|
Musa Khan (Bengal Ruler)
Musa Khan (; died April 1623) was a Bengali zamindar and the ruler of Bhati, a region in medieval Bengal that covered the greater districts of Dhaka, Mymensingh, Comilla, and Sylhet in present-day Bangladesh. He also served as the chief of the Baro-Bhuyans, a confederation of soldier-landowners who aimed to resist the Mughal invasion of Bengal and to continue the legacy of his father, Isa Khan. Early life and family Musa Khan was born into a Bengali Muslim family from Sarail. He was the eldest son of Isa Khan, probably by his first wife Fatima Bibi, who was the daughter of Ibrahim Danishmand. Khan's grandfather, Kalidas Gazdani, converted to Islam under the guidance of Ibrahim Danishmand. Musa Khan's grandfather, Sulaiman Khan, married the Sultan's daughter Syeda Momena Khatun and received the Zamindari of Sarail which passed onto Musa Khan's father. Musa Khan had two younger brothers, Abdullah Khan and Mahmud Khan. Along with his maternal cousin Alaul Khan, the three of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baro-Bhuyan
The ''Baro-Bhuyans'' (or ''Baro-Bhuyan Raj''; also ''Baro-Bhuians'' and ''Baro-Bhuiyans'') were confederacies of soldier-landowners in Assam and Bengal in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. The confederacies consisted of loosely independent entities, each led by a warrior chief or a landlord. The tradition of Baro-Bhuyan is peculiar to both Assam and Bengal and differ from the tradition of ''Bhuihar'' of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar—in Assam this phenomenon came into prominence in the 13th century when they resisted the invasion of Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah"The Bara Bhuyans of Kamarupa played a similar role in the country's history round about the thirteenth century...Jadunath Sarkar holds that Husamuddin Iwaz () reduced some of the Barabhuyans to submission when he attacked Kamarupa." and in Bengal when they resisted Mughal rule in the 16th century. ''Baro'' denotes the number twelve, but in general there were more than twelve chiefs or landlords, and the word ''baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
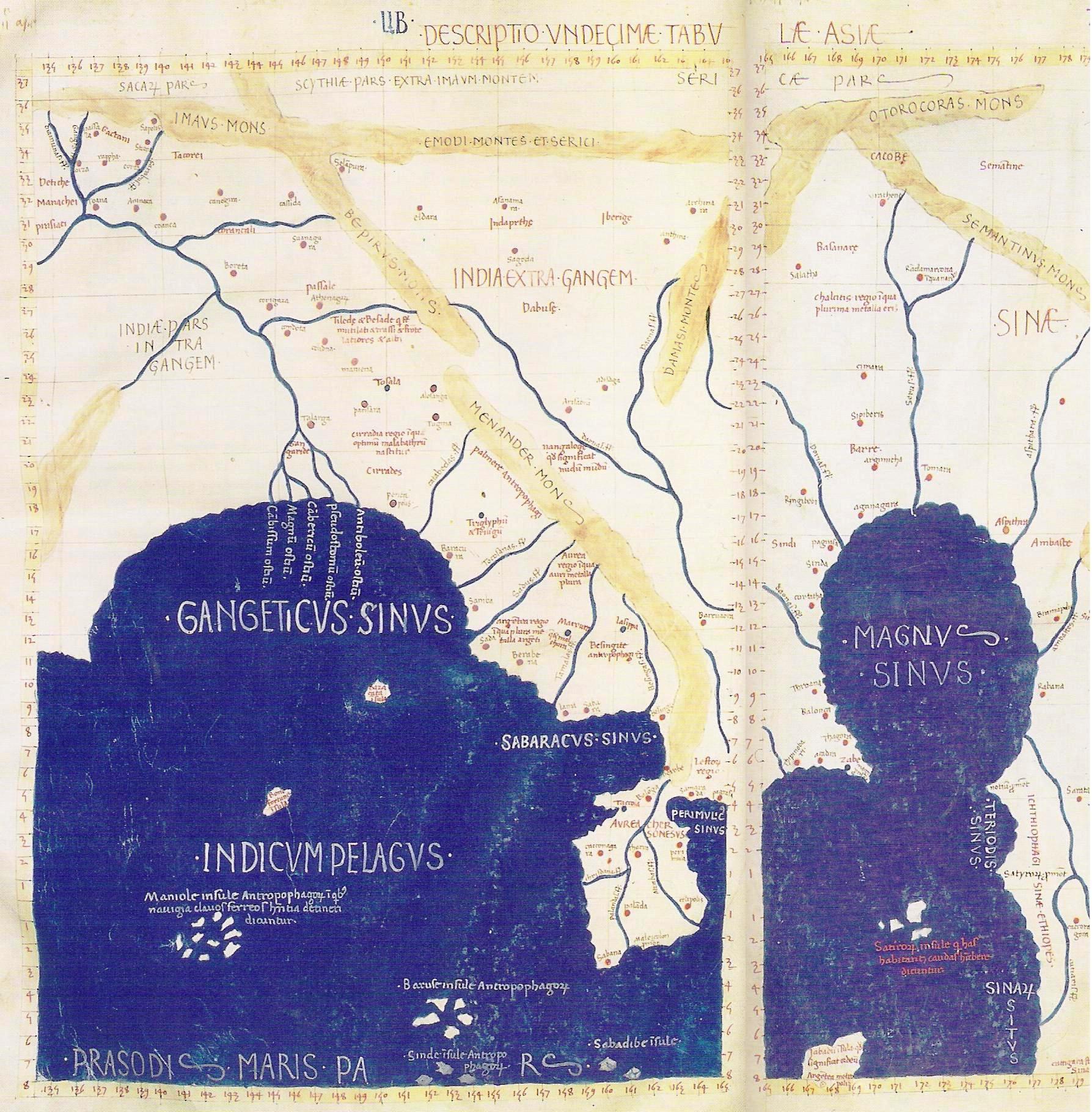
Mughal Invasion Of Bengal
The Mughal invasion of Bengal was an invasion of the Sultanate of Bengal, then ruled by the Afghan Karrani dynasty, by the Mughal Empire from 1572 to 1576. After a series of intense battles, the Mughals eventually defeated the Sultanate of Bengal in the Battle of Raj Mahal in 1576, and annexed the region into their empire as the province of Bengal. Background Before the Mughal conquest, Bengal was a flourishing region ruled by the Afghan Karrani dynasty. The dynasty had established its control over Bengal in the mid-16th century, after the decline of the Sur Empire. The Karrani rulers maintained a relatively strong hold over the region, fostering trade and cultural development. Bengal was known for its fertile land, which supported extensive agriculture, and its strategic location along the Bay of Bengal, which facilitated trade with various parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and China. The region's wealth and prosperity made it a coveted prize for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baro-Bhuiyan
The ''Baro-Bhuyans'' (or ''Baro-Bhuyan Raj''; also ''Baro-Bhuians'' and ''Baro-Bhuiyans'') were confederacies of soldier-landowners in Assam and Bengal in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. The confederacies consisted of loosely independent entities, each led by a warrior chief or a landlord. The tradition of Baro-Bhuyan is peculiar to both Assam and Bengal and differ from the tradition of ''Bhuihar'' of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar—in Assam this phenomenon came into prominence in the 13th century when they resisted the invasion of Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah"The Bara Bhuyans of Kamarupa played a similar role in the country's history round about the thirteenth century...Jadunath Sarkar holds that Husamuddin Iwaz () reduced some of the Barabhuyans to submission when he attacked Kamarupa." and in Bengal when they resisted Mughal rule in the 16th century. ''Baro'' denotes the number twelve, but in general there were more than twelve chiefs or landlords, and the word ''bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonargaon
Sonargaon (; ; Literary translation, lit. ''Golden Hamlet (place), Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division. Sonargaon is one of the old capitals of the historic region of Bengal and was an administrative center of eastern Bengal. It was also a river port. Its hinterland was the center of the muslin trade in Bengal, with a large population of weavers and artisans. According to Greco-Roman world, ancient Greek and Roman accounts, an Emporium (antiquity), emporium was located in this hinterland, which archaeologists have now identified with the Wari-Bateshwar ruins of the Gangaridai, Gangaridai Empire. The area was a base for the Vanga Kingdom, Vanga, Gangaridai, Samatata, Sena dynasty, Sena, and Deva dynasty, Deva dynasties. Sonargaon gained importance during the Delhi Sultanate. It was the capital of the Sonargaon Sultanate ruled by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah and his son Ikhtiyaruddin Gha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musa Khan's Mosque
Musa may refer to: Places *Mūša, a river in Lithuania and Latvia * Musa, Azerbaijan, a village in Yardymli Rayon * Musa, Iran, a village in Ilam province, Iran * Musa, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Iran * Musa Kalayeh, Gilan province, Iran *Abu Musa, an island in the Persian Gulf, Hormozgan province, Iran * Musa, Kerman, Kerman province, Iran * Musa, Bukan, West Azerbaijan province, Iran * Musa, Maku, West Azerbaijan province, Iran * Musa, Pakistan, a village in Chhachh, Attock, Punjab, Pakistan * Musa, La Molina, a neighborhood in Lima, Peru * Musa (crater), an impact crater on Saturn's moon Enceladus * Musa (Tanzanian ward), a ward in Tanzania * Musa (Pori), a district of Pori, Finland *Musa Dagh a mountain peak in Turkey *Jebel Musa (Morocco), a mountain known as one of the pillars of Hercules * Jabal Musa, or Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Desert believed to be a possible location of the Biblical Mount Sinai * Muza Emporion, an ancient port city near present day Mocha, Yem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, northeastern India by area and the largest in terms of population, with more than 31 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese language, Assamese and Bodo language, Bodo are two of the official languages for the entire state and Meitei language, Meitei (Manipuri language, Manipuri) is recognised as an additional official language in three districts of Barak Valley and Hojai district. in Hojai district and for the Barak valley region, alongside Bengali language, Bengali, which is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauhati
Guwahati () the largest city of the Indian state of Assam, and also the largest metropolis in northeastern India. Dispur, the capital of Assam, is in the circuit city region located within Guwahati and is the seat of the Government of Assam. The Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport is the 12th busiest in India, and the busiest in the North-East of the country. A major riverine port city along with hills, and one of the fastest growing cities in India, Guwahati is situated on the south bank of the Brahmaputra. The city is known as the "gateway to North East India". The ancient cities of Pragjyotishpura and Durjaya (North Guwahati) were the capitals of the ancient state of Kamarupa. Many ancient Hindu temples like the Kamakhya Temple, Ugratara Temple, Basistha Temple, Doul Govinda Temple, Umananda Temple, Navagraha Temple, Sukreswar Temple, Rudreswar Temple, Manikarneswar Devalaya, Aswaklanta Temple, Dirgheshwari Temple, Lankeshwar Temple, Bhubaneswari Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Assam
The Government of Assam or Assam Government abbreviated as GoAS, is the Subnational legislature, state government of the Indian state of Assam. It consists of the Governors of states of India, Governor appointed by the President of India as the head of the state, currently Lakshman Acharya, Lakshman Prasad Acharya. The head of government is the Chief Minister of Assam, Chief Minister, currently Dr. Himanta Biswa Sarma, who is the leader of the group that commands a majority in the unicameral Assam Legislative Assembly. The Assam Assembly is elected by universal adult suffrage for a period of five years. The Chief Minister is assisted by a Council of Ministers that he nominates, the size of which is restricted. In 2021, the National Democratic Alliance (India), National Democratic Alliance won a majority of seats in the legislature, with 75 seats, followed by Congress with 29 seats and AIUDF with 16. Cabinet Ministers Ministers sworn on 10 May 2021: Leaders References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud Khan Of Bengal
Mahmud Khan () was a 17th-century Bengali nobleman initially associated with the Baro-Bhuiyan confederacy which challenged Mughal invasions in Bengal. He was the son of Isa Khan, the confederacy's first chief. Biography Khan was born into an aristocratic Bengali Sunni Muslim ''zamindar'' family known as the Dewans of Sarail in the Bhati region of Bengal. The family served as ''dewans'' to the former Sultans of Bengal. His father, Isa Khan, was the leader of the Baro-Bhuiyan confederacy which arose as a result of the fall of the Bengal Sultanate and challenged Mughal invasion. His mother, Syeda Fatima Bibi, was the daughter of Ibrahim Danishmand, a Hanafite scholar from Sonargaon. After his father's death in 1599, Mahmud pledged allegiance to his elder brother Musa Khan and fought alongside him in the Battle of Dakchara where they were defeated by the Mughals and fled. They challenged the Mughals again shortly after from Katrabo (or Katrapur), which was not far from Islam Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamindar
A zamindar in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semi-autonomous feudal lord of a ''zamindari'' (feudal estate). The term itself came into use during the Mughal Empire, when Persian was the official language; ''zamindar'' is the Persian for ''landowner''. During the British Raj, the British began using it as a local synonym for "estate". Zamindars as a class were equivalent to lords and barons; in some cases, they were independent sovereign princes. Similarly, their holdings were typically hereditary and came with the right to collect taxes on behalf of imperial courts or for military purposes. During the Mughal Empire, as well as the British rule, zamindars were the land-owning nobility of the Indian subcontinent and formed the ruling class. Emperor Akbar granted them mansabs and their ancestral domains were treated as jagirs. Most of the big zamindars belonged to the Hindu high-caste, usually Brahmin, Rajput, Bhumihar, or Kayastha. During the colonial era, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim Danishmand
Syed Ibrāhīm Dānishmand (, ) was a 16th-century zamindar and Islamic scholar who belonged to the Qadiriyya Sufi order. Well respected during his lifetime, Danishmand was considered an expert in several Islamic and secular subjects. He is believed to be among the first of the Qadiriyya order to have operated and preached in Bengal. Early life Born into a Syed family, there are differing opinions on the exact origins of Danishmand, with one suggestion being that he was a native of Persia who migrated to Bengal in the 16th century. It may therefore be possible that he was among the many Syeds who were invited from Central Asia and Persia by the Sultan of Bengal, Alauddin Husain Shah, to aid in the administration of his kingdom. Alternatively, historian Achyut Charan Choudhury states that he was a great-grandson of the Sufi general Syed Nasiruddin and belonged to the Syeds of Taraf, a land owning family who had had a presence in Bengal since the 13th century. Life A prolific wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |