|
Mukurthi National Park
Mukurthi National Park is a national park in the western Nilgiris mountains of Tamil Nadu in South India. It was created to protect its keystone species, the Nilgiri tahr. It is part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, India's first International Biosphere Reserve. As part of the Western Ghats, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1 July 2012. It is characterised by montane grasslands and shrublands interspersed with sholas, high rainfall, near-freezing temperatures and strong winds. It harbours Bengal tiger and Asian elephant. History Native hill tribe communities including the Toda people have harvested firewood from the sholas and grazed their animals including the hill buffalo for centuries. Indiscriminate felling of the sholas started with the establishment of British settlements in Ootacamund, Coonoor and Wellington in the early 19th century. Beginning in 1841 authorities issued contracts to bidders to fell wood from specific sholas in a 'timber conservancy' program. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilgiri Tahr
The Nilgiri tahr (''Nilgiritragus hylocrius'') is an ungulate that is endemic to the Nilgiri Hills and the southern portion of the Western and Eastern Ghats in the states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala in southern India. It is the only species in the genus ''Nilgiritragus'' and is closely related to the sheep of the genus ''Ovis''. It is the state animal of Tamil Nadu. Etymology The genus name ''Nilgiritragus'' is derived from the Sanskrit words Nila(blue) and Giri(mountains) meaning "blue hills" and the Greek word '' trágos'' meaning "goat". Taxonomy The Nilgiri tahr was described as ''Capra warryato'' by Gray. Taxonomy The species was formerly placed in the genus ''Hemitragus'' together with the Himalayan tahr (''H. jemlahicus'') and the Arabian tahr (''Arabitragus jayakari''). A 2005 phylogenetic analysis showed that the Himalayan and Arabian tahr are sisters of the genus '' Capra'' while the Nilgiri tahr is a sister of the genus ''Ovis'' and it was therefore separated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Asian Water Buffalo
The wild water buffalo (''Bubalus arnee''), also called Asian buffalo, Asiatic buffalo and wild buffalo, is a large bovine native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as ''Endangered'' in the IUCN Red List since 1986, as the remaining population totals less than 4,000. A population decline of at least 50% over the last three generations (24–30 years) is projected to continue. The global population has been estimated at 3,400 individuals, of which 95% live in India, mostly in Assam. The wild water buffalo is the most likely ancestor of the domestic water buffalo. Taxonomy ''Bos arnee'' was the scientific name proposed by Robert Kerr in 1792 who described a skull with horns of a buffalo zoological specimen from Bengal in northern India. The specific name ''arnee'' is derived from Hindi ''arnī'', which referred to a female wild water buffalo; the term is related to Sanskrit ''áraṇya'' ("forest") and ''áraṇa'' ("strange, foreign.") ''Bubalus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs from the ''Cupressus'' genus of the '' Cupressaceae'' family, typically found in temperate climates and subtropical regions of Asia, Europe, and North America. The word ''cypress'' is derived from Old French ''cipres'', which was imported from -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''cipres'', which was imported from Latin ''cypressus'', the latinisation of the Greek language">Greek κυπάρισσος (''kyparissos''). The name derives from Cyparissus, a mythological figure who was turned into a tree after killing a stag. Description Cypress trees typically reach heights of up to and exhibit a pyramidal form, particularly in their youth. Many are characterised by their needle-like, evergreen foliage and acorn-like seed cones. Some species develop flattened, spreading heads at maturity, while certain variants may manife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus Globulus
''Eucalyptus globulus'', commonly known as southern blue gum or blue gum, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae. It is a tall, evergreen tree Endemism, endemic to southeastern Australia. This ''Eucalyptus'' species has mostly smooth bark, juvenile leaves that are whitish and waxy on the lower surface, glossy green, lance-shaped adult leaves, wikt:glaucous#Adjective, glaucous, ribbed flower buds arranged singly or in groups of three or seven in leaf wikt:axil, axils, white flowers and woody fruit. There are four subspecies, each with a different distribution across Australia, occurring in New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. The subspecies are the Victorian blue gum, Tasmanian blue gum, Maiden's gum, and Victorian eurabbie. Description ''Eucalyptus globulus'' is a tree that typically grows to a height of but may sometimes only be a stunted shrub, or alternatively under ideal conditions can grow as tall as , and forms a lignotuber. The bark is usually smo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Melanoxylon
''Acacia melanoxylon'', commonly known as the Australian blackwood, is an ''Acacia'' species native to south-eastern Australia. The species is also known as blackwood, hickory, mudgerabah, Tasmanian blackwood, or blackwood acacia. The tree belongs to the ''Plurinerves'' section of ''Acacia'' and is one of the most wide-ranging tree species in eastern Australia and is quite variable mostly in the size and shape of the phyllodes. Description ''Acacia melanoxylon'' is able to grow to a height of around and has a bole that is approximately in diameter. It has deeply fissured, dark-grey to black coloured bark that appears quite scaly on older trees. It has angular and ribbed branches. The bark on older trunks is dark greyish-black in colour, deeply fissured and somewhat scaly. Younger branches are glabrous, ribbed and angular to flattened near the greenish coloured tips. The stems of younger plants are occasionally hairy. Like most species of ''Acacia'', it has phyllodes rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Decurrens
''Acacia decurrens'', commonly known as black wattle or early green wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub native to eastern New South Wales, including Sydney, the Greater Blue Mountains Area, the Hunter Region, and southwest to the Australian Capital Territory. It grows to a height of 2–15 m (7–50 ft) and it flowers from July to September. Cultivated throughout Australia and in many other countries, ''Acacia decurrens'' has naturalised in most Australian states and in Africa, the Americas, Europe, New Zealand and the Pacific, the Indian Ocean area, and Japan. Description ''Acacia decurrens'' is a fast-growing tree, reaching anywhere from 2 to 15 m (7–50 ft) high. The bark is brown to dark grey colour and smooth to deeply fissured longitudinally with conspicuous intermodal flange marks. The branchlets have longitudinal ridges running along them that are unique to the species. Young foliage tips are yellow. . Alternately arranged leaves are dark green on both side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Dealbata
''Acacia dealbata'', the silver wattle, blue wattle or mimosa, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is native to southeastern Australia and widely introduced in other warm climates. Description It is a fast-growing evergreen tree or shrub growing up to tall, typically a pioneer species after fire. The leaves are bipinnate, glaucous blue-green to silvery grey, and the leaves resemble those of a fern. They are , occasionally up to 17 cm, in length and 1–11 cm broad, with 6–30 pairs of pinnae. Each pinna is divided into 10–68 pairs of leaflets, which are 0.7–6 mm long and 0.4–1 mm broad. The flowers are produced in large racemose inflorescences made up of numerous smaller globose bright yellow flowerheads of 13–42 individual flowers. The fruit is a flattened pod 2–11.5 cm long and 6–14 mm broad, containing several seeds.Flora of Australia Online''Acacia dealbata'' Trees generally do not live longer th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Mollissima
''Acacia mearnsii'', commonly known as black wattle, late black wattle or green wattle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is usually an erect tree with smooth bark, bipinnate leaves and spherical heads of fragrant pale yellow or cream-coloured flowers followed by black to reddish brown pods. In some other parts of the world, it is regarded as an invasive species. Description ''Acacis mearnsii'' is a spreading shrub or erect tree that typically grows to a height of and has smooth bark, sometimes corrugated at the base of old specimens. The leaves are bipinnate with 7 to 31 pairs of pinnae, each with 25 to 78 pairs of pinnules. There is a spherical gland up to below the lowest pair of pinnae. The scented flowers are arranged in spherical heads of 20 to 40, pale yellow or cream-coloured, with the heads on hairy peduncles long. Flowering mainly occurs from October to December and black to reddish-brown pods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Australasia, but is now reserved for species mainly from Australia, with others from New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean. The genus name is Neo-Latin, borrowed from Koine Greek (), a term used in antiquity to describe a preparation extracted from '' Vachellia nilotica'', the original type species. Several species of ''Acacia'' have been introduced to various parts of the world, and two million hectares of commercial plantations have been established. Description Plants in the genus ''Acacia'' are shrubs or trees with bipinnate leaves, the mature leaves sometimes reduced to phyllodes or rarely absent. There are 2 small stipules at the base of the leaf, but sometimes fall off as the leaf matures. The flowers are borne in spik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tobacco, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, opium, sisal, oil seeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees and forest trees. Protectionist policies and natural comparative advantage have sometimes contributed to determining where plantations are located. In modern use, the term usually refers only to large-scale estates. Before about 1860, it was the usual term for a farm of any size in the southern parts of British North America, with, as Noah Webster noted, "farm" becoming the usual term from about Maryland northward. The enslavement of people was the norm in Maryland and states southward. The plantations there were forced-labor farms. The term "plantation" was used in most British colonies but very rarely in the United Kingdom itself i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. Known as the City of Spices, Kozhikode is listed among the City of Literature, UNESCO's Cities of Literature. It is the nineteenth largest urban agglomeration in the country and the second largest one in Kerala. Calicut city is the second largest city proper in the state with a corporation limit population of 609,224 Calicut is classified as a Tier-2 city by the Government of India. It is the largest city on the Malabar Coast and was the capital of the British-era Malabar District, Malabar district. It was the capital of an independent kingdom ruled by the Samoothiris (Zamorins). The port at Kozhikode acted as the gateway to the medieval South Indian coast for the Chinese people, Chinese, the Persians, the Arabs, and finally the Europeans. According to data compiled by economics research firm Indicus Analytics in 2009 on residences, earnings and investments, Kozhikode was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
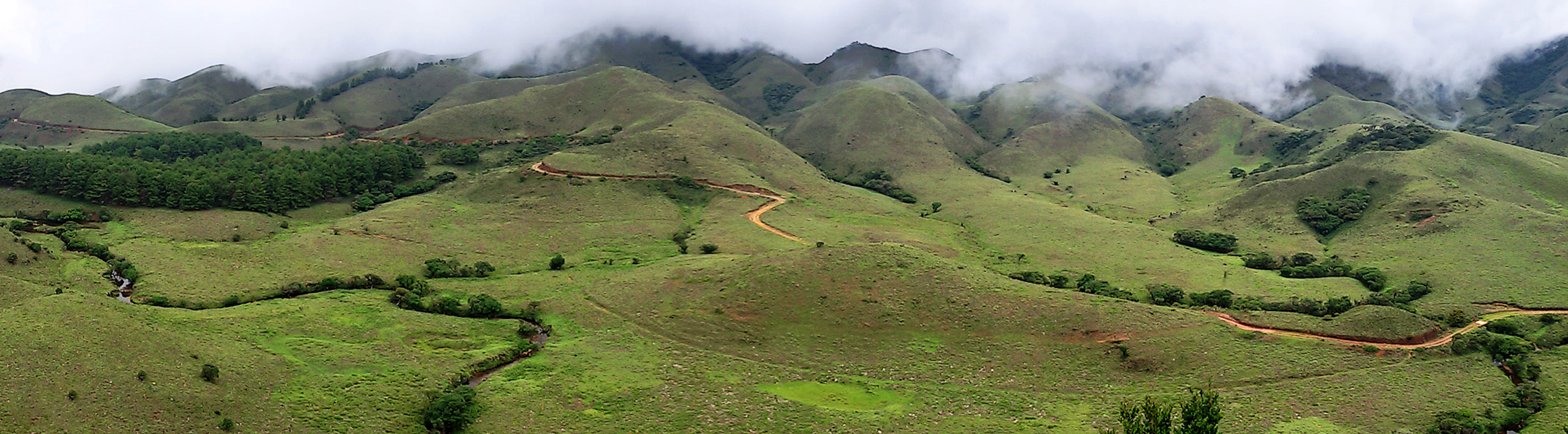
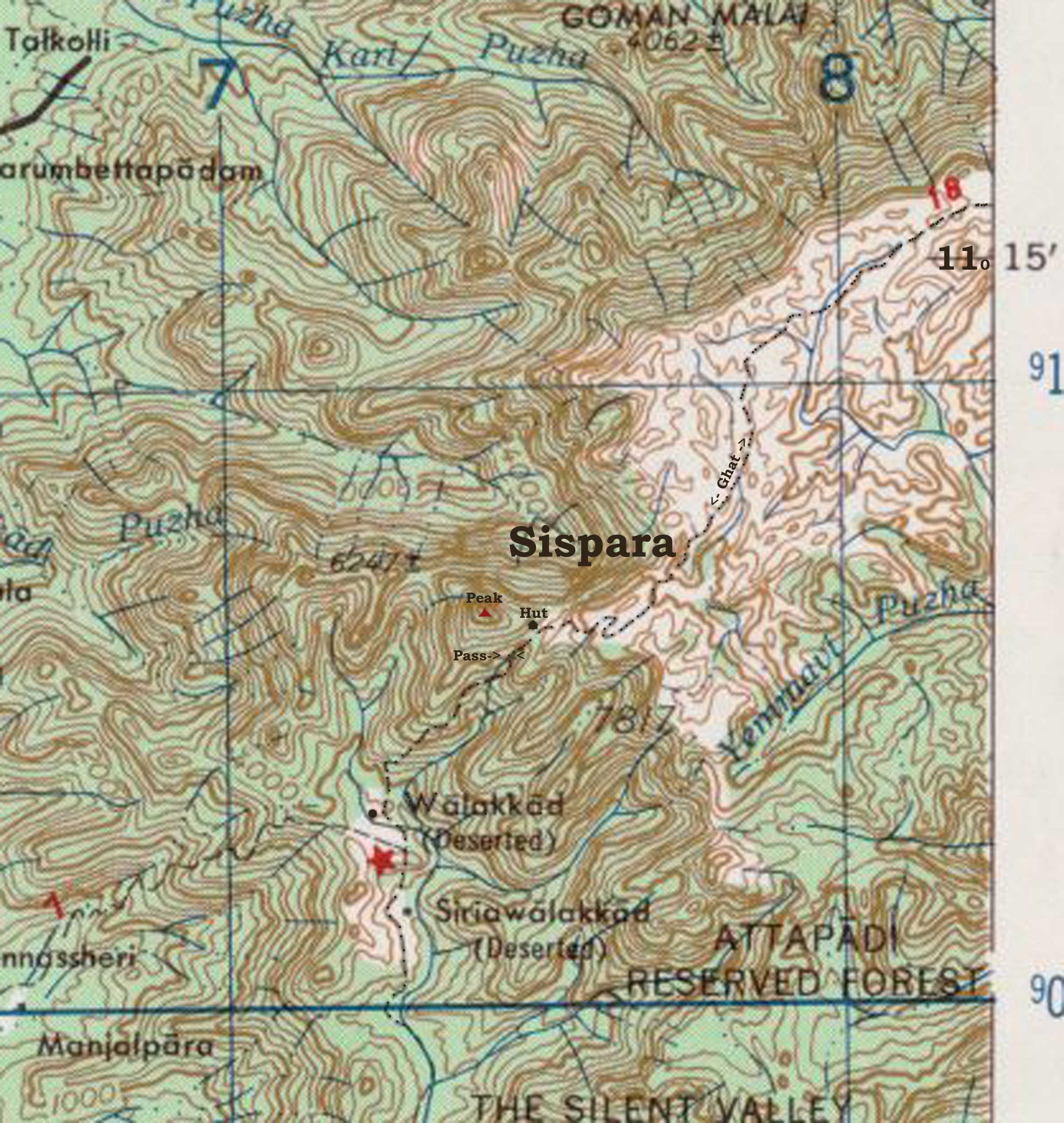
Sispara
Sispara , സിസ്പാര (Sisapara, Sisparra, Sisparah, Su:spore), a proper noun, is a combination of the Badaga language words ''si:su'' + ''pore''; meaning: magnetite bearing rock + gorge. It may refer to: *Sispara#Sispara peak, Sispara peak, a large hill in Kerala; *Sispara#Sispara bungalow, Sispara bungalow, the shelter at the base of the peak; *Sispara#Sispara pass, Sispara pass, the low gap between hills where the shelter is located; or *Sispara#Sispara ghat, Sispara ghat, the mountain trail that goes through the pass. Sispara peak Sispara peak (സിസ്പാര മല), elevation at , is in the northeast end of Silent Valley National Park, Palakkad district of the Kerala state, in the core area of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, in the Western Ghats of South India. It is near the southwest end of Mukurthi National Park in Tamil Nadu state. One can approach this peak by passing northwest up behind the bungalow, and ascending the high bluff below the peak. Hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |