|
My Number Card
The , officially called the Individual Number Card in English, is an identity document issued to citizens of Japan and foreign residents which contains a unique 12-digit that serves as a national identification number in Japan. Unlike similar-looking identity cards in Europe, the My Number Card can be issued to both Japanese citizens and foreign residents, and is not proof of nationality. The My Number Card is used in Japan to streamline administrative purposes like filing taxes and social security, and it is also utilized to provide disaster response to those in need. It is the de facto Japanese equivalent to a U.S. Social Security Number. The My Number Card stores information such as personal name, photo, address, birthday, and sex. Residents who wish to obtain the card can request an application form from the municipality (via a ward office or city hall) where they reside. History Background Many countries around the world, including Japan, require residents and cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zairyū Card
was a system used to record information regarding aliens resident in Japan. It was handled at the municipal level, parallel to (but separately from) the koseki (family register) and juminhyo (resident register) systems used to record information regarding Japanese nationals. Foreigners staying in Japan for more than 90 days (excluding military personnel under a status of forces agreement and diplomatic personnel) were required to register within 90 days of landing in Japan. The applicant was required to provide a completed application form, passport (for applicants 16 years old or older) and two identification photos. The system was voluntary for shorter-term visitors. Alien registration was a prerequisite to many activities in Japan, such as purchasing a mobile phone, opening a bank account or obtaining a driver's license. As described below, the alien registration system was replaced with a foreign residents' registration system on July 9, 2012. The new system of foreign resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naha City
is the capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 persons per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). The total area is Naha is located on the East China Sea coast of the southern part of Okinawa Island, the largest of Okinawa Prefecture. The modern city was officially founded on May 20, 1921. Before that, Naha had been for centuries one of the most important and populous sites in Okinawa. Naha is the political, economic and education center of Okinawa Prefecture. In the medieval and early modern periods, it was the commercial center of the Ryukyu Kingdom. Geography City center Central Naha consists of the Palette Kumoji shopping mall, the Okinawa Prefecture Office, Naha City Hall, and many banks and corporations, located at the west end of Kokusai-dōri, the city's main street. boasts a 1.6 kilometer (1 mile) long stretch of stores, restaurants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Japan Times
''The Japan Times'' is Japan's largest and oldest English-language daily newspaper. It is published by , a subsidiary of News2u Holdings, Inc.. It is headquartered in the in Kioicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo. History ''The Japan Times'' was launched by Motosada Zumoto on 22 March 1897, with the goal of giving Japanese people an opportunity to read and discuss news and current events in English to help Japan to participate in the international community. The newspaper was independent of government control, but from 1931 onward, the paper's editors experienced mounting pressure from the Japanese government to submit to its policies. In 1933, the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs appointed Hitoshi Ashida, former ministry official, as chief editor. During World War II, the newspaper served as an outlet for Imperial Japanese government communication and editorial opinion. It was successively renamed ''The Japan Times and Mail'' (1918–1940) following its merger with ''The Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mascot
A mascot is any human, animal, or object thought to bring luck, or anything used to represent a group with a common public identity, such as a school, professional sports team, society, military unit, or brand name. Mascots are also used as fictional, representative spokespeople for consumer products. In sports, mascots are also used for merchandising. Team mascots are often related to their respective team nicknames. This is especially true when the team's nickname is something that is a living animal and/or can be made to have humanlike characteristics. For more abstract nicknames, the team may opt to have an unrelated character serve as the mascot. For example, the athletic teams of the University of Alabama are nicknamed the Crimson Tide, while their mascot is an elephant named Big Al. Team mascots may take the form of a logo, person, live animal, inanimate object, or a costumed character, and often appear at team matches and other related events, sports mascots are ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister For Digital Transformation
The is a member of the cabinet of Japan and is the leader and chief executive of the Digital Agency. The minister is responsible for overseeing Japan's transformation to a digital economy. The minister is nominated by the Prime Minister and is appointed by the Emperor of Japan. It began operations on 1 September 2021 after being formed as a result of the Digital Agency Establishment Act, making it the newest Ministerial position in the Cabinet. The current Minister for Digital Transformation is Taro Kono, who took office on 10 August 2022 as part of the Second Kishida Cabinet (First Reshuffle). English title The Ministerial position has gone through changes in its official English title. During deliberations of the Digital Agency Establishment Act, the official English title provided on the outline of the legislation was "Digital Minister". After the appointment of Takuya Hirai, there was no official English title, as the English version of the Cabinet Office's List of Minist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Economy
The digital economy is a portmanteau of digital computing and economy, and is an umbrella term that describes how traditional brick-and-mortar economic activities (production, distribution, trade) are being transformed by Internet, World Wide Web, and blockchain technologies. The digital economy is variously known as the ''Internet Economy'', ''Web Economy'', '' Cryptoeconomy'', and '' New Economy''. Since the digital economy is continuously replacing and expanding the traditional economy, there is no clear delineation between the two integrated economy types. The digital economy results from billions of daily online transactions among people, organizations (businesses, educational institutions, non-profits), and distributed computing devices (servers, laptops, smartphones, etc.) enabled by Internet, World Wide Web, and blockchain technologies. The digital economy is rapidly evolving into an Internet of Things (IoT), and could not exist in its current form without the Internet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
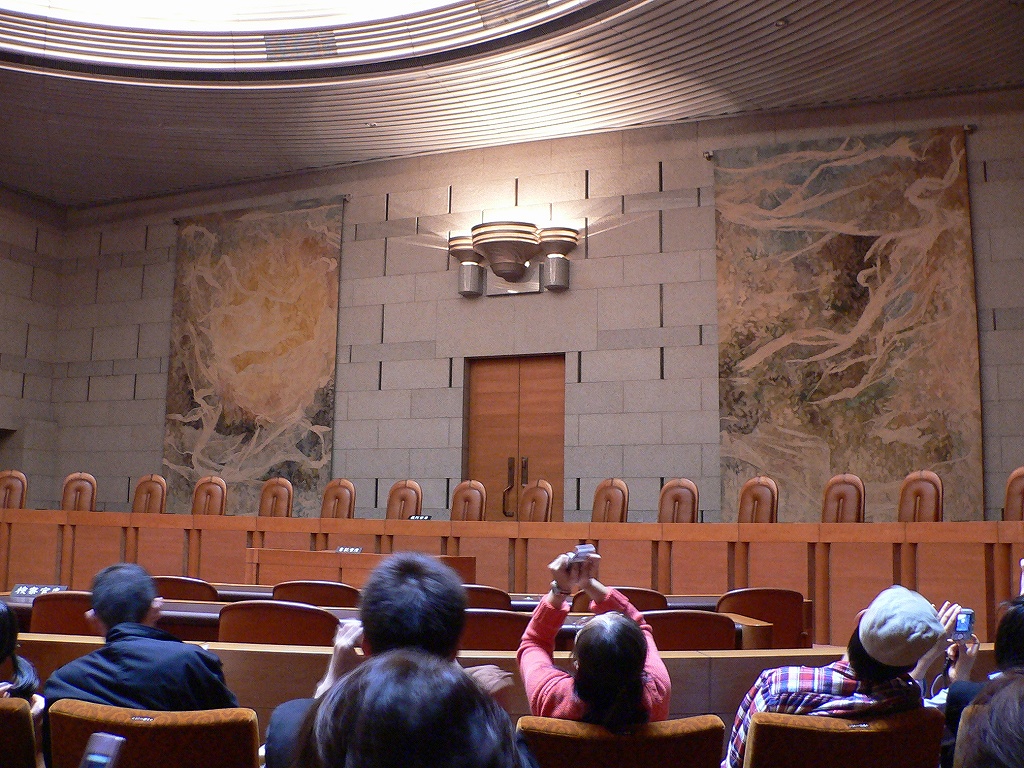
Supreme Court Of Japan
The , located in Hayabusachō, Chiyoda, Tokyo, is the highest court in Japan. It has ultimate judicial authority to interpret the Japanese constitution and decide questions of national law. It has the power of judicial review, which allows it to determine the constitutionality of any law or official act. History The modern Supreme Court was established in Article 81 of the Constitution of Japan in 1947. There was some debate among the members of the SCAP legal officers who drafted the constitution and in the Imperial Diet meeting of 1946 over the extent of the power of the judiciary, but it was overshadowed by other major questions about popular sovereignty, the role of the emperor, and the renunciation of war. Although the ratified wording in Article 81 states that court possesses the power of judicial review, a part of the court's early history involved clarifying the extent of this power. In 1948, the court declared that the constitution meant to establish the type of ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefectures Of Japan
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures (, ''todōfuken'', ), which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper (, '' ken''), two urban prefectures (, '' fu'': Osaka and Kyoto), one "circuit" or "territory" (, ''dō'': Hokkai-dō) and one metropolis (, '' to'': Tokyo). In 1868, the Meiji ''Fuhanken sanchisei'' administration created the first prefectures (urban ''fu'' and rural ''ken'') to replace the urban and rural administrators ('' bugyō'', '' daikan'', etc.) in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/ Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains ''( han)'' were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Transistor count, Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koseki
A or family register is a Japanese family registry. Japanese law requires all Japanese households (basically defined as married couples and their unmarried children) to make notifications of their vital records (such as births, adoptions, deaths, marriages and divorces) to their local authority, which compiles such records encompassing all Japanese citizens within their jurisdiction. Marriages, divorces by mutual consent, acknowledgements of paternity of non-marital children and adoptions (among others) become legally effective only when such events are recorded in the ''koseki''. Births and deaths become legally effective as they happen, but such events must be filed by family members or other persons as allowed by law. Loss of Japanese or foreign nationalities have to be recorded in the ''koseki'', too. Format There are two main types of certified copies of ''koseki'': the Comprehensive Copy of ''Koseki'' (戸籍謄本, ''koseki tōhon'') and Selected Copy of ''Koseki'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Passport
are issued to Japanese citizens to facilitate international travel. As of 2022, with holders able to travel visa-free to 193 countries and territories, it has been ranked as the most powerful passport in the world. History The first travel documents for overseas travel by Japanese citizens were introduced in 1866, near the end of the Tokugawa shogunate. These documents took the form of a stamped "letter of request" allowing Japanese citizens to travel overseas for business and educational purposes. The first person to be issued with a Japanese travel document was the acrobat and magician Namigorō Sumidagawa ( ja:隅田川浪五郎), who received his travel document on 17 October 1866 in order to perform at the 1867 World's Fair held in Paris, France. The term "passport" was formally introduced into the Japanese language in 1878, and in 1900 the first regulations governing the usage of Japanese passports were introduced. The modern form of the Japanese passport first came about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)