|
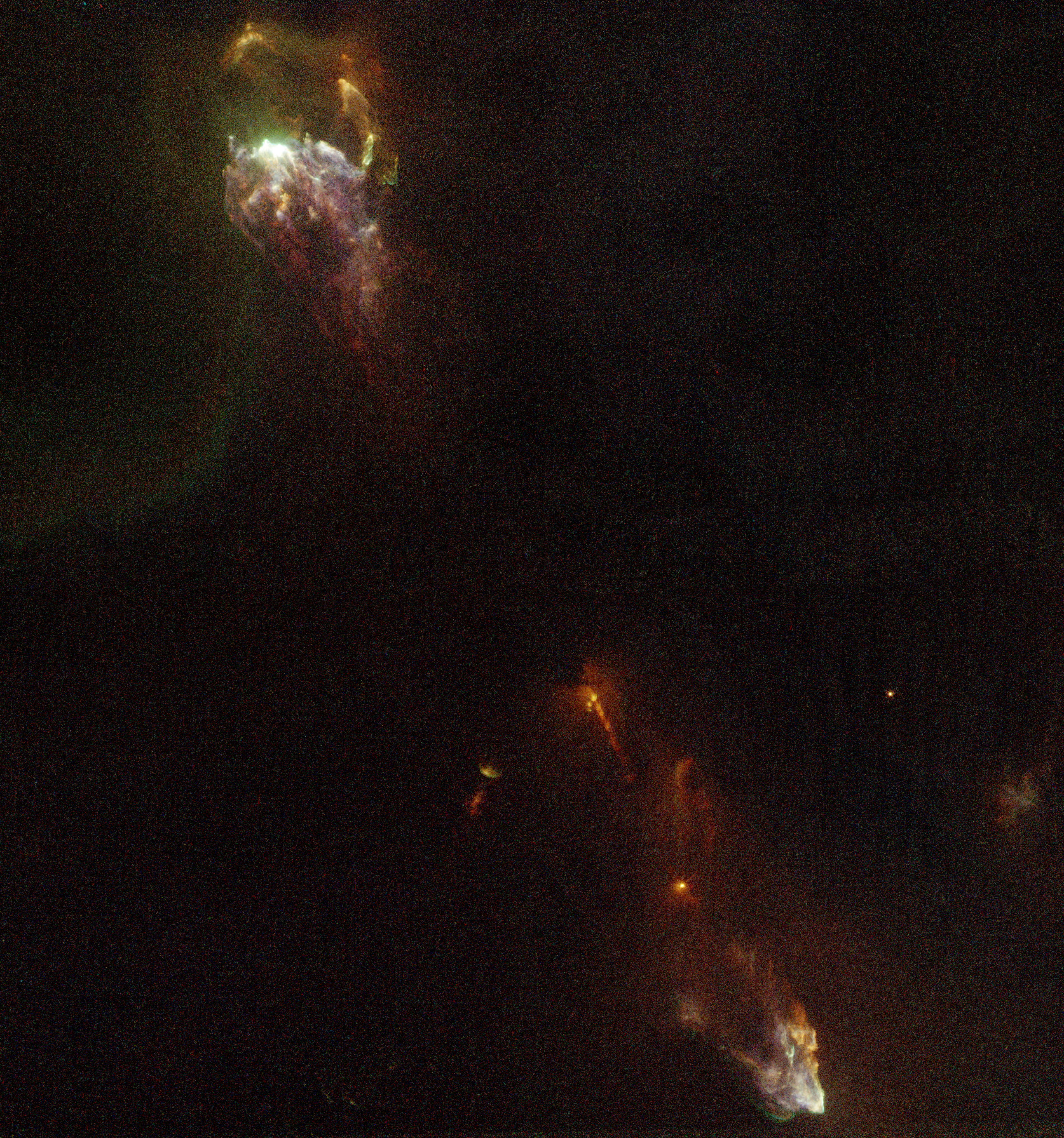
NGC 1999
NGC 1999, also known as The Cosmic Keyhole, is a dust-filled bright nebula with a vast hole of empty space represented by a black patch of sky, as can be seen in the photograph. It is a reflection nebula, and shines from the light of the variable star V380 Orionis. It was previously believed that the black patch was a dense cloud of dust and gas which blocked light that would normally pass through, called a dark nebula. Analysis of this patch by the infrared telescope Herschel (October 9, 2009), which has the capability of penetrating such dense cloud material, resulted in continued black space. This led to the belief that either the cloud material was immensely dense or that an unexplained phenomenon had been detected. With support from ground-based observations done using the submillimeter bolometer cameras on the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment radio telescope (November 29, 2009) and the Mayall (Kitt Peak) and Magellan telescopes (December 4, 2009), it was determined that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William Herschel, William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the Celestial sphere, celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolometer
A bolometer is a device for measuring radiant heat by means of a material having a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley. Principle of operation A bolometer consists of an absorptive element, such as a thin layer of metal, connected to a thermal reservoir (a body of constant temperature) through a thermal link. The result is that any radiation impinging on the absorptive element raises its temperature above that of the reservoir – the greater the absorbed power, the higher the temperature. The intrinsic thermal time constant, which sets the speed of the detector, is equal to the ratio of the heat capacity of the absorptive element to the thermal conductance between the absorptive element and the reservoir. The temperature change can be measured directly with an attached resistive thermometer, or the resistance of the absorptive element itself can be used as a thermometer. Metal bolometers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Nebulae
In astronomy, reflection nebulae are clouds of interstellar dust which might reflect the light of a nearby star or stars. The energy from the nearby stars is insufficient to ionize the gas of the nebula to create an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust visible. Thus, the frequency spectrum shown by reflection nebulae is similar to that of the illuminating stars. Among the microscopic particles responsible for the scattering are carbon compounds (e. g. diamond dust) and compounds of other elements such as iron and nickel. The latter two are often aligned with the galactic magnetic field and cause the scattered light to be slightly polarized. Discovery Analyzing the spectrum of the nebula associated with the star Merope in the Pleiades, Vesto Slipher concluded in 1912 that the source of its light is most likely the star itself, and that the nebula reflects light from the star (and that of the star Alcyone). Calculations by Ejnar H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's '' General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as '' spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbig–Haro Object
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are bright patches of nebula, nebulosity associated with newborn stars. They are formed when narrow jets of partially plasma (physics), ionised gas ejected by stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at several hundred kilometers per second. Herbig–Haro objects are commonly found in Star formation#Stellar nurseries, star-forming regions, and several are often seen around a single star, aligned with its axis of rotation, rotational axis. Most of them lie within about one parsec (3.26 light-years) of the source, although some have been observed several parsecs away. HH objects are transient phenomena that last around a few tens of thousands of years. They can change visibly over timescales of a few years as they move rapidly away from their parent star into the gas clouds of interstellar space (the interstellar medium or ISM). Hubble Space Telescope observations have revealed the complex evolution of HH objects over the period of a few years, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HH 1/2
The Herbig–Haro object, Herbig-Haro objects HH 1/2 are the first such objects to be recognized as Herbig-Haro objects and were discovered by George Herbig and Guillermo Haro. They are located at a distance of about 1343 light-years (412 parsec) in the constellation Orion (constellation), Orion near NGC 1999. HH 1/2 are among the brightest Herbig-Haro objects in the sky and consist of a pair of oppositely oriented bow shocks, separated by 2.5 Minute and second of arc, arcminutes (a projected separation of about 1.1 light year). The HH 1/2 pair were the first Herbig-Haro objects with detected proper motion and HH 2 was the first Herbig-Haro object to be detected in X-ray astronomy, x-rays. Some of the structures in the Herbig-Haro Objects move with a speed of 400 km/s. The central region The central region contains an opaque cloud core with an astrophysical jet and a highly embedded Star system, multiple-star system that remains invisible below 3 Microns. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Despite its inclusion of the word "year", the term should not be misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years). Definitions As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the light-year is the product of the Julian year (365.25 days, as opposed to the 365.2425-day Gregorian year or the 365.24219-day Tropical year that both approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellan Telescopes
The Magellan Telescopes are a pair of optical telescopes located at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. The two telescopes are named after the astronomer Walter Baade and the philanthropist Landon T. Clay. First light for the telescopes was on September 15, 2000 for the Baade, and September 7, 2002 for the Clay. A consortium consisting of the Carnegie Institution for Science, University of Arizona, Harvard University, the University of Michigan and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology built and operate the twin telescopes. The telescopes were named after the sixteenth-century Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. The Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) is an extremely large telescope under construction, as part of the US Extremely Large Telescope Program. Current instruments on the Magellan Telescopes Baade telescope: * Inamori Magellan Areal Camera and Spectrograph (IMACS) * FourStar * Folded port InfraRed Echellette (FIRE) * Magellan Echellete (MagE) Clay telescope: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas U
Nicholas is a male name, the Anglophone version of an ancient Greek name in use since antiquity, and cognate with the modern Greek , . It originally derived from a combination of two Greek words meaning 'victory' and 'people'. In turn, the name means "victory of the people." The name has been widely used in countries with significant Christian populations, owing in part to the veneration of Saint Nicholas, which became increasingly prominent in Western Europe from the 11th century. Revered as a saint in many Christian denominations, the Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and Anglican Churches all celebrate Saint Nicholas Day on December 6. In maritime regions throughout Europe, the name and its derivatives have been especially popular, as St Nicholas is considered the protector saint of seafarers. This remains particularly so in Greece, where St Nicholas is the patron saint of the Hellenic Navy. Origins The name derives from the . It is understood to mean 'victory of the people' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, just as optical telescopes are used to make observations in the visible light, visible portion of the spectrum in traditional optical astronomy. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxy, galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large Parabolic antenna, parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in tracking and communicating with satellites an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |