|
Mundzuk
Mundzuk was a Hunnic chieftain, brother of the Hunnic rulers Octar and Rugila, and father of Bleda and Attila by an unknown consort. Jordanes in ''Getica'' recounts "''For this Attila was the son of Mundzucus, whose brothers were Octar and Ruas, who were supposed to have been kings before Attila, although not altogether of the same erritoriesas he''". Etymology The etymology of the name "Mundzuk" is disputed. It is recorded as ''Mundzucus'' by Jordanes, ''Mundiucus'' by Cassiodorus, ''Μουνδίουχος'' (Moundioukhos) by Priscus, and ''Μουνδίου'' (Moundiou) by Theophanes of Byzantium. A Germanic etymology was proposed by Karl Müllenhoff in the 19th century: he noted the similarity of the name's second element to that of the Burgundian king Gundioc and the Frankish king Merovech. According to Gerhard Doerfer, the name can be derived from a Gothic ''*Mundiweihs'', from ''mund-'' (protection) and ''weihs'' (battle). Gottfried Schramm rejects a Germanic origin fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attila
Attila ( or ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. As nephews to Rugila, Attila and his elder brother Bleda succeeded him to the throne in 435, ruling jointly until the death of Bleda in 445. During his reign, Attila was one of the most feared enemies of the Western Roman Empire, Western and Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empires. He crossed the Danube twice and plundered the Balkans but was unable to take Constantinople. In 441, he led an invasion of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, the success of which emboldened him to invade the West. He also attempted to conquer Roman Gaul (modern France), crossing the Rhine in 451 and marching as far as Aurelianum (Orléans), before being stopped in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. He subsequently invaded Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleda
Bleda () was a Hunnic ruler, the brother of Attila the Hun. As nephews to Rugila, Attila and his elder brother Bleda succeeded him to the throne. Bleda's reign lasted for eleven years until his death. While it has been speculated by Jordanes that Attila murdered him on a hunting trip, it is unknown exactly how he died. One of the few things known about Bleda is that, after the great Hun campaign of 441, he acquired a Moorish dwarf named Zerco. Bleda was highly amused by Zerco and went so far as to make a suit of armor for the dwarf so that Zerco could accompany him on campaign. Etymology Greek sources have ''Βλήδας'' and ''Βλέδας'' (Bledas), Chronicon Paschale ''Βλίδας'' (Blidas), and Latin ''Bleda''. Otto Maenchen-Helfen considered the name to be of Germanic or Germanized origin, a short form of ''Bladardus'', ''Blatgildus'', ''Blatgisus''. Denis Sinor considered that the name begins with consonant cluster, and as such it cannot be of Altaic origin. In 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugila
Rugila or Ruga (also Ruas; died second half of the 430s AD),Lee, A.D. (2013) ''From Rome to Byzantium AD 363 to 565: The Transformation of Ancient Rome''. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, pp. 118-119. was a ruler who was a major factor in the Huns' early victories over the Roman Empire. He served as an important forerunner with his brother Octar, with whom he initially ruled in dual kingship, possibly a geographical division where Rugila ruled over Eastern Huns while Octar over Western Huns, during the 5th century AD. Etymology The name is mentioned in three variants, (Rougas), (Rouas), and (Roilas). Common spellings are Ruga, Roas, Rugila. Otto Maenchen-Helfen included this name among those of Germanic or Germanized origin, but without any derivation, only comparison with Rugemirus and Rugolf. Denis Sinor considered a name with initial ''r-'' not of Altaic origin (example Ragnaris). Omeljan Pritsak derived it from Old Turkic and considered it to be of composite form, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himnusz
The "" () is the national anthem of Hungary. The lyrics were written by Ferenc Kölcsey, a nationally renowned poet, in 1823, and its currently official musical setting was composed by the romantic composer Ferenc Erkel in 1844, although other lesser known musical versions exist. The poem bore the subtitle ('From Stormy Centuries of the Hungarian Folk'); it is often argued that this subtitle – by emphasising past rather than contemporary national troubles – was added expressly to enable the poem to pass Austrian Empire, Habsburg censorship. The full meaning of the poem's text is evident only to those well acquainted with Hungarian history. The first stanza is sung at official ceremonies and as well in common. It was ''de facto'' used as hymn of the Kingdom of Hungary from its composition in 1844, and was officially adopted as national anthem of the Third Hungarian Republic in 1989. The lyrics of the "Himnusz" are a Prayer in Christianity, prayer beginning with the words ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octar
Octar or Ouptaros was a Hunnic ruler. He ruled in dual kingship with his brother Rugila, possibly with a geographical division, ruling the Western Huns while his brother ruled the Eastern Huns. Etymology The name is recorded in two variants, Greek ''Ούπταρος'' (Ouptaros), and Latin ''Octar''. The change from ''-ct-'' to ''-pt-'' is characteristic of Balkan Latin. Otto J. Maenchen-Helfen considered the name to be of unknown origin. Omeljan Pritsak derived the name from Turko- Mongolic word ''*öktem'' (strong, brave, imperious; proud, boastful; pride) and verb ''ökte-'' / ''oktä-'' (to encourage). He argued that the deverbal Turkic-Mongolian suffix ''m'' was replaced in Turkic by ''z'' while in Mongolian by ''ri''. The reconstructed form is appellative ''*öktä-r''. History Octar ruled along with his brother Rugila as reported by Jordanes in his ''Getica'': "''...Mundzucus, whose brothers were Octar and Ruas, who were supposed to have been kings before Attila, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, causing the westwards movement of Goths and Alans. By 430, they had established a vast, but short-lived, empire on the Danubian frontier of the Roman empire in Europe. Either under Hunnic hegemony, or fleeing from it, several central and eastern European peoples established kingdoms in the region, including not only Goths and Alans, but also Vandals, Gepids, Heruli, Suebians and Rugians. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868. As the publishing arm of the University of California system, the press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The press has its administrative office in downtown Oakland, California, an editorial branch office in Los Angeles, and a sales office in New York City, New York, and distributes through marketing offices in Great Britain, Asia, Australia, and Latin America. A Board consisting of senior officers of the University of Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
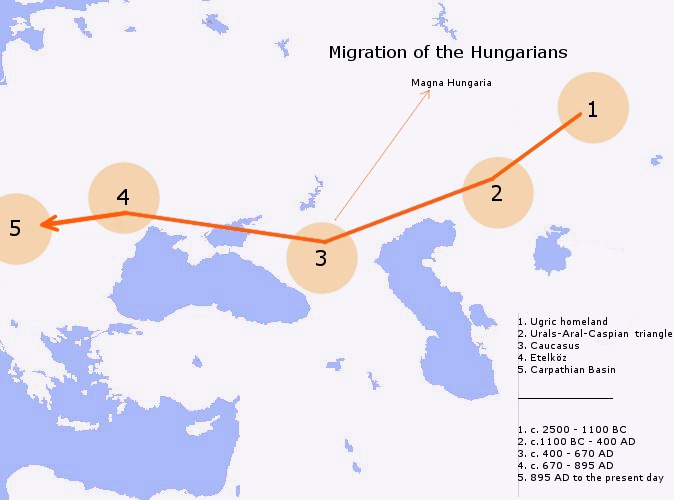
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconstructions Of Old Chinese
Although Old Chinese is known from written records beginning around 1200 BC, the logographic script provides much more indirect and partial information about the pronunciation of the language than alphabetic systems used elsewhere. Several authors have produced reconstructions of Old Chinese phonology, beginning with the Swedish sinologist Bernhard Karlgren in the 1940s and continuing to the present day. The method introduced by Karlgren is unique, comparing categories implied by ancient rhyming practice and the structure of Chinese characters with descriptions in medieval rhyme dictionaries, though more recent approaches have also incorporated other kinds of evidence. Although the various notations appear to be very different, they correspond with each other on most points. By the 1970s, it was generally agreed that Old Chinese had fewer points of articulation than Middle Chinese, a set of voiceless sonorants, and labiovelar and labio-laryngeal initials. Since the 1990s, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Chinese
Old Chinese, also called Archaic Chinese in older works, is the oldest attested stage of Chinese language, Chinese, and the ancestor of all modern varieties of Chinese. The earliest examples of Chinese are divinatory inscriptions on oracle bones from around 1250 BC, in the Late Shang period. Chinese bronze inscriptions, Bronze inscriptions became plentiful during the following Zhou dynasty. The latter part of the Zhou period saw a flowering of literature, including Four Books and Five Classics, classical works such as the ''Analects'', the ''Mencius (book), Mencius'', and the ''Zuo Zhuan''. These works served as models for Literary Chinese (or Classical Chinese), which remained the written standard until the early twentieth century, thus preserving the vocabulary and grammar of late Old Chinese. Old Chinese was written with several early forms of Chinese characters, including Oracle bone script, oracle bone, Chinese bronze inscriptions, bronze, and seal scripts. Throughout t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |