|
Mysore Dasara 2013
The Mysore Dasara 2013 is the 403rd edition of the annual royal festive gala event, a show of pomp and tradition that is held in the Mysore city in Karnataka, India for 10 days. The festival is called the Navaratri (meaning nine nights or Dussehra or Vijayadashami which conforms to the bright half (Shukla Paksha) of the month of ''Ashvin'' (''Ashwayuj''a), from ''pratipada'' (first day) ''thithi'' (day) to ''navami'' (ninth) ''thithi'' (first nine days of the month) in the Hindu calendar corresponding to 5 to 13 October during 2013. The festival is also called ''Nada Habba'' (festival of the country) in Kannada language. The first day of the nine-day festivity started on 5 October with the traditional and religious special Puja (Hinduism), puja (worship) performed to Goddess Chamundeshwari in the Chamundeshwari Temple, Chamundi Temple on top of the Chamundi Hill, which forms the backdrop to the city; the temple was beautifully decorated with flowers and tourist from Gujarat, Raja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
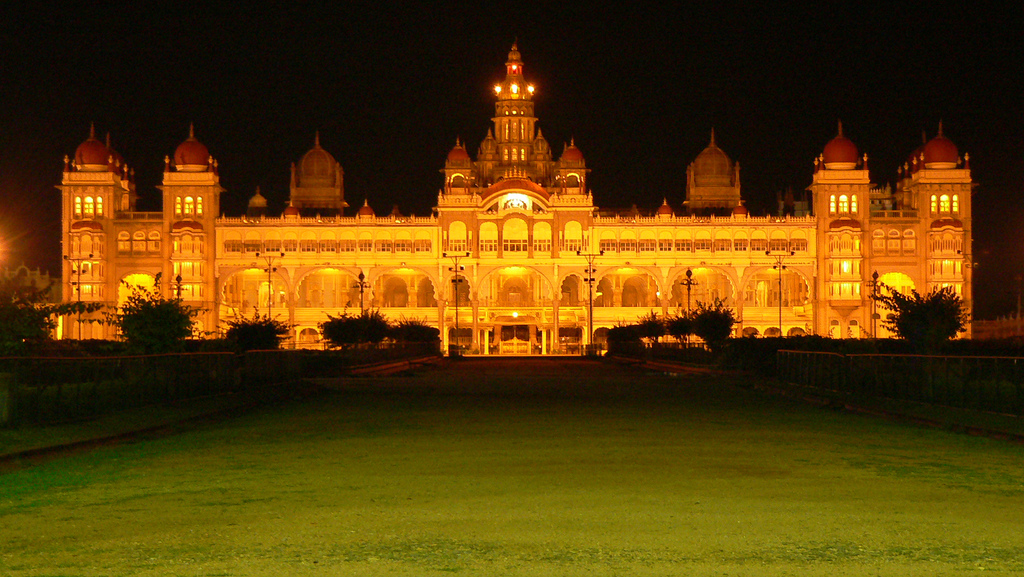
Mysore Palace
Mysore Palace, also known as Amba Vilas Palace, is a historical palace and a royal residence. It is located in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It used to be the official residence of the Wadiyar dynasty and the seat of the Kingdom of Mysore. The palace is in the centre of Mysore, and faces the Chamundi Hills eastward. Mysore is commonly described as the 'City of the Palaces', and there are List of Heritage Buildings in Mysore, seven palaces including this one. However, the Mysore Palace refers specifically to the one within the new fort. The land on which the palace now stands was originally known as ''mysuru'' (literally, "citadel"). The first palace inside the Old Fort was built in the 14th century, which was set ablaze and reconstructed multiple times. The Old Fort was built of wood and thus easily caught fire, while the current fort was built of stone, bricks and wood. The current structure was constructed between 1897 and 1912, after the Old Palace burnt down, the current structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jnanpith Award
The Jnanpith Award is the oldest and the highest Indian literary award presented annually by the Bharatiya Jnanpith to an author for their "outstanding contribution towards literature". Instituted in 1961, the award is bestowed only on Indian writers writing in Indian languages included in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India and English, with no posthumous conferral. From 1965 till 1981, the award was given to the authors for their "most outstanding work" and consisted of a citation plaque, a cash prize and a bronze replica of Saraswati, the Hindu goddess of knowledge and wisdom. The first recipient of the award was the Malayalam writer G. Sankara Kurup who received the award in 1965 for his collection of poems, Odakkuzhal (''The Bamboo Flute''), published in 1950. The rules were revised in subsequent years to consider only works published during the preceding twenty years, excluding the year for which the award was to be given and the cash prize was increased t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted substantially throughout the kingdom's lifetime. While originally a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire, it became a princely state in British Raj from 1799 to 1947, marked in-between by major political changes. The kingdom, which was founded and ruled for the most part by the Wadiyars, initially served as a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire. With the gradual decline of the Empire, the 16th-century Timmaraja Wodeyar II declared independence from it. The 17th century saw a steady expansion of its territory and, during the rules of Narasaraja Wodeyar I and Devaraja Wodeyar II, the kingdom annexed large expanses of what is now southern Karnataka and parts of Tamil Nadu, becoming a formidable power in the Deccan. During a brief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Wadiyar
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the ''Rigveda'', where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". The title has equivalent cognates in other Indo-European languages, notably the Latin Rex and the Celtic Rix. Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdur Razzaq (traveller)
Abd-al-Razzāq Samarqandī (, ''Kamal-ud-Din Abd-ur-Razzaq ibn Ishaq Samarqandi''; 7 November 1413 – August 1482) was a Persian Timurid chronicler and Islamic scholar. He was for a while the ambassador of Shah Rukh, the Timurid dynasty ruler of Persia. In his role as ambassador he visited Kozhikode in south India in the early 1440s. He wrote a narrative of what he saw in Calicut which is valuable as information on Calicut's society and culture. He is also the producer of a lengthy narrative or chronicle of the history of the Timurid dynasty and its predecessors in Central Asia, but this is not so valuable because it is mostly a compilation of material from earlier written sources that are mostly available from elsewhere in the earlier form. Early life Abd-al-Razzāq was born in Herat on 7 November 1413. His father Jalal-ud-Din Ishaq was the qazi and imam of the Shah Rukh's court in Herat. He studied with his father and his elder brother Sharif-ud-Din Abdur Qahhar and together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vijayanagar Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belonging to the Yadava clan of Chandravamsa lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts by the southern powers to ward off Muslim invasions by the end of the 13th century. At its peak in the early 16th century under Krishnadevaraya, it subjugated almost all of Southern India's ruling dynasties and pushed the Deccan sultanates beyond the Tungabhadra- Krishna River doab region, in addition to annexing the Gajapati Empire ( Odisha) up to the Krishna River, becoming one of the most prominent states in India. The empire's territory covered most of the lands of the modern-day Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa, and some parts of Telangana and Maharashtra. The empire lasted until 1646, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devaraya II
Deva Raya I (reigned 5 November 1406 – 25 February 1423) was an Emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire (of the Sangama Dynasty). After Harihara II died, there was a dispute among his sons over succession, in which Deva Raya I eventually emerged victor. He was a very capable ruler noted for his military exploits and his support to irrigation works in his empire.Kulakarṇī, Nayeem, De Souza (1996), p.106 He modernized the Vijayanagara army by improving the cavalry, employed skilled archers of the Turkic clans and raised the fighting capacity of his bowmen and imported horses from Arabia and Persia.Bowman,(2013) p.271 The Italian traveler Niccolo Conti, who visited Vijayanagara 1420, described Deva Raya I thus: "In this city, there are 90,000 men fit to bear arms... their king is more powerful than all the kings of India".Chopra, Ravindran and Subrahmanian (2003), p.31 Conti also noted that the royal city had grown to a circumference of 60 mi.Kamath (1980), p.163 Deva Raya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srikanta Wadiyar Of Mysore
Srikanta may refer to: * Srikanta Acharya, Indian singer * Srikanta Mahata, Indian politician * Srikanta Wadiyar (born 1953), Indian prince and politician * ''Srikanta'' (book), a Bengali novel by Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay * ''Srikanta'' (film), a 2017 Indian Kannada-language romantic action thriller * Srikanta (mountain) A mountain in Garhwal Himalaya See also * * * *Srikanth (other) * Srikantha (other) *Shrikant Shrikant is a male Indian given name. People with the name *Shrikant Bhasi (born 1968), Indian businessman *Shrikant Jadhav (born 1960), Indian cricketer *Shrikant Jichkar (1954–2004), Indian politician *Shrikant Joshi (born 1958), Indian busin ..., an Indian male given name {{disambiguation Indian masculine given names Masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore Palace
Mysore Palace, also known as Amba Vilas Palace, is a historical palace and a royal residence. It is located in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It used to be the official residence of the Wadiyar dynasty and the seat of the Kingdom of Mysore. The palace is in the centre of Mysore, and faces the Chamundi Hills eastward. Mysore is commonly described as the 'City of the Palaces', and there are List of Heritage Buildings in Mysore, seven palaces including this one. However, the Mysore Palace refers specifically to the one within the new fort. The land on which the palace now stands was originally known as ''mysuru'' (literally, "citadel"). The first palace inside the Old Fort was built in the 14th century, which was set ablaze and reconstructed multiple times. The Old Fort was built of wood and thus easily caught fire, while the current fort was built of stone, bricks and wood. The current structure was constructed between 1897 and 1912, after the Old Palace burnt down, the current structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banni Mantap
Banni is a village in the Gambia. It is located in Wuli District in the Upper River Division Upper River was one of the five Subdivisions of the Gambia, Divisions of the Gambia. Its capital was Basse Santa Su. It was subsequently reorganised as the Basse (Gambia), Basse Local Government Area, without any change in the area covered. Per .... As of 2009, it has an estimated population of 461. References Populated places in the Gambia Upper River Division {{Gambia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
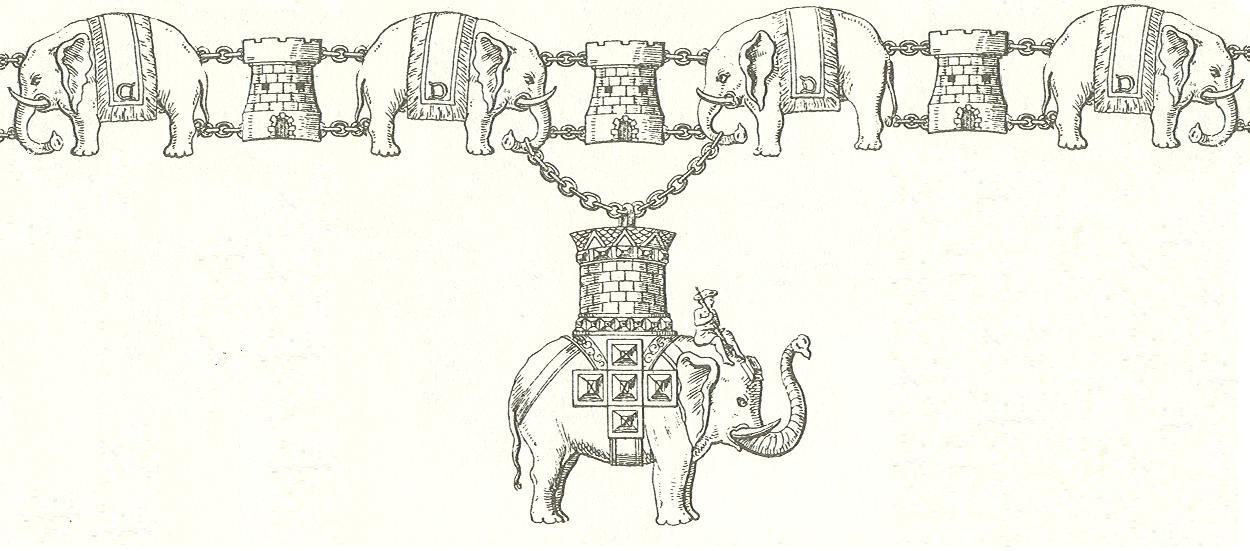
Howdah
A howdah or houdah (, derived from the Arabic which means 'bed carried by a camel') also known as hathi howdah ( ), is a carriage which is positioned on the back of an elephant, or occasionally some other animal, such as a camel, used most often in the past to carry wealthy people during progresses or processions, hunting or in warfare. It was also a symbol of wealth for the owner and as a result might be elaborately decorated, even with expensive gemstones. Notable howdahs are the Golden Howdah, on display at the Napier Museum at Thiruvananthapuram, which was used by the Maharaja of Travancore and that is used traditionally during the Elephant Procession of the famous Mysore Dasara. The Mehrangarh Fort Museum in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, has a gallery of royal howdahs. Today, howdahs are used mainly for tourist or commercial purposes in South East Asia and are the subject of controversy as animal rights groups and organizations, such as Millennium Elephant Foundation, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore Dasara
Mysore Dasara is the state festival in the state of Karnataka in India. It is a 10-day festival, starting with nine nights called Navaratri and the last day being Vijayadashami. The festival is observed on the tenth day in the Hindu calendar month of ''Ashvina'', which typically falls in the Gregorian months of September and October. The Hindu festival of Navaratri and its occasion of Vijayadashami celebrates the victory of good over evil. According to Hindu mythology, it commemorates the day the goddess Chamundeshwari (Durga) slew the demon Mahishasura. Mahishasura is also believed to be the demon whose slaying by the goddess gave the city the name Mysuru. The Mysuru tradition celebrates the warriors and the state fighting for the good during this festival, ritually worshipping and displaying the state sword, weapons, elephants, horses, along with the goddess in her warrior form (predominantly) as well as the avatar of Vishnu, Rama. The ceremonies and a major procession is tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |