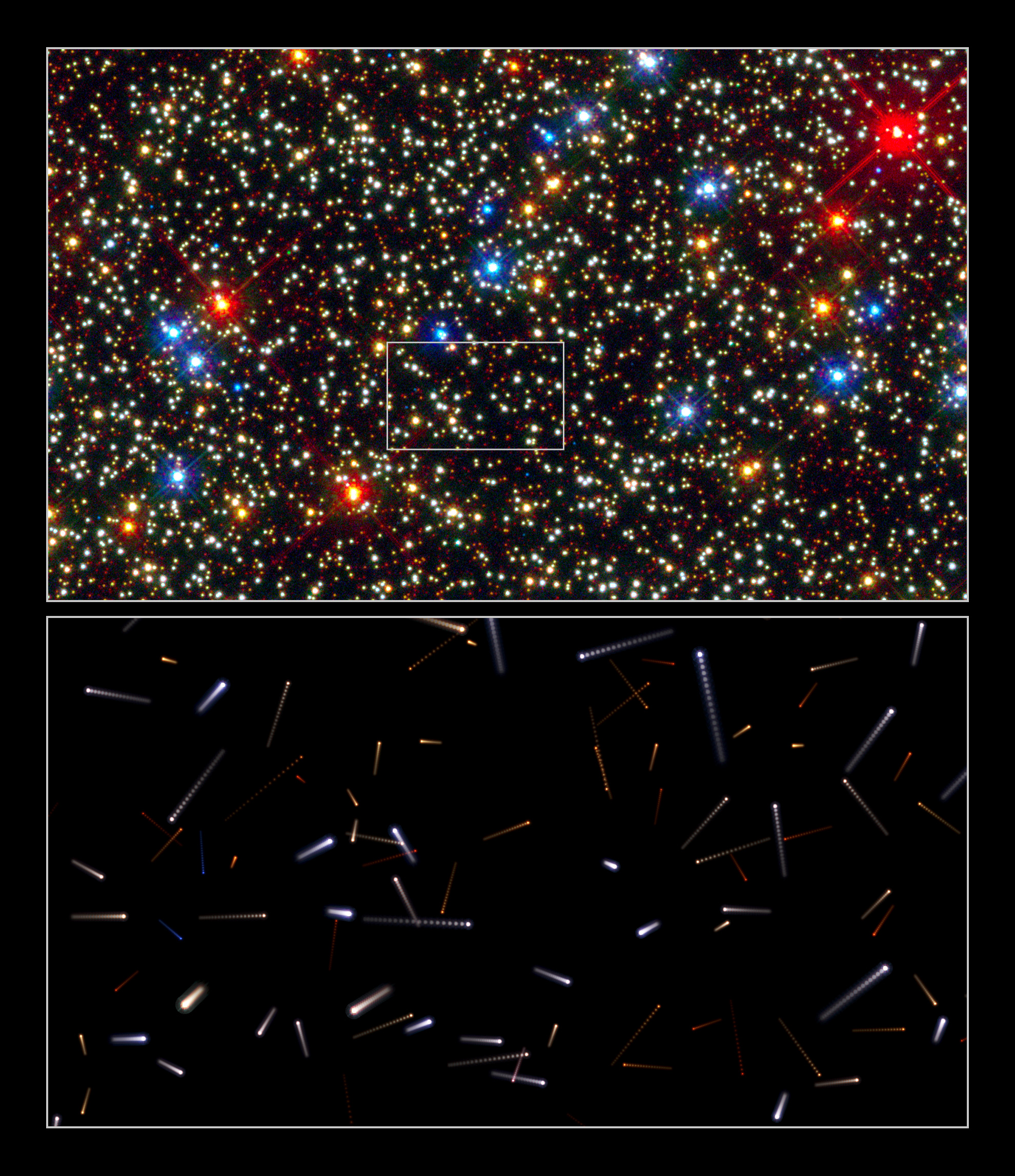
NGC 2419
NGC 2419 (also known as Caldwell 25) is a globular cluster in the constellation Lynx. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 31, 1788. NGC 2419 is at a distance of about 300,000 light years from the Solar System and at the same distance from the Galactic Center. NGC 2419 bears the nickname "the Intergalactic Wanderer," which was bestowed when it was erroneously thought not to be in orbit around the Milky Way. Its orbit takes it farther away from the galactic center than the Magellanic Clouds, but it can (with qualifications) be considered as part of the Milky Way. At this great distance it takes three billion years to make one trip around the galaxy.Ferris, Timothy. ''Seeing in the Dark''. 2002. p. 244 The cluster is dim in comparison to more famous globular clusters such as M13. Nonetheless, NGC 2419 is a 9th magnitude object and is readily viewed, in good sky conditions, with good quality telescopes as small as 102mm (four inches) in aperture. Intrinsically it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble Space Telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories program, Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible spectrum, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are the following: * Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), about away * Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), about away The Magellanic Clouds are visible to the unaided eye from the Southern Hemisphere, but cannot be observed from the most northern latitudes. History They may be the objects mentioned by the polymath Ibn Qutaybah (d. 889 CE), in his book on ''Al-Anwā̵’'' (the stations of the Moon in pre-Islamic Arabian culture): وأسفل من سهيل قدما سهيل . وفى مجرى قدمى سهيل، من خلفهما كواكب زهر كبار، لا ترى بالعراق، يسميها أهل تهامة الأعبار And be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's '' General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting in a stable, compact formation. Globular clusters are similar in form to dwarf spheroidal galaxies, and though globular clusters were long held to be the more luminous of the two, discoveries of outliers had made the distinction between the two less clear by the early 21st century. Their name is derived from Latin (small sphere). Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars". Although one globular cluster, Omega Centauri, was observed in antiquity and long thought to be a star, recognition of the clusters' true nature came with the advent of telescopes in the 17th century. In early telescopic observations, globular clusters appeared as fuzzy blobs, leading French astronomer Charles Messier to include many of them in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayall II
Mayall II, also known as NGC-224-G1, SKHB 1, GSC 2788:2139, HBK 0-1, M31GC J003247+393440 or Andromeda's Cluster, is a globular cluster orbiting M31, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is located from the Andromeda Galaxy's galactic core, and is the brightest (by absolute magnitude) globular cluster in the Local Group, with an absolute visual magnitude of −10.94 and the luminosity of 2 million Suns. It has an apparent magnitude of 13.81 in V band. Mayall II is considered to have twice the mass of Omega Centauri, and may contain a central, intermediate-mass (~ 2 M⊙) black hole. It was first identified as a possible globular cluster by American astronomers Nicholas Mayall and Olin J. Eggen in 1953 using a Palomar Schmidt plate exposed in 1948. Because of the widespread distribution of metallicity, indicating multiple star generations and a large stellar creation period, many contend that it is not a true globular cluster, but is actually the galactic core that remains of a dwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy and is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way. It was originally named the Andromeda Nebula and is cataloged as Messier 31, M31, and NGC 224. Andromeda has a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter of about and is approximately from Earth. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after Andromeda (mythology), the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology. The virial mass of the Andromeda Galaxy is of the same order of magnitude as that of the Milky Way, at . The mass of either galaxy is difficult to estimate with any accuracy, but it was long thought that the Andromeda Galaxy was more massive than the Milky Way by a margin of some 25% to 50%. However, this has been called into question by early-21st-century studies indicating a possibly lower mass for the Andromeda Galaxy and a higher mass for the Milky Way. The Androm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
A dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) is a term in astronomy applied to small, low-luminosity galaxies with very little dust and an older stellar population. They are found in the Local Group as companions to the Milky Way and as systems that are companions to the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). While similar to dwarf elliptical galaxies in appearance and properties such as little to no gas or dust or recent star formation, they are approximately spheroidal in shape and generally have lower luminosity. Discovery Despite the radii of dSphs being much larger than those of globular clusters, they are much more difficult to find due to their low luminosities and surface brightnesses. Dwarf spheroidal galaxies have a large range of luminosities, and known dwarf spheroidal galaxies span several orders of magnitude of luminosity. Their luminosities are so low that Ursa Minor, Carina, and Draco, the known dwarf spheroidal galaxies with the lowest luminosities, have mass-to-light ratios (M/L) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest known globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150 light-years. It is estimated to contain approximately 10 million stars, with a total mass of 4 million solar masses, making it the most massive known globular cluster in the Milky Way. Omega Centauri is very different from most other galactic globular clusters to the extent that it is thought to have originated as the core remnant of a disrupted dwarf galaxy. Observation history Around 150 AD, Greco-Roman writer and astronomer Ptolemy catalogued this object in his ''Almagest'' as a star on the centaur's back, "Quae est in principio scapulae". German cartographer Johann Bayer used Ptolemy's data to designate this object "Omega Centauri" with his 1603 publication of '' Uranometria''. Using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in astronomy, astrophysics and related fields. It publishes original research in two formats: papers (of any length) and letters (limited to five pages). MNRAS publishes more articles per year than any other astronomy journal. The learned society journal has been in continuous existence since 1827 and became online only in 2020. It operates as a partnership between the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), who select and peer-review the contents, and Oxford University Press (OUP), who publish and market the journal. Despite its name, MNRAS is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the RAS. In 2024 MNRAS became a purely gold open access journal. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 13
Messier 13, or M13 (also designated NGC 6205 and sometimes called the Great Globular Cluster in Hercules, the Hercules Globular Cluster, or the Great Hercules Cluster), is a globular cluster of several hundred thousand stars in the constellation of Hercules (constellation), Hercules. Discovery and visibility Messier 13 was discovered by Edmond Halley in 1714, and cataloged by Charles Messier on June 1, 1764, into his list of objects not to mistake for comets; Messier's list, including Messier 13, eventually became known as the Messier object, Messier catalog. It is located at right ascension 16h 41.7m, declination +36° 28'. Messier 13 is often described by astronomers as the most magnificent globular cluster visible to northern observers. About one third of the way from Vega to Arcturus, four bright stars in Hercules (constellation), Hercules form the Keystone Asterism (astronomy), asterism, the broad torso of the hero. M13 can be seen in this asterism of the way north (Points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |