|
Myriazoa
The Benthozoa or Myriazoa are a proposed basal animal clade consisting of the Porifera and ParaHoxozoa as a sister group of Ctenophora. An alternative phylogeny is given by the Porifera-sister hypothesis in which Porifera are the first diverging animal group. References Animal taxa {{animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
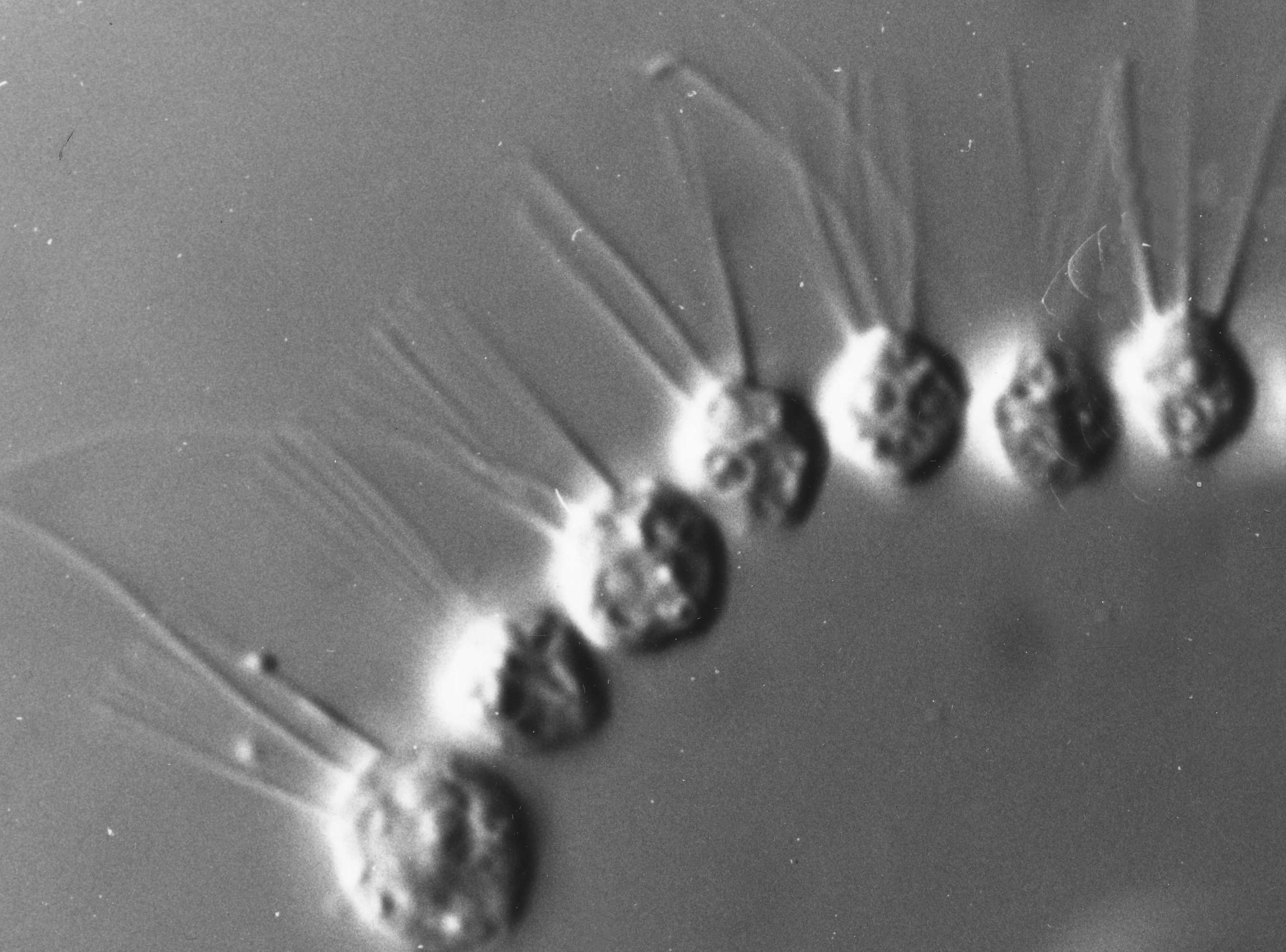
Comb Jelly
Ctenophora (; : ctenophore ) is a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. 186 living species are recognised. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with a pair of retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat, generally combless platyctenids, and the large-mouthed beroids, which prey on other ctenophores. Almost all ctenophores function as predators, taking prey ranging from microscopic larvae and rotifers to the adults of small crustaceans; the exceptions are juveniles of two species, which live as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; : ctenophore ) is a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. 186 living species are recognised. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with a pair of retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat, generally combless platyctenids, and the large-mouthed beroids, which prey on other ctenophores. Almost all ctenophores function as predators, taking prey ranging from microscopic larvae and rotifers to the adults of small crustaceans; the exceptions are juveniles of two species, which live a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetazoa
Eumetazoa (), also known as Epitheliozoa or Histozoa, is a proposed basal animal subkingdom as a sister group of Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen as a eumetazoan in the ParaHoxozoa. The competing hypothesis is the Myriazoa clade. The subkingdom Parazoa and Agnotozoa are the other taxa, and agnotozoa may be fake or even nonexistent at studies. Parazoa or Agnotozoa are a main sister group to eumetazoans, forming clade Blastozoa/Diploblastozoa. Alternatively, Parazoa was considered as a sister group to Agnotozoa(now considered polyphyletic). Several other extinct or obscure life forms, such as '' Iotuba'' and '' Thectardis'', appear to have emerged in the group. Characteristics of eumetazoans include true tissues organized into germ layers, the presence of neurons and muscles, and an embryo that goes through a gastrula stage. Some phylogenists once speculated the sponges and eumetazoans evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrozoa
Nephrozoa is a proposed major clade of bilaterian animals. Under this hypothesis, Xenacoelomorpha forms the earliest diverging branch of Bilateria, with all other bilaterians placed in Nephrozoa. It contrasts with the Xenambulacraria hypothesis, which instead posits that Xenacoelomorpha is most closely related to Ambulacraria (usually placed as Deuterostome, deuterostomes). Which hypothesis is correct has been debated, and as of 2024 the issue is unresolved. The clade is named after a key synapomorphy of the group: the presence of specialized excretory organs known as Nephridium, nephridia. Below is a proposed phylogenetic tree of Nephrozoa: References Further reading * * * External links * Bilaterians Ediacaran first appearances {{zoology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterostomia
Deuterostomes (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryogenesis, embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three Phylum, phyla: chordate, Chordata, Echinodermata, hemichordate, Hemichordata, and the extinct clade Cambroernida. In deuterostomes, the developing embryo's first opening (the blastopore) becomes the anus and cloaca, while the mouth is formed at a different site later on. This was initially the group's distinguishing characteristic, but deuterostomy has since been discovered among protostomes as well. The deuterostomes are also known as enterocoelomates, because their coelom develops through pouching of the gut, enterocoely. Deuterostomia's sister clade is Protostomia, animals that develop mouth first and whose digestive tract development is more varied. Protostomia includes the ecdysozoans and spiralians, as well as the extinct ''Kimberella'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other Taxon, taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a neural tube, hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anus, anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three phylum, subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinus Carpio3
''Cyprinus'' is the genus of typical carps in family Cyprinidae. Most species in the genus are of East Asia origin with only the common carp (''C. carpio'') in Western Asia and Europe; this invasive species has also been introduced to many other regions around the world. ''Cyprinus'' are closely related to some more barb-like genera, such as ''Cyclocheilichthys'' and ''Barbonymus'' (tinfoils). The crucian carps (''Carassius'') of western Eurasia, which include the goldfish (''C. auratus''), are apparently not as closely related. This genus's most widespread and well-known member is the common carp (''C. carpio'') species complex. Although traditionally considered a single species, recent authorities have split the European and West Asian populations from the East Asian, with the latter named '' C. rubrofuscus'' ( syn. ''C. carpio haematopterus''). Members of the species complex are famed as a food fish and have been widely traded and introduced since antiquity, but in certain ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulacraria
Ambulacraria , or Coelomopora , is a clade of invertebrate phyla that includes echinoderms and hemichordates; a member of this group is called an ambulacrarian. Phylogenetic analysis suggests the echinoderms and hemichordates separated around 533 million years ago. The Ambulacraria are part of the deuterostomes, a clade that also includes the many Chordata, and the few extinct species belonging to the Vetulicolia. Phylogeny The two living clades with representative organisms are: * Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins, brittle stars, sea cucumbers, feather stars, sea lilies, etc.) * Hemichordata ( acorn worms (Enteropnuesta) and Pterobranchia (including Graptolithina)) (These together sometimes are called the ''lower deuterostomes''.) Whether the Xenacoelomorpha clade is the sister group to the Ambulacraria remains a contentious issue, with some authors arguing that the former should be placed more basally among metazoans, and other authors asserting that the best choice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important sponge reef , reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cell (biology) , cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can cellular differentiation , transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous system , nervous, digestive system , digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenacoelomorpha
Xenacoelomorpha () is a small phylum of bilaterian invertebrate animals, consisting of two sister groups: xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs. This new phylum was named in February 2011 and suggested based on morphological synapomorphies (physical appearances shared by the animals in the clade), which was then confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data (similarities in the DNA of the animals within the clade). Phylogenetics Prior to molecular studies, xenacoelomorphs were considered to be flatworms based on their superficial similarities. Like flatworms, they do not have a coelom and are dorsoventrally flattened. With the advent of phylogenetics, '' Xenoturbella'' and Acoelomorpha were found to be sister groups and only distantly related to flatworms. Initially this phylum was considered to be a member of the deuterostomes, but because of recent transcriptome analyses, it was concluded that phylum Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group to the Nephrozoa, which includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |