|
NASA Astronaut Group 14
NASA Astronaut Group 14 ("The Hogs") was a group of 24 astronauts announced by NASA on 31 March 1992. The group's name derived from ''The Muppet Show'' skit " Pigs in Space" and from the group's sponsorship of a pot-bellied pig at the Houston Zoo. Pilots * Scott J. Horowitz (born 1957), U.S. Air Force (4 flights) :STS-75 :STS-82 :STS-101 :STS-105 * Brent W. Jett Jr. (born 1958), U.S. Navy (4 flights) :STS-72 :STS-81 :STS-97 :STS-115 * Kevin R. Kregel (born 1956), U.S. Air Force (4 flights) :STS-70 :STS-78 :STS-87 :STS-99 * Kent V. Rominger (born 1956), U.S. Navy (5 flights) :STS-73 :STS-80 : STS-85 :STS-96 :STS-100 Mission Specialists * Daniel T. Barry (born 1953), Scientist (3 flights) :STS-72 :STS-96 :STS-105 * Charles E. Brady Jr. (1951-2006), U.S. Navy (1 flight) :STS-78 * Catherine Coleman (born 1960), U.S. Air Force (3 flights) :STS-73 :STS-93 : Soyuz TMA-20 :Expedition 26/ 27 * Michael Gernhardt (born 1956), Bioengineer (4 flights) :STS-69 : S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Astronaut Group 13
NASA Astronaut Group 13 (the Hairballs) was a group of 23 astronauts announced by NASA on 17 January 1990. The group name came from its selection of a black cat as a mascot, to play against the traditional unlucky connotations of the number 13. Pilots *Kenneth Cockrell (born 1950), U.S. Navy (5 flights) :STS-56 (Science Mission; Flew as a Mission specialist) :STS-69 (2nd flight of the Wake Shield Facility) :STS-80 (3rd flight of the Wake Shield Facility) :STS-98 ( ISS Assembly Mission - Launched the Destiny Laboratory Module) :STS-111 ( ISS Resupply Mission; Launched Expedition 5) *Eileen Collins (born 1956), U.S. Air Force (4 flights) :STS-63 ( Shuttle-Mir Mission; became the first female pilot of a U.S. Spacecraft) : STS-84 ( Shuttle-Mir Mission) :STS-93 (Deployed Chandra X-Ray Observatory; became the first female commander of a U.S. Spacecraft) :STS-114 ( Return to Flight) * William G. Gregory (born 1957), U.S. Air Force (1 flight) :STS-67 (2nd flight of the AS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-81
STS-81 was a January 1997 Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Atlantis, ''Atlantis'' mission to the Mir space station. Crew Crew seat assignments Mission highlights STS-81 was the fifth of nine planned missions to Mir and the second one involving an exchange of U.S. astronauts. Astronaut John Blaha, who had been on Mir since September 19, 1996, was replaced by astronaut Jerry Linenger. Linenger spent more than four months on Mir. He returned to Earth on Space Shuttle Mission STS-84. ''Atlantis'' carried the SPACEHAB double module providing additional middeck locker space for secondary experiments. During the five days of docked operations with Mir, the crews transferred water and supplies from one spacecraft to the other. A spacewalk by Linenger and one of his Russian cosmonaut crewmates occurred after the departure of ''Atlantis''. The STS-81 mission included several experiments in the fields of advanced technology, Earth sciences, fundamental biology, human life sciences, micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
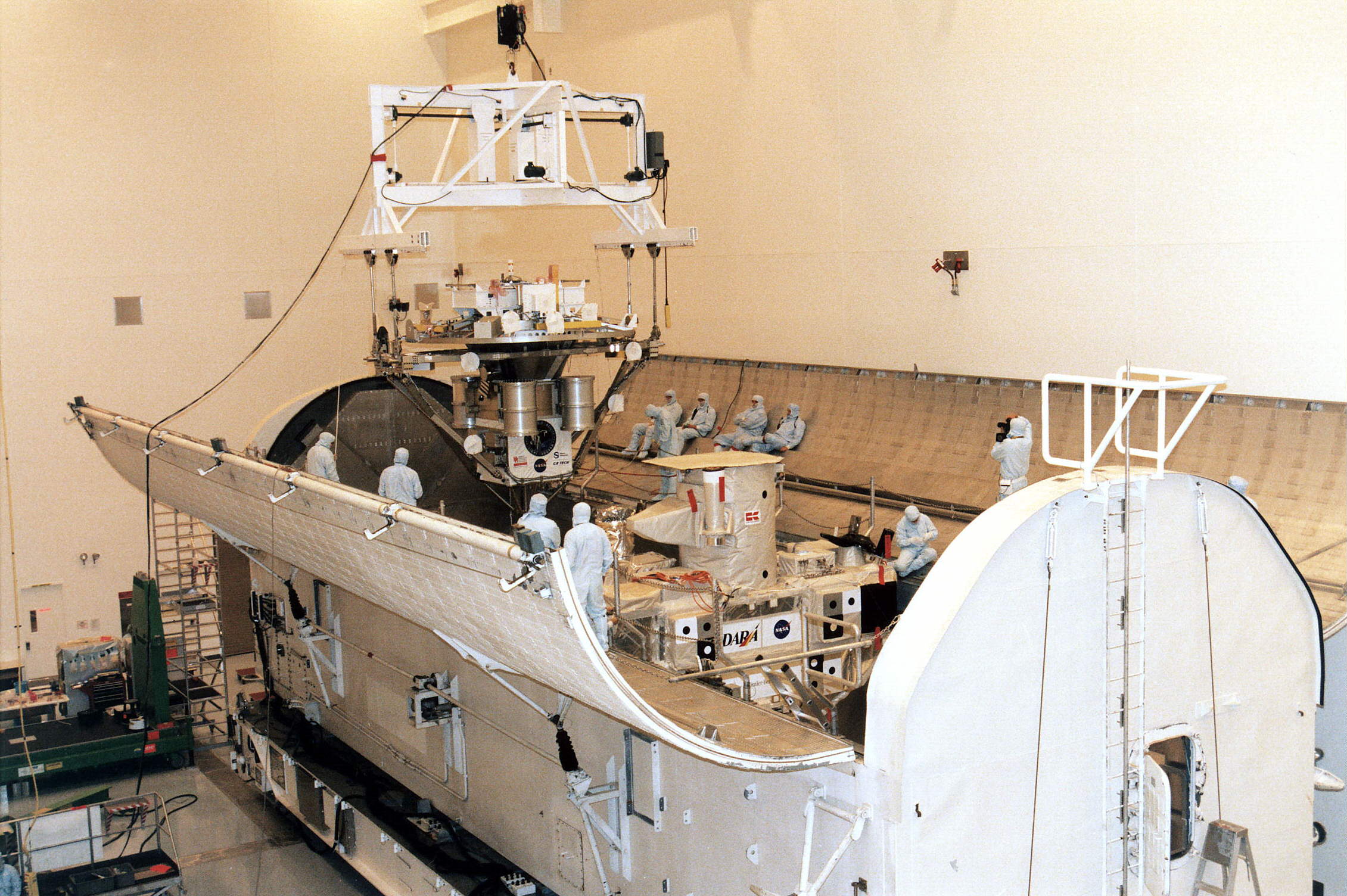
STS-100
STS-100 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. STS-100 launch on 19 April 2001, and installed the ISS Canadarm2 robotic arm. Crew Mission highlights The highest priority objectives of the flight were the installation, activation and checkout of the Canadarm2 robotic arm on the station. The arm - manufactured by MDA Space Missions under contract of the Canadian Space Agency and NASA, went into operation on 28 April 2001. It was critical to the capability to continue assembly of the International Space Station. The arm was also necessary to attach a new airlock to the station on the subsequent shuttle flight, mission STS-104. The final component of the Canadarm is the Mobile Base System (MBS), which was installed on board the station during the STS-111 flight. Other major objectives for ''Endeavours mission were to berth the ''Raffaello'' logistics module to the station, activate it, transfer cargo betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-96
STS-96 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery'', and the first shuttle flight to dock at the International Space Station. It was Discovery's 26th flight. The shuttle carried the Spacehab module in the payload, filled with cargo for station outfitting. STS-96 launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 27 May 1999 at 06:49:42 AM EDT and returned to Kennedy on 6 June 1999, 2:02:43 AM EDT. Crew Space walk *''Jernigan and Barry ''– EVA 1 *EVA 1 Start: 30 May 1999 – 02:56 UTC *EVA 1 End: 30 May 1999 – 10:51 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 55 minutes Crew seat assignments Mission highlights ISSafterSTS96.jpg, Illustration of the International Space Station (ISS) during Space Shuttle flight STS-96 01 ICC STS-96.jpg, Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC), with among other the Russian cargo crane "STRELA", which was mounted on the ISS STS-96 was a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station carry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-85
STS-85 was the 23rd flight of Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' that performed multiple space science packages. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 7 August 1997. The main STS-85 payloads included the satellite known as Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 CRISTA-SPAS-02. Crew Jeffrey Ashby was originally assigned to be pilot on this mission, but asked to be relieved in order to take care of his wife, who was dying from cancer. He was replaced by Kent Rominger and was assigned to pilot STS-93 instead. The launch occurred on Rominger's 41st birthday. Crew seat assignments Mission highlights The deployment and retrieval of a satellite designed to study Earth's middle atmosphere along with a test of potential International Space Station hardware highlighted NASA's sixth Shuttle mission of 1997. The prime payload for the flight, the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-80
STS-80 was a Space Shuttle mission flown by Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. The launch was originally scheduled for October 31, 1996, but was delayed to November 19 for several reasons. Likewise, the landing, which was originally scheduled for December 5, was pushed back to December 7 after bad weather prevented landing for two days. It was the longest Shuttle mission ever flown at 17 days, 15 hours, and 53 minutes. Although two spacewalks were planned for the mission, they were both canceled after problems with the airlock hatch prevented astronauts Tom Jones and Tammy Jernigan from exiting the orbiter. Crew Crew seat assignments Musgrave was supposed to sit in Seat 5 during landing, however, he actually stood on the flight deck behind Cockrell in Seat 1 throughout re-entry and landing to film the spacecraft's reentry through the overhead windows. Mission highlights * The mission deployed two satellites and successfully recovered them after they had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-73
STS-73 was a Space Shuttle program mission, during October–November 1995, on board the Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. The mission was the second mission for the United States Microgravity Laboratory. The crew, who spent 16 days in space, were broken up into 2 teams, the red team and the blue team. The mission also included several Detailed Test Objectives or DTO's. Crew Backup crew Crew seat assignments Mission highlights The second United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) Spacelab mission was the prime payload on STS-73. The 16-day flight continued a cooperative effort of the U.S. government, universities and industry to push back the frontiers of science and technology in "microgravity", the near-weightless environment of space. On October 26, through pre-recorded video, Mission Commander Ken Bowersox threw out the first pitch for Game 5 of the 1995 World Series between the Cleveland Indians and the Atlanta Braves from orbit. Some of the experiments carried on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent V
Kent is a ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Greater London to the north-west. The county town is Maidstone. The county has an area of and had population of 1,875,893 in 2022, making it the fifth most populous county in England. The north of the county contains a conurbation which includes the towns of Chatham, Gillingham, and Rochester. Other large towns are Maidstone and Ashford, and the borough of Canterbury holds city status. For local government purposes Kent consists of a non-metropolitan county, with twelve districts, and the unitary authority area of Medway. The county historically included south-east Greater London, and is one of the home counties. The north of Kent is a plain bordering the Thames Estuary. South of this is the North Downs, a chalk downland ridge which crosses the county from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-99
STS-99 was a Space Shuttle mission using ''Endeavour'', that launched on 11 February 2000 from Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The primary objective of the mission was the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) project. This was also the last solo flight of ''Endeavour''; all future flights for ''Endeavour'' became devoted to the International Space Station. STS-99 was also the first Shuttle mission of the 2000s. Crew Crew seat assignments Mission highlights The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) was an international project spearheaded by the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (now the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency), an agency within the U.S. Department of Defense, and NASA, with participation of the German Aerospace Center DLR. Its objective was to obtain the most complete high-resolution digital topographic database of the Earth. SRTM consisted of a specially modified radar system that flew onboard ''Endeavour'' during its 11-day mission. This radar sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-87
STS-87 was a Space Shuttle mission launched from Launch Complex 39B of the Kennedy Space Center on 19 November 1997. It was the 88th flight of the Space Shuttle and the 24th flight of '' Columbia''. The mission goals were to conduct experiments using the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-4), conduct two EVAs, and deploy the SPARTAN-201 experiment. This mission marked the first time an EVA was performed from ''Columbia''. EVAs from ''Columbia'' were originally planned for STS-5 in 1982 and STS-80 in 1996, but were canceled due to spacesuit and airlock problems, respectively. It also marked the first EVA conducted by a Japanese astronaut, Takao Doi. Crew Backup crew Space walks *'' Scott and Doi'' – EVA 1 *EVA 1 Start: 25 November 1997 – 00:02 UTC *EVA 1 End: 25 November 1997 – 07:45 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 43 minutes *'' Scott and Doi'' – EVA 2 *EVA 2 Start: 3 December 1997 – 09:09 UTC *EVA 2 End: 3 December 1997 – 14:09 UTC *Duration: 4 hours, 59 minutes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-78
STS-78 was the fifth dedicated Life and Microgravity Spacelab mission for the Space Shuttle program, flown partly in preparation for the International Space Station project. The mission used the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'', which lifted off successfully from Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B on June 20, 1996. This marked the 78th flight of the Space Shuttle and 20th mission for ''Columbia''. Crew Backup crew Mission objectives * Research into the effects of long-duration spaceflight on human physiology in preparation for flights on the International Space Station. * 22 life science and microgravity experiments using the Orbiter's pressurized Life & Microgravity Spacelab module (LM2). * Tests into the use of the Orbiter's Reaction Control System jets to raise the altitude of orbiting satellites. Crew seat assignments Mission highlights During the 16-day, 21-hour mission, the crew of ''Columbia'' assisted in the preparations for the International Space Station by stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-70
STS-70 was the 21st flight of the Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Discovery, ''Discovery'', and the last of 7 shuttle missions to carry a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS). This was the first shuttle mission controlled from the new mission control center room at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. STS-70 was also the first flight of the new Block 1 orbiter main engine, designed to improve both engine performance and safety. The mission was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 1995, only six days after the landing of sister ship ''Atlantis'', marking the fastest turnaround between flights in the history of the program. Crew Crew seat assignments Preparations and launch STS-70 had originally moved ahead of STS-71 because of a delay in the launch of the Russian Spektr laboratory module to the Russian space station Mir. However, on May 31, 1995, shuttle managers assessed damage to the External Tank of STS-70 caused by nesting northern flicker, flicker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |