|
Mweka, Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Mweka is a town in southern-central Democratic Republic of the Congo, situated on the Kasai railway line between Kananga (250 km away) and the Kasai River port of Ilebo (172 km away). Mweka is also the headquarters of the Territoire de Mweka (administrative district which is one of the territories of the Democratic Republic of the Congo ) of the present Kasai Province. Its cathedral is the episcopal see of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Mweka. Transport When the rail connection to the Katanga line is functioning, trains reach Lubumbashi, 1,406 km to the south-east of Mweka. The train/boat journey in the other direction from Mweka via Ilebo to the capital, Kinshasa is about 1,000 km. Although "remote" is the default international media description for any DR Congo town outside Kinshasa, Mweka is relatively accessible by the standards of the country. Mweka Airport is 372 nm (690 km) east of Kinshasa. Accident In early August 2007, a freig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubumbashi
Lubumbashi ( , ; former ; former ) is the second-largest Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in the country's southeasternmost part, along the border with Zambia. The capital and principal city of the Haut-Katanga Province, Lubumbashi is the center of mining in the region, acting as a hub for many of the country's largest mining companies. No definite population figures are available, but the population of the city's urban area is estimated to be around 2,584,000 in 2021. History Élisabethville under Belgian rule The Belgian government established the modern-day government in the city of ''Élisabethville'' (sometimes Elizabethville, both in French, or Elisabethstad in Dutch) in 1910, named in honour of Elisabeth of Bavaria (1876–1965), Queen Elisabeth, consort to King Albert I of the Belgians. By that time, the government had taken over the colony from King Leopold II, and renamed it as the Belgian Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VHFs
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of diseases. "Viral" means a health problem caused by infection from a virus, "hemorrhagic" means to bleed, and "fever" means an unusually high body temperature. Bleeding and fever are common signs of VHFs, which is how the group of infections got its common name. There are five known families of RNA viruses which cause VHFs: '' Arenaviridae'', ''Filoviridae'', ''Flaviviridae'', ''Hantaviridae'', and ''Rhabdoviridae''. Some VHFs are usually mild, such as nephropathia epidemica (within the family ''Hantaviridae''). But some are usually severe and have a high death rate, such as Ebola virus (within the family ''Filoviridae''). All VHFs can potentially cause severe blood loss, high fever, and death. Both humans and non human animals can be infected. Signs and symptoms The following are signs and symptoms of most or all VHFs. *Circulatory shock *Diarrhea (feces which resemble more liquid than solid) *Headache *Hypotension (lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharps Waste
Sharps waste is a form of biomedical waste composed of used "sharps", which includes any device or object used to puncture or lacerate the skin. Sharps waste is classified as biohazardous waste and must be carefully handled. Common medical materials treated as sharps waste are hypodermic needles, disposable scalpels and blades, contaminated glass and certain plastics, and guidewires used in surgery. Qualifying materials In addition to needles and blades, anything attached to them, such as syringes and injection devices, is also considered sharps waste. Blades can include razors, scalpels, X-Acto knives, scissors, or any other items used for cutting in a medical or biological research setting, regardless of whether they have been contaminated with biohazardous material. While glass and sharp plastic are considered sharps waste, their handling methods can vary. Glass items which have been contaminated with a biohazardous material are treated with the same concern as needles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Remover
A needle remover is a device used to physically remove a needle from a syringe. In developing countries, there is still a need for improvements in needle safety in hospital settings as most of the needle removal processes are done manually and under severe risk of hazard from needles puncturing skin risking infection. These countries cannot afford needles with individual safety devices attached, so needle-removers must be used to remove the needle from the syringe. This lowers possible pathogen spread by preventing the reuse of the syringes, reducing incidents of accidental needle-sticks, and facilitating syringe disposal. Background In regions surveyed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in the early 2000s, the reported number of needle-stick injuries in developing world countries ranged from .93 to 4.68 injuries per person and per year, which is five times higher than in industrialized nations.Department of Essential Health Technology. (2004).Proposed Agenda to Evaluate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Precautions
Universal precautions refers to the practice, in medicine, of avoiding contact with patients' bodily fluids, by means of the wearing of nonporous articles such as medical gloves, goggles, and face shields. The infection control techniques were essentially good hygiene habits, such as hand washing and the use of gloves and other barriers, the correct handling of hypodermic needles, scalpels, and aseptic techniques. Following the AIDS outbreak in the 1980s, the US CDC formally introduced them in 1985–88. Every patient was treated as if infected, and therefore precautions were taken to minimize risk. In 1987, the practice of universal precautions was adjusted by a set of rules known as body substance isolation. In 1996, both practices were replaced by the latest approach known as Transmission-based precautions#Standard precautions, standard precautions. Use of personal protective equipment is now recommended in all health care settings. Historical significance Universal precaut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
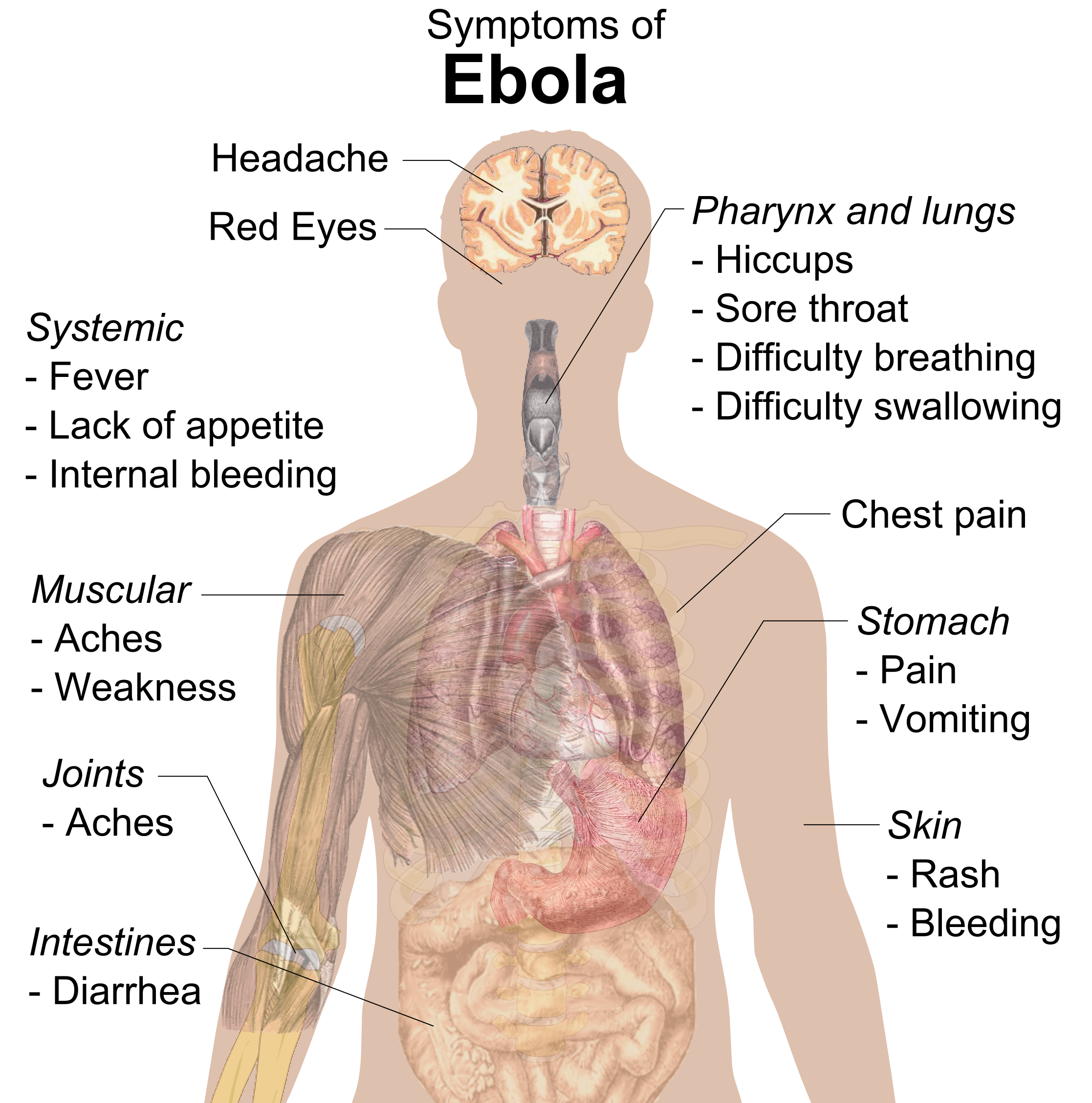
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between 6 and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start.Ebola in Uganda: An Ebola vaccine was approved by the US FDA in December 2019. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rail Accidents (2000–present)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rail accidents ...
A rail accident (or train wreck) is a type of disaster involving one or more trains. Train wrecks often occur as a result of miscommunication, as when a moving train meets another train on the same track, when the wheels of train come off the track or when a boiler explosion occurs. Train accidents have been widely covered in popular media and in folklore. Lists By year By type *By country * By death toll *Terrorist incidents See also * Derailment * Rail transport * Tram accident * Train-pedestrian fatalities A level crossing is an intersection where a railway line crosses a road, Trail, path, or (in rare situations) airport runway, at the same level, as opposed to the railway line or the road etc. crossing over or under using an Overpass#Railway, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (), is the Capital city, capital and Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-growing Megacity, megacities, with an estimated population of 17 million in 2024. It is the List of cities and towns in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, most densely populated city in the DRC, the List of cities in Africa by population, most populous city and List of urban areas in Africa by population, third-largest metropolitan area in Africa, and the world's List of largest cities, twenty-second most populous city and List of national capitals by population, fourth-most populous capital city. It is the leading Economy, economic, Politics, political, and cultural center of the DRC, housing several industries including manufacturing, telecommunications, List of banks in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, banking, and entertainment. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is a rich mining region which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered from the south by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is the List of African countries by area, second-largest country in Africa and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the DR Congo is the most populous nominally List of countries and territories where French is an official language, Francophone country in the world. Belgian French, French is the official and most widely spoken language, though there are Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, over 200 indigenous languages. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, the Cabinda Province, Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west; the Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Mweka
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Mweka () is a Latin suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of The Metropolitan of Kananga in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, it depends on the missionary Roman Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples. Its cathedral episcopal see is the Cathédrale Saint-Martin, in the city of Mweka in Kasai Province. Statistics As per 2014, it pastorally served 346,580 Catholics (41.2% of 840,645 total) on 21,700 km² in 14 parishes with 43 priests (32 diocesan, 11 religious), 34 lay religious (21 brothers, 13 sisters) and 35 seminarians. History * Established on 24 March 1953 as the Apostolic Prefecture of Mweka, on territory split off from the then Apostolic Vicariate of Luluabourg * Promoted on 29 September 1964 as the Diocese of Mweka. Ordinaries (all Latin Rite) ;''Apostolic Prefects of Mweka'' * Apostolic administrator Bernard Mels, Scheutists (C.I.C.M.) (1953-1957), while Titular Bishop of Belali (10 March 1949 – 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |