|
Myofibrillar
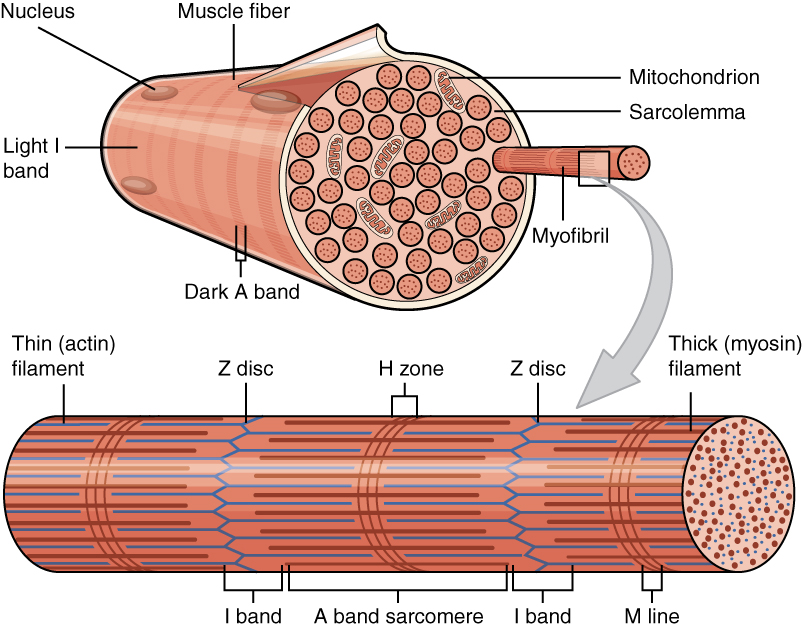
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titin
Titin (; also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. The protein, which is over 1 μm in length, functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscle. It comprises 244 individually folded protein domains connected by unstructured peptide sequences. These domains unfold when the protein is stretched and refold when the tension is removed. Titin is important in the contraction of striated muscle tissues. It connects the Z disc to the M line in the sarcomere. The protein contributes to force transmission at the Z disc and resting tension in the I band region. It limits the range of motion of the sarcomere in tension, thus contributing to the passive stiffness of muscle. Variations in the sequence of titin between different types of striated muscle ( cardiac or skeletal) have been correlated with differences in the mechanical properties of these muscles. Titin is the third most abundant protein in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Striated Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1002 Organization Of Muscle Fiber
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-tubule
T-tubules (transverse tubules) are extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. With membranes that contain large concentrations of ion channels, transporters, and pumps, T-tubules permit rapid transmission of the action potential into the cell, and also play an important role in regulating cellular calcium concentration. Through these mechanisms, T-tubules allow heart muscle cells to contract more forcefully by synchronising calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum throughout the cell. T-tubule structure and function are affected beat-by-beat by cardiomyocyte contraction, as well as by diseases, potentially contributing to heart failure and arrhythmias. Although these structures were first seen in 1897, research into T-tubule biology is ongoing. Structure T-tubules are tubules formed from the same phospholipid bilayer as the surface membrane or sarcolemma of skeletal or cardiac muscle cells. They connect dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridescence
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear gradually to change colour as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Iridescence is caused by wave interference of light in microstructures or thin films. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfly wings and seashell nacre, and minerals such as opal. Pearlescence is a related effect where some or most of the reflected light is white. The term pearlescent is used to describe certain paint finishes, usually in the automotive industry, which actually produce iridescent effects. Etymology The word ''iridescence'' is derived in part from the Greek word ἶρις ''îris'' ( gen. ἴριδος ''íridos''), meaning ''rainbow'', and is combined with the Latin suffix ''-escent'', meaning "having a tendency toward". Iris in turn derives from the goddess Iris of Greek mythology, who is the personification of the rainbow and acted as a messenger of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Coloration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of Biological pigment, pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination with pigments. For example, peacock tail feathers are pigmented brown, but their microscopic structure makes them also reflect blue, turquoise, and green light, and they are often iridescence, iridescent. Structural coloration was first described by English scientists Robert Hooke and Isaac Newton, and its principle—wave interference—explained by Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young a century later. Young described iridescence as the result of interference between reflections from two or more surfaces of thin films, combined with refraction as light enters and leaves such films. The geometry then determines that at certain angles, the light reflected from both surfaces interferes constructively, while at other angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuts Of Meat
A primal cut or cut of meat is a piece of meat initially separated from the carcass of an animal during butchering. Examples of primals include the round, loin, rib, and chuck for beef or the ham, loin, Boston butt, and picnic for pork. Different countries and cultures make these cuts in different ways, and primal cuts also differ between type of carcass. The British, American and French primal cuts all differ in some respects. For example, rump steak in British and Commonwealth English is commonly called ''sirloin'' in American English. British ''sirloin'' is called ''porterhouse'' by Americans. Another notable example is fatback Fatback is a layer of subcutaneous fat taken from under the skin of the back of a domestic pig, with or without the skin (referred to as pork rind). In cuisine Fatback is a preferred fat for various forms of charcuterie, particularly sau ..., which in Europe is an important primal cut of pork, but in North America is regarded as trimmings t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Tissue
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. Muscle tissue contains special contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation from peripheral plexus or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striated Muscle Tissue
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. Under the microscope, sarcomeres are visible along muscle fibers, giving a striated appearance to the tissue. The two types of striated muscle are skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. Structure Striated muscle tissue contains T-tubules which enables the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle includes skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Skeletal muscle is wrapped in epimysium, allowing structural integrity of the muscle despite contractions. The perimysium organizes the muscle fibers, which are encased in collagen and endomysium, into Muscle fascicle, fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, and sarcoplasmic reticulum. The functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a sarcomere. Each muscle cell contains myofibrils composed of actin and myosin myofilaments repeated as a sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actomyosin
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments. Structure There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thick filaments consist primarily of a type of myosin, a motor protein – myosin II. Each thick filament is ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |