|
Mên-an-Tol
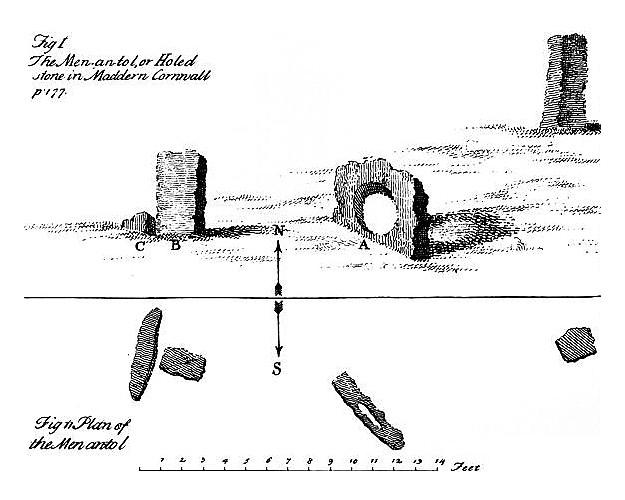
The Mên-an-Tol (Cornish language, Cornish: ''Men an Toll'') is a small formation of standing stones in Cornwall, England (). It is about three miles northwest of Madron. It is also known locally as the "Crick Stone". Location The Mên-an-Tol stands near the Madron to Morvah road in Cornwall. Other antiquities in the vicinity include the Mên Scryfa inscribed stone about 300 metres to the north and the Boskednan stone circle less than 1 kilometre to the northeast. Etymology The Cornish language, Cornish name ''Men a Toll'' translates into English as "the stone with a hole". Description The Mên-an-Tol consists of three upright granite stones: a round stone with its middle holed out with two standing stones to each side, in front of and behind the hole. The two side stones are both about 1.2 metres high. The westernmost stone was moved and brought into a straight line with the other two stones sometime after 1815. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitgeist (Levellers Album)
''Zeitgeist'' is the fourth album by the Levellers. It was released in August 1995 and reached 1 in the UK album charts, making it the band's most successful album. Two singles were released from the album – "Hope St.", which reached No.12 in the UK single charts, and "Fantasy", which reached 16. Additionally, a re-recorded version of "Just the One" featuring Joe Strummer was released, reaching No.12, as well as a live version of "Exodus" from the later ''Headlights, White Lines, Black Tar Rivers (Best Live)'' album the next year, which reached No.24. Track listing # "Hope St." # "The Fear" # "Exodus" # "Maid of the River" # "Saturday to Sunday" # "4 a.m." # "Forgotten Ground" # "Fantasy" # "P.C. Keen" # "Just the One" # "Haven't Made It" # "Leave This Town" # " Men-an-Tol" The 2007 re-issue included the bonus tracks: # "Miles Away" # "Your 'Ouse" # "Drinking for England" # "Searchlights" Personnel Musicians * Mark Chadwick - guitars, vocals * Charlie Heather - drums/pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changeling
A changeling, also historically referred to as an auf or oaf, is a human-like creature found throughout much of European folklore. According to folklore, a changeling was a substitute left by a supernatural being when kidnapping a human being. Sometimes the changeling was a "stock" (a piece of wood made magically to resemble the kidnapped human), more often the changeling was a supernatural being made magically to look like the kidnapped human. Supernatural beings blamed for stealing children included Fairy, fairies, demons, trolls, nereids and many others. Usually, the kidnapped human was a child; but there were cases, particularly in Scandinavia and Ireland, where adults were taken. Some modern scholars have argued these stories of replaced children originated as folklore explanations for autism or other developmental conditions. Description A changeling is typically identifiable via several traits, which vary from culture to culture. In Irish mythology, Irish legend, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mên Scryfa
Mên Scryfa (or ''Mên Scrifa'', literally "stone with writing") is an inscribed standing stone in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom (). The inscription, dating to the early medieval period, commemorates "Rialobranus son of Cunovalus." Location Mên Scryfa stands near the Madron to Morvah road in Cornwall. It stands in the middle of a field.Bernard Deacon, (2010), ''Exploring Cornwall's Past'', page 56. The prehistoric Mên-an-Tol standing stones lie about 300 metres to the south. Description The stone is 1.7 metres high and roughly rectangular in section, with sides of 0.4 metres by 0.5 metres.MEN SCRYFA Pastscape, retrieved 9 November 2013 The inscription is on the northern face, although the bottom of the inscription is buried in the ground. At one time two plain crosses were said to be viewable at the upper end of the sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boskednan Stone Circle
Boskednan stone circle () is a partially restored prehistoric stone circle near Boskednan, around northwest of the town of Penzance in Cornwall, United Kingdom. The megalithic monument is traditionally known as the Nine Maidens or Nine Stones of Boskednan, although the original structure may have contained as many as 22 upright stones around its 69-metre perimeter. Location The stone circle is in southwest Cornwall north of the road from Madron to Morvah, and is approximately 1 km northwest of the village of Boskednan and can only be reached on foot. The enigmatic Mên-an-Tol stones (which may also be the remains of a stone circle) are less than 1 kilometre to the southwest.MEN AN TOL , Pastscape, retrieved 9 November 2013 Construction The stone circle once probably consisted of 22 |
Churches Of West Cornwall 04
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church, a former electoral ward of Kensington and Chelsea London Borough Council that existed from 1964 to 2002 * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota * Church, Michigan, ghost town Arts, entertainment, and media * '' Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Men An Tol Cornwall By Kernow Skies
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy. Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father. Sex differentiation of the male fetus is governed by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. During puberty, hormones which stimulate androgen production result in the development of secondary sexual characteristics that result in even more differences between the sexes. These include greater muscle mass, greater height, the growth of facial hair and a lower body fat composition. Male anatomy is distinguished from female anatomy by the male reproductive system, which includes the testicles, sperm ducts, prostate gland and epididymides, and penis. Secondary sex characteristics include a narrower pelvis and hips, and smaller breasts and nipples. Throughout human history, traditional gender roles have often defined men's activities and opportuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomalacia
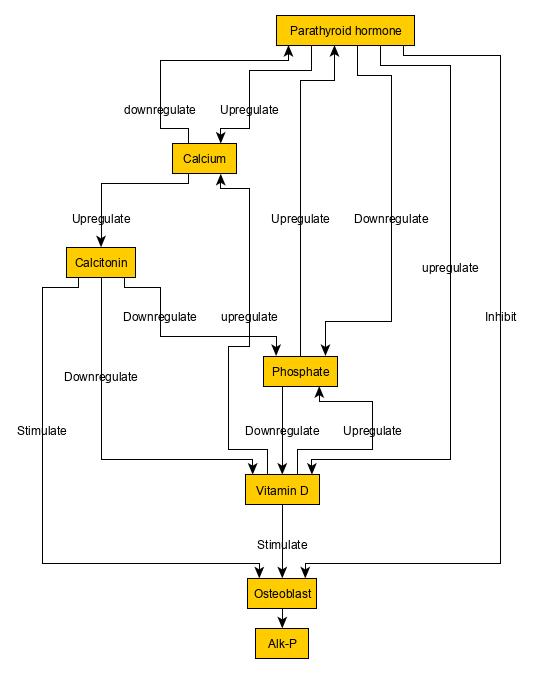
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions (for example, caused by vitamin D deficiency or renal phosphate wasting) that result in decreased bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides (such as osteopontin and ASARM peptides), and small inhibitory molecules (such as pyrophosphate), can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piskie
A pixie (also called pisky, pixy, pixi, pizkie, piskie, or pigsie in parts of Cornwall and Devon) is a mythical creature of British folklore. Pixies are speculated to be particularly concentrated in the high moorland areas around Devon and Cornwall, suggesting some Celtic origin for the belief and name. However, the word 'pixie' (under various forms) also appears in Dorset, Somerset and to a lesser extent in Sussex, Wiltshire and Hampshire. Similar to the Irish and Scottish ''Aos Sí'' (also spelled ''Aos Sidhe''), pixies are believed to inhabit ancient underground sites such as stone circles, barrows, dolmens, ringforts, or menhirs. In traditional regional lore, pixies are generally benign, mischievous, short of stature, and childlike; they are fond of dancing and wrestling outdoors, of which they perform through the night. In the modern era, they are usually depicted with pointed ears, often wearing a green outfit and pointed hat. Traditional stories describe them as wearin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy
A fairy (also called fay, fae, fae folk, fey, fair folk, or faerie) is a type of mythical being or legendary creature, generally described as anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic, found in the folklore of multiple European cultures (including Celtic mythology, Celtic, Slavic paganism, Slavic, Germanic folklore, Germanic, and French folklore, French folklore), a form of Supernatural#Spirit, spirit, often with metaphysical, supernatural, or preternatural qualities. Myths and stories about fairies do not have a single origin but are rather a collection of folk beliefs from disparate sources. Various folk theories about the origins of fairies include casting them as either demoted angels or demons in a Christian mythology, Christian tradition, as deities in Paganism, Pagan belief systems, as Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits of the dead, as Prehistory, prehistoric precursors to humans, or as spirits of nature. The label of ''fairy'' has at times applied only to specific Magic (su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mên An Tol (small) (9705213)
Menes ( ; ; , probably pronounced *; and Μήν) was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period (Egypt), Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt, credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt, and as the founder of the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty. The identity of Menes is the subject of ongoing debate, although mainstream Egyptological consensus inconclusively identifies Menes with the Naqada III ruler Narmer or his successor, the First Dynasty pharaoh Hor-Aha. Name and identity The name ''Menes'' is first documented in the work of Manetho, an Egyptian historian and priest of the relatively late Ptolemaic Kingdom, Ptolemaic period. Manetho noted the name in Greek as Μήνης (Romanization, transliterated: ''Mênês'').Manetho, Fr. 6, 7a, 7b. Text and translation in ''Manetho'', translated by W.G. Waddell (Cambridge: Harvard University, 1940), pp.26–35 An alternative Greek form, Μιν (transliterated: ''Min''), was cited by the fifth-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boscawen-Un
Boscawen-Ûn () is a Bronze Age stone circle close to St Buryan in Cornwall, UK. It consists of nineteen upright stones in an ellipse with another, leaning, middle stone just south of the centre. There is a west-facing gap in the circle, which may have formed an entrance. The elliptical circle has diameters . It is located at . The Gorsedh Kernow was inaugurated here in 1928. An old Welsh triad mentions one of the three principal ''gorseddau'' of the Island of Britain as "Beisgawen yn Nyfnwal" (Boscawen in Dumnonia), which was taken to refer to Boscawen-Ûn by the Gorsedh's founders. That Welsh triad dates to only the 18th century when it was made up by Iolo Morganwg, Edward Williams. Location Boscawen-Un is in southwest Cornwall, in the Penwith district north of St Buryan, by the A30 road from Penzance to Land's End. Both the Merry Maidens stone circle and the two Pipers standing stones can be seen as can the sea. Boscawen-Un is a Cornish name, from the words ''bos'' (farmst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |