|
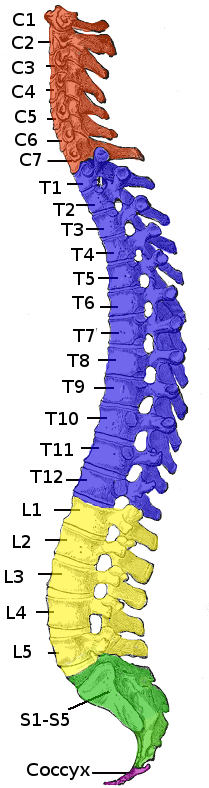
Myelopathy
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. The most common form of myelopathy in humans, '' cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM)'', also called ''degenerative cervical myelopathy'', results from narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis) ultimately causing compression of the spinal cord. When due to trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular myelopathy. In Asian populations, spinal cord compression often occurs due to a different, inflammatory process affecting the posterior longitudinal ligament. Presentation Clinical signs and symptoms depend on which spinal cord level (cervical, thoracic, or lumbar) is affected and the extent (anterior, posterior, or lateral) of the pathology, and may include: * Upper motor neuron signs—weakness, spasticity, clumsiness, altered tonus, hyperreflexia and pathological reflexes, including Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfer's Myelopathy
Surfer's myelopathy is a rare nontraumatic injury causing paraplegia which is paralysis below the waist. It is a spinal cord injury caused by hyperextension of the back. When the back is hyperextended, a blood vessel leading to the spine can become kinked, depriving the spinal cord of oxygen The first reported case of a patient with surfer's myelopathy undergoing acute spinal angiography revealed anterior spinal artery compromise. The condition gets its name because the phenomenon is most often seen in those surfing for the first time, but it can be caused by any activity in which the back is hyperextended (yoga, pilates Pilates (; ) is a type of mind–body intervention, mind-body exercise developed in the early 20th century by German physical trainer Joseph Pilates, after whom it was named. Pilates called his method "Contrology". It is practiced worldwide, es ..., etc.). In some cases the paralysis is permanent. Prevention According to DPT Sergio Florian, some recommenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with leaning forward. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction. Causes may include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, spinal tumors, trauma, Paget's disease of the bone, scoliosis, spondylolisthesis, and the genetic condition achondroplasia. It can be classified by the part of the spine affected into cervical, thoracic, and lumbar stenosis. Lumbar stenosis is the most common, followed by cervical stenosis. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms and medical imaging. Treatment may involve medications, bracing, or surgery. Medications may include NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or steroid injections. Stretching and strengthening exercises may also be useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Disc Herniation
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture. When a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings, the disc is said to be herniated. Disc herniation is frequently associated with age-related degeneration of the outer ring, known as the '' annulus fibrosus'', but is normally triggered by trauma or straining by lifting or twisting. Tears are almost always posterolateral (on the back sides) owing to relative narrowness of the posterior longitudin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Compression
Spinal cord compression is a form of myelopathy in which the spinal cord is compressed. Causes can be bone fragments from a vertebral fracture, a tumor, abscess, ruptured intervertebral disc or other lesion. When acute it can cause a medical emergency independent of its cause, and require swift diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term disability due to irreversible spinal cord injury. Causes The most common causes of cord compression are tumors, but abscesses and granulomas (e.g. in tuberculosis) are equally capable of producing the syndrome. Tumors that commonly cause cord compression are lung cancer (non-small cell type), breast cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, thyroid cancer, lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Development Typically, the symptoms of spinal cord compression develop slowly and progress steadily over several years. In some patients, however, the condition may worsen more rapidly. Subacute compression develops over days to weeks. Acute compressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Myelopathy
Vascular myelopathy (vascular disease of the spinal cord) refers to an abnormality of the spinal cord in regard to its blood supply. The blood supply is complicated and supplied by two major vessel groups: the posterior spinal arteries and the anterior spinal arteries—of which the Artery of Adamkiewicz is the largest. Both the posterior and anterior spinal arteries run the entire length of the spinal cord and receive anastomotic (conjoined) vessels in many places. The anterior spinal artery has a less efficient supply of blood and is therefore more susceptible to vascular disease. Whilst atherosclerosis of spinal arteries is rare, necrosis (death of tissue) in the anterior artery can be caused by disease in vessels originating from the segmental arteries such as atheroma (arterial wall swelling) or aortic dissection (a tear in the aorta). Spinal cord infarction Anterior spinal artery syndrome Anterior spinal artery syndrome is necrosis of tissue in the anterior spinal artery o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Disorders
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. There is no universally accepted, strict definition of the bounds of the X-ray band. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse generator, or stimulator, is connected to a magnetic coil connected to the scalp. The stimulator generates a changing electric current within the coil which creates a varying magnetic field, inducing a current within a region in the brain itself.NICE. January 201Transcranial magnetic stimulation for treating and preventing migraine/ref>Michael Craig Miller for Harvard Health Publications. July 26, 201Magnetic stimulation: a new approach to treating depression?/ref> TMS has shown diagnostic and therapeutic potential in the central nervous system with a wide variety of disease states in neurology and mental health, with research still evolving. Adverse effects of TMS appear rare and include fainting and seizure. Other potential issues inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Subtraction Angiography
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is a fluoroscopy technique used in interventional radiology to clearly visualize blood vessels in a bony or dense soft tissue environment. Images are produced using contrast medium by subtracting a "pre-contrast image" or ''mask'' from subsequent images, once the contrast medium has been introduced into a structure. Hence the term "digital ''subtraction'' angiography. Subtraction angiography was first described in 1935 and in English sources in 1962 as a manual technique. Digital technology made DSA practical starting in the 1970s. Procedure DSA and fluoroscopy In traditional angiography, images are acquired by exposing an area of interest with time-controlled x-rays while injecting a contrast medium into the blood vessels. The image obtained includes the blood vessels, together with all overlying and underlying structures. The images are useful for determining anatomical position and variations, but unhelpful for visualizing blood vessels acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |