|
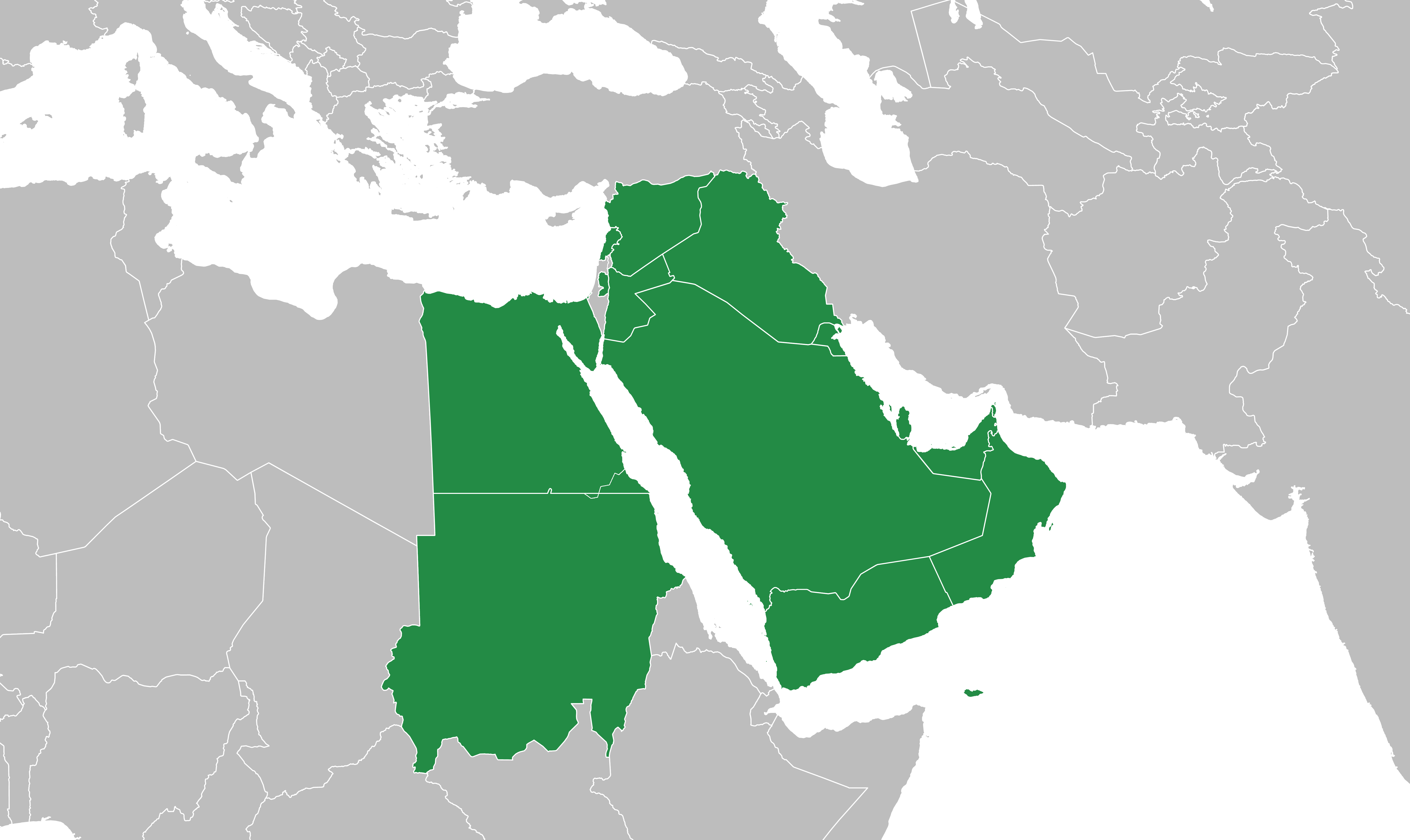
Mashriqi Arabic
Mashriqi Arabic, or Mashriqi ʿAmmiya, encompasses the varieties of Arabic spoken in the Mashriq, including the countries of Egypt, Lebanon, Palestine, Kuwait, Jordan, Syria, Cyprus, Turkey, Iraq, Sudan, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Bahrain and Qatar. The variety is sometimes referred to as Eastern Arabic, as opposed to Western Arabic (Maghrebi Arabic or Darija) and includes Mesopotamian Arabic and Peninsular Arabic, along with Egyptian Arabic, Sudanese Arabic, and Levantine Arabic. Speakers of Mashriqi call their language ''ʿAmmiya'', which means "language of the majority" in Modern Standard Arabic. Modern Standard Arabic ( ''al-fuṣḥá'') is the primary language used in the government, legislation, and judiciary of countries in the Mashriq region. Mashriqi Arabic is used for almost all spoken communication, as well as in television and advertising in Egypt and Lebanon, but Modern Standard Arabic is used in written communication. In Lebanon, where Mashriqi Arabic was taug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to '' Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part ( Cyrenaica) being link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Oman shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, while sharing maritime borders with Iran and Pakistan. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast. The Madha and Musandam exclaves are surrounded by the United Arab Emirates on their land borders, with the Strait of Hormuz (which it shares with Iran) and the Gulf of Oman forming Musandam's coastal boundaries. Muscat is the nation's capital and largest city. From the 17th century, the Omani Sultanate was an empire, vying with the Portuguese and British empires for influence in the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. At its peak in the 19th century, Omani influence and control extended across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijazi Arabic
Hejazi Arabic or Hijazi Arabic (HA) ( ar, حجازي, ḥijāzī), also known as West Arabian Arabic, is a variety of Arabic spoken in the Hejaz region in Saudi Arabia. Strictly speaking, there are two main groups of dialects spoken in the Hejaz region, one by the urban population, originally spoken mainly in the cities of Jeddah, Mecca, Medina and partially in Ta'if and another dialect by the urbanized rural and bedouin populations. However, the term most often applies to the urban variety which is discussed in this article. In antiquity, the Hejaz was home to the Old Hejazi dialect of Arabic recorded in the consonantal text of the Qur'an. Old Hejazi is distinct from modern Hejazi Arabic, and represents an older linguistic layer wiped out by centuries of migration, but which happens to share the imperative prefix vowel /a-/ with the modern dialect. Classification Also referred to as the sedentary Hejazi dialect, this is the form most commonly associated with the term "Hej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koiné Language
In linguistics, a koiné language, koiné dialect, or simply koiné (Ancient Greek κοινή, "common anguage) is a standard or common language or dialect that has arisen as a result of the contact, mixing, and often simplification of two or more mutually intelligible varieties of the same language. As speakers already understood one another before the advent of the koiné, the process of koineization is not as drastic as pidginization and creolization. Unlike pidginization and creolization, there is no "target" in koineization, which thus involves continuity in that speakers do not need to abandon their own linguistic varieties. The normal influence between neighbouring dialects is not regarded as koineization. A koiné variety emerges as a new spoken variety in addition to the originating dialects. It does not change any existing dialect, which distinguishes koineization from the normal evolution of dialects. While similar to zonal auxiliary languages koiné languages ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varieties Of Arabic
The varieties (or dialects or vernacular languages) of Arabic, a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family originating in the Arabian Peninsula, are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize (or distinguish) the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be different languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic. In terms of sociolinguistics, a major distinction exists between the formal standardized language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also refers to spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – the written language prior to the mid-19th century – although there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami ( autonym: or ), is a group of mutually intelligible vernacular Arabic varieties spoken in the Levant, in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, and Turkey (historically in Adana, Mersin and Hatay only). With over 44 million speakers, Levantine is, alongside Egyptian, one of the two prestige varieties of spoken Arabic comprehensible all over the Arab world. Levantine is not officially recognized in any state or territory. Although it is the majority language in Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, it is predominantly used as a spoken vernacular in daily communication, whereas most written and official documents and media in these countries use the official Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), a form of literary Arabic only acquired through formal education that does not function as a native language. In Israel and Turkey, Levantine is a minority language. The Palestinian dialect is the closest vernacular Arabic variety to MSA, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudanese Arabic
Sudanese Arabic, also referred to as the Sudanese dialect (), Colloquial Sudanese () or locally as Common Sudanese () refers to the various related varieties of Arabic spoken in Sudan as well as parts of Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Chad. Sudanese Arabic has also influenced a number of Arabic-based pidgins and creoles, including Juba Arabic, widely used in South Sudan, as well as Ki-Nubi, spoken by the Nubi communities of Kenya and Uganda. Sudanese Arabic is highly diverse. Famed Sudanese linguist Awn ash-Sharif Gasim noted that "it is difficult to speak of a 'Sudanese colloquial language' in general, simply because there is not a single dialect used simultaneously in all the regions where Arabic is the mother tongue. Every region, and almost every tribe, has its own brand of Arabic." However, Gasim broadly distinguishes between the varieties spoken by sedentary groups along the Nile (such as the Ja'aliyyin) and pastoralist groups (such as the Baggara groups of west Suda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian ( ar, العامية المصرية, ), or simply Masri (also Masry) (), is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic dialect in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The ca. 100 million Egyptians speak a continuum of dialects, among which Cairene is the most prominent. It is also understood across most of the Arabic-speaking countries due to broad Egyptian influence in the region, including through Egyptian cinema and Egyptian music. These factors help to make it the most widely spoken and by far the most widely studied variety of Arabic. While it is primarily a spoken language, the written form is used in novels, plays and poems ( vernacular literature), as well as in comics, advertising, some newspapers and transcriptions of popular songs. In most other written media and in radio and television news reporting, literary Arabic is used. Literary Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular Arabic
Peninsular Arabic are the varieties of Arabic spoken throughout the Arabian Peninsula. This includes the countries of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Southern Iran, and Southern Iraq. The modern dialects spoken in the Arabian Peninsula are closer to Classical Arabic than elsewhere. Some of the local dialects have retained many archaic features lost in other dialects, such as the conservation of nunation for indeterminate nouns. They retain most Classical syntax and vocabulary but still have some differences from Classical Arabic like the other dialects. Varieties Ingham and Holes both note the existence of two peninsular dialect groups: # A southwestern dialect group that includes most of the dialects of South Arabia, stretching as far north as Al Bahah. Holes generalizes it to a "sedentary" or "peripheral" group that also includes dialects of historically sedentary populations on the Persian Gulf coast, such as Omani Arabic and Bahrani A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamian Arabic
Mesopotamian Arabic, ( ar, لهجة بلاد ما بين النهرين) also known as Iraqi Arabic ( ar, اللهجة العراقية), or Gilit Mesopotamian Arabic (as opposed to Qeltu Mesopotamian Arabic) is a continuum of mutually intelligible varieties of Arabic native to the Mesopotamian basin of Iraq as well as spanning into southeastern Turkey, Iran, Syria, Kuwait, and spoken in Iraqi diaspora communities. Mesopotamian Arabic has a Syriac-Aramaic substrate, and also shares significant influences from ancient Mesopotamian languages of Sumerian and Akkadian, as well as influences from Persian, Turkish, and Greek. Mesopotamian Arabic is said to be the most Syriac-Aramaic influenced dialect of Arabic, due to Syriac-Aramaic having originated in Mesopotamia, and spread throughout the Middle East (Fertile Crescent) during the Neo-Assyrian period, eventually becoming the lingua franca of the entire region before Islam. Mesopotamian Arabs and Assyrians are the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |