|
Mushika Kingdom
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, also Eli or Ezhi, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala (hill, Kannur), Ezhimala) in present-day Kannur district, Kannur, North Malabar, Kerala, northern Kerala, south India. The country of the Ezhimala, ruled by an ancient chiefly lineage ("the Muvan"), appears in Sangam period, early historic (pre-Pallava) south India. Sangam literature, Early Tamil poems contain several references to the exploits of Nannan, the ruler of Ezhimala (''fl. c.'' 180 AD) who famously defeated the Tagadur Athiyamān, Satiyaputra ruler. Nannan was known as a great enemy of the early Chera dynasty, Chera rulers. The famous Kottayam Coin Hoard, a massive cache of mostly Julio-Claudian dynasty, Julio-Claudian (Roman) coins, was also discovered from the Ezhimala country. The Ezhimala polity gradually developed into a monarchical state (known as the "Kolladesham") in the early medieval period and came under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tamil
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning from the 3rd century BCE to the seventh century CE. Prior to Old Tamil, the period of Tamil linguistic development is termed as Proto-Tamil. After the Old Tamil period, Tamil becomes Middle Tamil. The earliest records in Old Tamil are inscriptions from between the 3rd and 1st century BCE in caves and on pottery. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the Brahmi script called Tamil-Brahmi. The earliest long text in Old Tamil is the ''Tolkāppiyam'', an early work on Tamil grammar and poetics, whose oldest layers could be as old as the mid-2nd century BCE.Zvelebil, K. ''The Smile of Murugan: On Tamil Literature of South '' p. xx Old Tamil preserved many features of Proto-Dravidian, the reconstructed common ancestor of the Dravidian languages, including inventory of consonants, the syllable structure, and various grammatical features. History According to Bhadriraju Krishnamurti, Tamil, as a Dravidian language, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
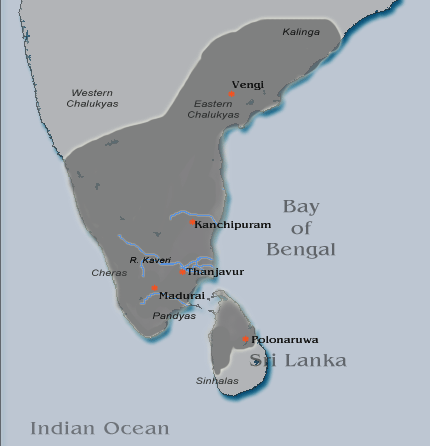
Rajaraja I
Rajaraja I ( Middle Tamil: ''Rājarāja Cōḻaṉ''; Classical Sanskrit: ''Rājarāja Śōḷa''; 3 November 947 – January/February 1014), also known as Rajaraja the Great, was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 to 1014. He was known for his conquests of southern India and Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka, as well as increasing Chola influence across the Indian Ocean. Rajaraja's birth name is variously given as Arul Mozhi Varman and Arul Moli Varman. Rajaraja's empire encompassed vast territories, including regions of the Pandya country, the Chera country, and northern Sri Lanka. He also extended his influence over strategic islands such as Lakshadweep, Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and parts of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. His conquests weren't limited to the south; he also launched successful campaigns against the Western Gangas and the Western Chalukyas, extending Chola authority as far as the Tungabhadra River. In the east, Rajaraja faced fierce opposition fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succession between two groups of princely cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandava, Pāṇḍavas. It also contains Hindu philosophy, philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha (sage), Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an Ramopakhyana, abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyasa, Vy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezhimala Beach
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, South India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Academy at Ezhimala is Asia's largest, and the world's third-largest, naval academy. As the former capital of the ancient Kolathunadu Kingdom of the Mushikas, Ezhimala is considered to be an important historical site. A flourishing seaport and center of trade around the beginning of the Common Era, it was also one of the major battlefields of the Chola- Chera Wars in the 11th century. It is believed by some that Buddha had visited Ezhimala. The Kolathunadu (Kannur) Kingdom at the peak of its power, reportedly extended from Netravati River (Mangalore) in the north to Korapuzha (Kozhikode) in the south with Arabian Sea on the west and Kodagu hills on the eastern boundary, also including the isolated islands of Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (, , , also written as ''Tamizhil'' according to linguistic pronunciation) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world,. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). attested since 300 BC, 300 BCE.: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900" at p. 610 Tamil was the lingua franca for early maritime traders in South India, with Tamil inscriptions found outside of the Indian subcontinent, such as Indonesia, Thailand, and Egypt. The language has a well-documented history wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardamom
Cardamom (), sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genus (biology), genera ''Elettaria'' and ''Amomum'' in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They are recognized by their small seed pods: triangular in cross-section and spindle-shaped, with a thin, papery outer shell and small, black seeds; ''Elettaria'' pods are light green and smaller, while ''Amomum'' pods are larger and dark brown. Species used for cardamom are native throughout tropical and subtropical Asia. The first references to cardamom are found in Sumer, and in Ayurveda. In the 21st century, it is cultivated mainly in India, Indonesia, and Guatemala. Etymology The word ''cardamom'' is derived from the Latin , as a Latinisation (literature), Latinisation of the Greek language, Greek (), a compound of (, "Garden cress, cress") and (), of unknown origin. The earliest attested form of the word signifying "cres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter (fresh and fully mature), dark red, and contains a stone which encloses a single pepper seed. Peppercorns and the ground pepper derived from them may be described simply as ''pepper'', or more precisely as ''black pepper'' (cooked and dried unripe fruit), ''green pepper'' (dried unripe fruit), or ''white pepper'' (ripe fruit seeds). Black pepper is native to the Malabar Coast of India, and the Malabar pepper is extensively cultivated there and in other tropical regions. Ground, dried, and cooked peppercorns have been used since antiquity, both for flavour and as a traditional medicine. Black pepper is the world's most traded spice, and is one of the most common spices added to cuisines around the world. Its spiciness is due to the che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heheya Kingdom
In the Mahabharata epic, the Haihaya kingdom (also spelled Heheya, Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya, etc.) is one of the kingdoms ruled by Chandravanshi (Yadava) kings in central and western India. It was ruled by Kartavirya Arjuna, who defeated Ravana. Its capital was Mahishmati on the banks of river Narmada River, Narmada in present-day Madhya Pradesh. Talajangha was an allied kingdom to the east of Heheya. They conquered many other kingdoms of India until enmity with the warrior ''Bhargavas'' resulted in their demise. Parasurama was the Bhargava leader who ended the kingdom. Haihaya clans The Haihayas () were an ancient confederacy of five ''gana''s (clans), who claimed their common ancestry from Yadu. According to the Harivamsa, Harivamsha Purana (34.1898) Haihaya was the great-grandson of Yadu and grandson of Sahasrajit.Pargiter, F.E. (1972) [1922]. ''Ancient Indian Historical Tradition'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, p.87. In the Vishnu Purana (IV.11), all the five Haihaya clans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshatriya
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the context of later Vedic society wherein members were organised into four classes: ''brahmin'', kshatriya, '' vaishya,'' and '' shudra''. History Early Rigvedic tribal monarchy The administrative machinery in Vedic India was headed by a tribal king called a Rajan whose position may or may not have been hereditary. The king may have been elected in a tribal assembly (called a Samiti), which included women. The Rajan protected the tribe and cattle; was assisted by a priest; and did not maintain a standing army, though in the later period the rulership appears to have risen as a social class. The concept of the fourfold varna system is not yet recorded. Later Vedic period The hymn '' Purusha Sukta'' in the ''Rigveda'' describes the symbolic crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penguin Books
Penguin Books Limited is a Germany, German-owned English publishing, publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Allen Lane with his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers the Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year."About Penguin – company history" , Penguin Books. Penguin revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, sold through Woolworths (United Kingdom), Woolworths and other stores for Sixpence (British coin), sixpence, bringing high-quality fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Its success showed that large audiences existed for several books. It also affected modern British popular culture significantly through its books concerning politics, the arts, and science. Penguin Books is now an imprint (trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atula
Athula (IAST: Atula), ''fl.'' 11th century AD, was a medieval Sanskrit-language poet from the Mushika or Ezhimala kingdom, located in present-day northern Kerala (the Malabar Coast The Malabar Coast () is the southwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It generally refers to the West Coast of India, western coastline of India stretching from Konkan to Kanyakumari. Geographically, it comprises one of the wettest regio ...), south India. He is best known for composing the '' Mushika-vamsa-kavya'', a mahakavya (epic poem) about the ruling dynasty of the kingdom. The dynastic chronicle was composed in the court of Mushika ruler Srikantha ("Kantan Karivarman", in Malayalam). Athula is sometimes alternatively dated to the first half of the 12th century AD (Unni, 1980). It has also been suggested that he might be identical to the Chera court poet Tholan. References Sanskrit poets {{India-poet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |