|
Myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments. Structure There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thick filaments consist primarily of a type of myosin, a motor protein – myosin II. Each thick filament is approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
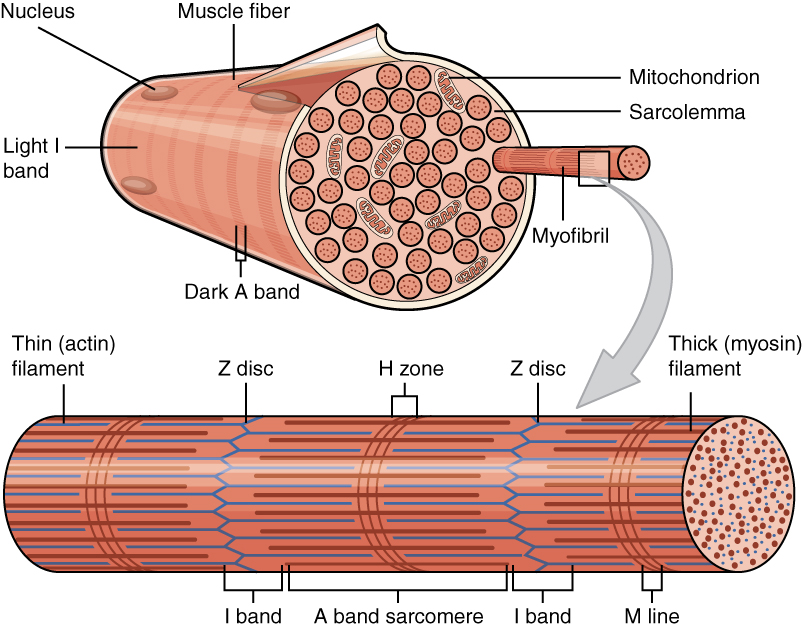
Myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myofibrils
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
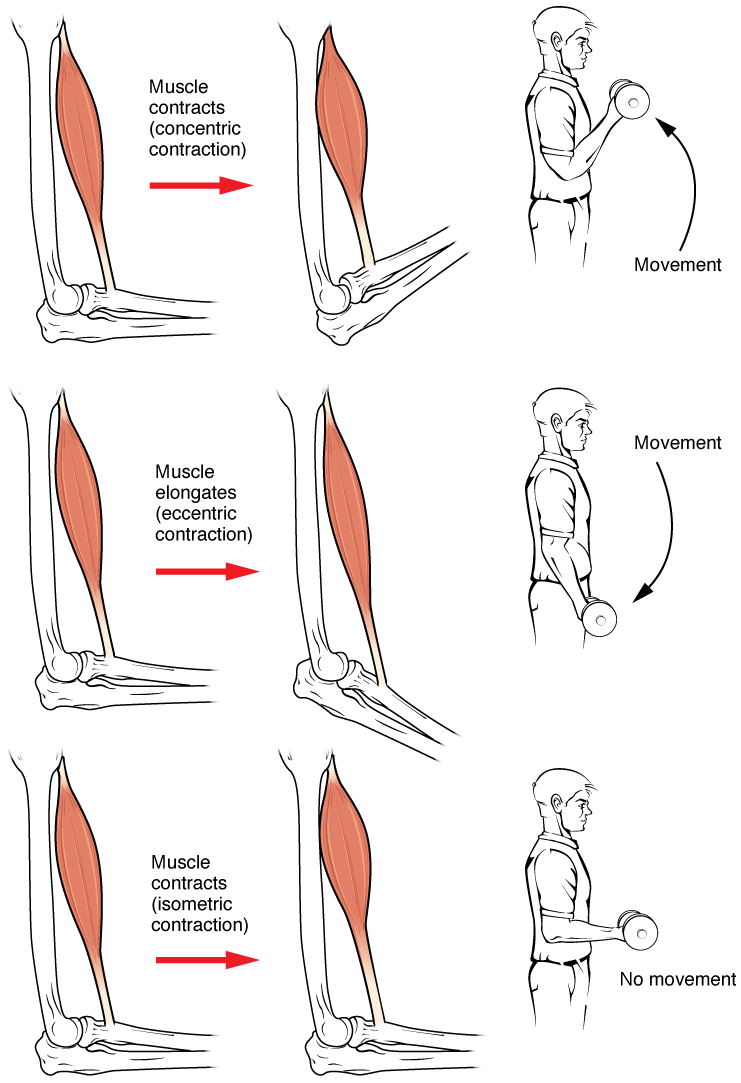
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Cell
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
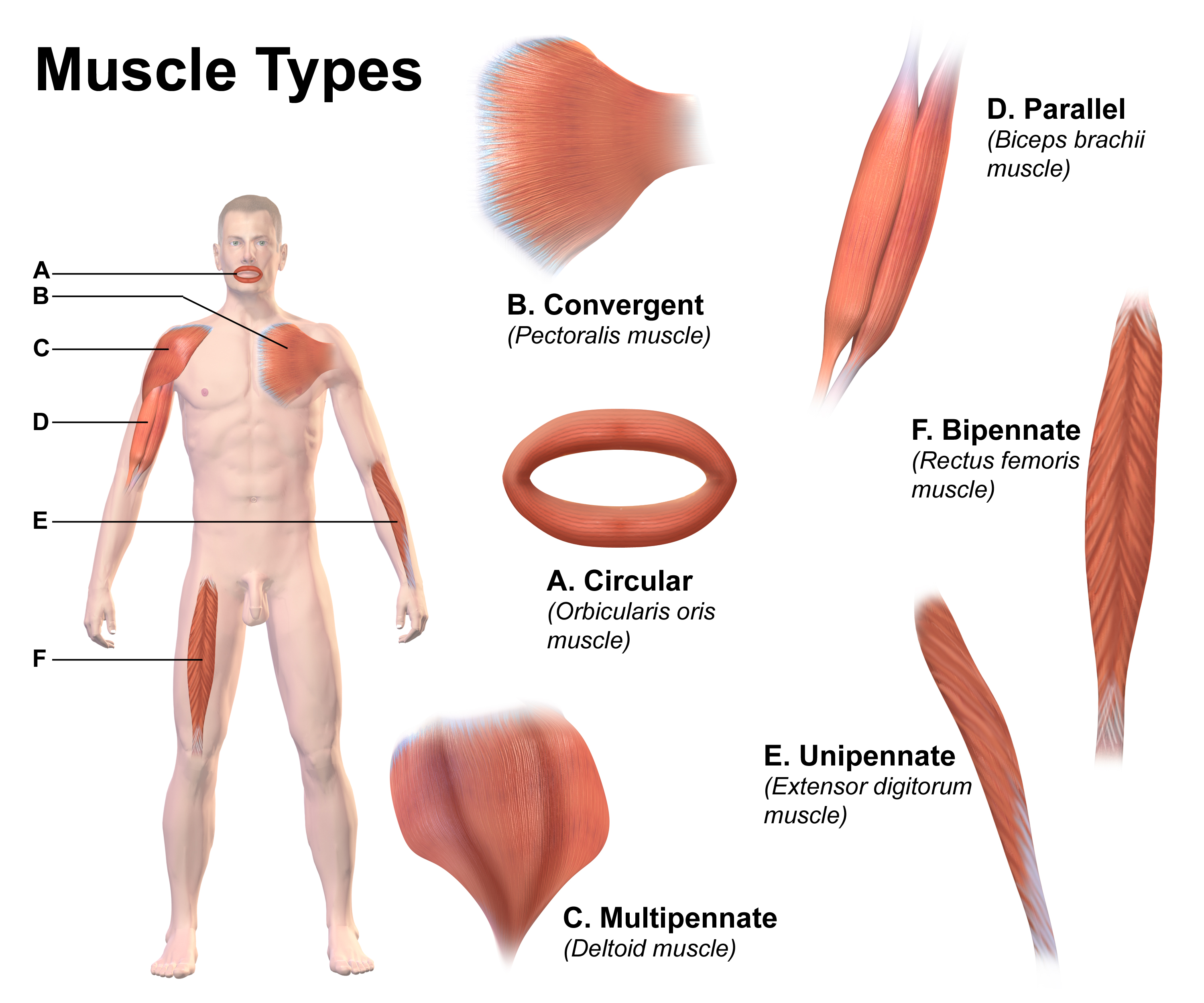
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myosin Head
The myosin head is the part of the thick myofilament made up of myosin that acts in muscle contraction, by sliding over thin myofilaments of actin. Myosin is the major component of the thick filaments and most myosin molecules are composed of a head, neck, and tail domain; the myosin head binds to thin filamentous actin, and uses ATP hydrolysis to generate force and "walk" along the thin filament. Myosin exists as a hexamer of two heavy chains, two alkali light chains, and two regulatory light chains. The heavy chain can be subdivided into the globular head at the N-terminal and the coiled-coil rod-like tail at the C-terminal, although some forms have a globular region in their C-terminal. There are many cell-specific isoforms of myosin heavy chains, coded for by a multi-gene family. Myosin interacts with actin to convert chemical energy, in the form of ATP, to mechanical energy In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a protein family, family of Globular protein, globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in myofibril, muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 micromolar, μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric Protein subunit, subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the Muscle contraction, contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the Motility, mobility and contraction of cell (biology), cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long, fibrous tail and a globular head, which binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to ATP, which is the source of energy for muscle movement. Myo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin
image:Troponin Ribbon Diagram.png, 400px, Ribbon representation of the human cardiac troponin core complex (52 kDa core) in the calcium-saturated form. Blue = troponin C; green = troponin I; magenta = troponin T.; ; rendered with PyMOL Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and T are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators in the management of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome. Blood troponin levels may be used as a diagnostic marker for stroke or other myocardial injury that is ongoing, although the sensitivity of this measurement is low. Function Troponin is attached to the protein tropomyosin and lies within the groove between actin filaments in muscle tissue. In a relaxed muscle, tropomyosin blocks the attachment site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |