|
Myc-tag
A myc tag is a polypeptide protein tag derived from the c-myc gene product that can be added to a protein using recombinant DNA technology. It can be used for affinity chromatography, then used to separate recombinant, overexpressed protein from wild type protein expressed by the host organism. It can also be used in the isolation of protein complexes with multiple subunits. A myc tag can be used in many different assays that require recognition by an antibody and was originally identified in 1985. If there is no antibody against the studied protein, adding a myc-tag allows one to follow the protein with an antibody against the Myc epitope. Examples are cellular localization studies by immunofluorescence or detection by Western blotting. The peptide sequence of the myc-tag is (in 1- and 3-letter codes, respectively): EQKLISEEDL and Glu-Gln-Lys-Leu-Ile-Ser-Glu-Glu-Asp-Leu. The tag is approximately 1202 daltons in atomic mass and has 10 amino acids. It can be fused to the C-termin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Protein Tag
Protein tags are peptide sequences genetically grafted onto a recombinant protein. Tags are attached to proteins for various purposes. They can be added to either end of the target protein, so they are either C-terminus or N-terminus specific or are both C-terminus and N-terminus specific. Some tags are also inserted at sites within the protein of interest; they are known as internal tags. Affinity tags are appended to proteins so that they can be purified from their crude biological source using an affinity technique. Affinity tags include chitin binding protein (CBP), maltose binding protein (MBP), Strep-tag and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). The Polyhistidine-tag, poly(His) tag is a widely used protein tag, which binds to matrices bearing immobilized metal ions. Solubilization tags are used, especially for recombinant proteins expressed in species such as ''E. coli'', to assist in the proper folding in proteins and keep them from aggregating in inclusion bodies. These tags ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
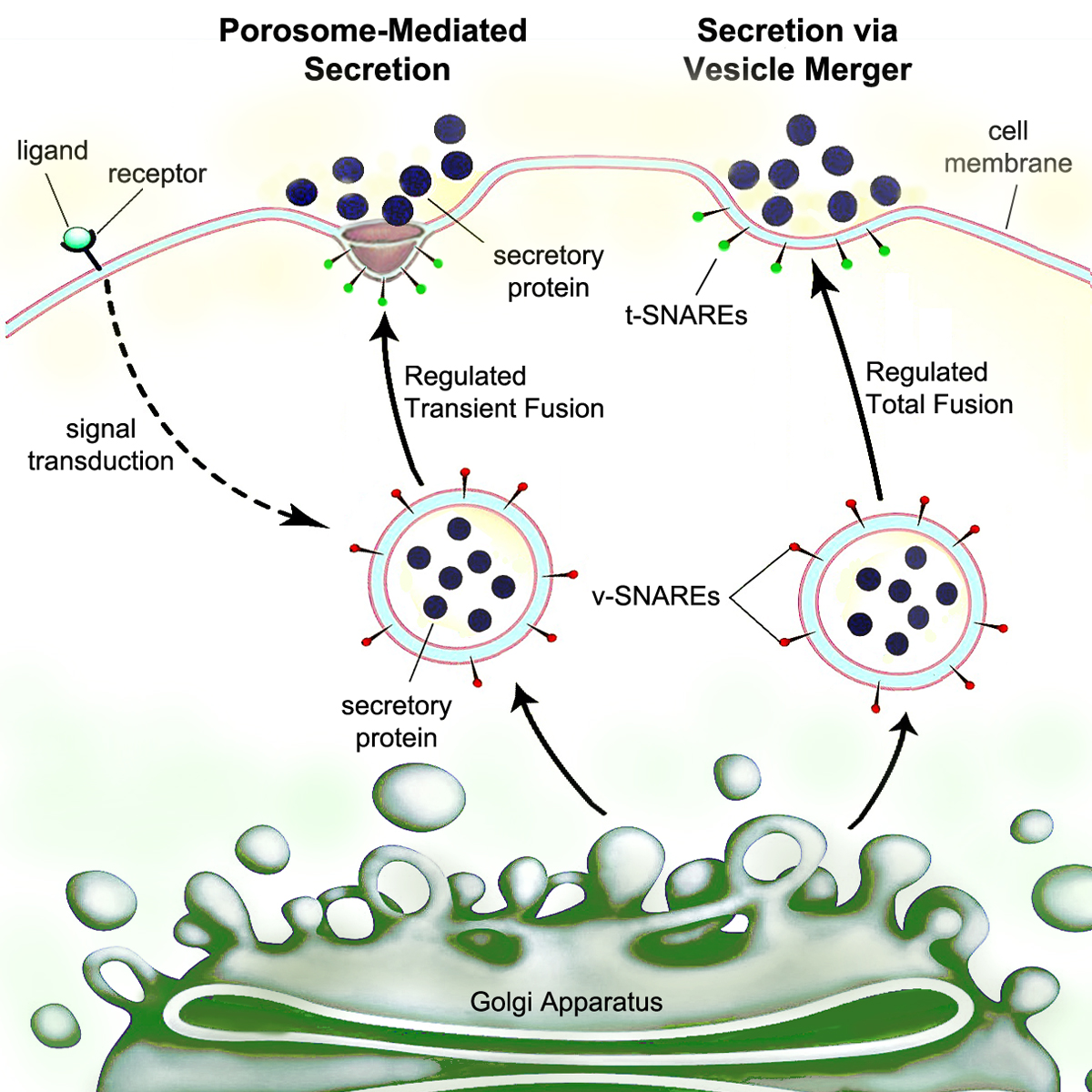 |
Secretory Pathway
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell (biology), cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the Cell membrane, plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Bacterial secretion system, Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules. For example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Flag Tag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countries. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
SpyCatcher
''Spycatcher: The Candid Autobiography of a Senior Intelligence Officer'' (1987) is a memoir written by Peter Wright, former MI5 officer and assistant director, and co-author Paul Greengrass. Wright drew on his experiences and research into the history of the British intelligence community. Published first in Australia, the book was banned in England (but not Scotland) due to its allegations about government policy and incidents. These efforts ensured the book's notoriety, and it earned considerable profit for Wright. In 2021 and 2023, the Cabinet Office was still blocking or redacting freedom of information requests for files on the ''Spycatcher'' affair despite the rule that documents should be released after 30 years. Information belonging to the security services is absolutely exempted from the Freedom of Information Act. Content In ''Spycatcher'', Wright says that one of his assignments was to unmask a Soviet mole in MI5, who he says was Roger Hollis, a former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Polyhistidine-tag
A polyhistidine-tag, best known by the trademarked name His-tag, is an amino acid motif in proteins that typically consists of at least six histidine (''His'') residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as a hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, or His6 tag. The tag was invented by Roche, although the use of histidines and its vectors are distributed by Qiagen. Various purification kits for histidine-tagged proteins are commercially available from multiple companies. The total number of histidine residues may vary in the tag from as low as two, to as high as 10 or more His residues. N- or C-terminal His-tags may also be followed or preceded, respectively, by a suitable amino acid sequence that facilitates removal of the polyhistidine-tag using endopeptidases. This extra sequence is not necessary if exopeptidases are used to remove N-terminal His-tags (e.g., Qiagen TAGZyme). Furthermore, exopeptidase cleavage may solve the unspecific cleavage observed when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Protein Tag
Protein tags are peptide sequences genetically grafted onto a recombinant protein. Tags are attached to proteins for various purposes. They can be added to either end of the target protein, so they are either C-terminus or N-terminus specific or are both C-terminus and N-terminus specific. Some tags are also inserted at sites within the protein of interest; they are known as internal tags. Affinity tags are appended to proteins so that they can be purified from their crude biological source using an affinity technique. Affinity tags include chitin binding protein (CBP), maltose binding protein (MBP), Strep-tag and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). The Polyhistidine-tag, poly(His) tag is a widely used protein tag, which binds to matrices bearing immobilized metal ions. Solubilization tags are used, especially for recombinant proteins expressed in species such as ''E. coli'', to assist in the proper folding in proteins and keep them from aggregating in inclusion bodies. These tags ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank
The Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) is a National Resource established by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1986 to bank and distribute at cost hybridomas and the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) they produce to the basic science community worldwide. It is housed in the Department of Biology at the University of Iowa. Description The DSHB is directed by David R. Soll at the University of Iowa. There are currently over 5000 hybridomas in the DSHB collection. The DSHB has obtained hybridomas from a variety of individuals and institutions, the latter including the Muscular Dystrophy Association, the National Cancer Institute, the NIH Common Fund, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). The DSHB eagerly awaits new contributions. First time customers must agree to the DSHB terms of usage that products will be used for research purposes only, and that they cannot be commercialized or distributed to a third party. Researchers also agree to acknowledge both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes. The epitopes of protein antigens are divided into two categories, conformational epitopes and linear epitopes, based on their structure and interaction with the paratope. Conformational and linear epitopes interact with the paratope based on the 3-D conformation adopted by the epitope, which is determined by the surface features of the involved epitope residues and the shape or tertiary structure of other segments of the antigen. A conformational epitope is formed by the 3-D conformation adopted by the interaction of discontiguous amino acid residues. In contrast, a linear epitope i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
C-myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes referred to as ''MYC'') was the first gene to be discovered in this family, due to homology with the viral gene ''v-myc''. In cancer, ''c-myc'' is often constitutively (persistently) expressed. This leads to the increased expression of many genes, some of which are involved in cell proliferation, contributing to the formation of cancer. A common human translocation involving ''c-myc'' is critical to the development of most cases of Burkitt lymphoma. Constitutive upregulation of ''Myc'' genes have also been observed in carcinoma of the cervix, colon, breast, lung and stomach. Myc is thus viewed as a promising target for anti-cancer drugs. Unfortunately, Myc possesses several features that have rendered it difficult to drug to date, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ... or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |