|
Muhammad As A Diplomat
The diplomatic career of Muhammad ( – 8 June 632) encompasses Muhammad's leadership over the growing Muslim community (''Ummah'') in early Arabia and his correspondences with the rulers of other nations in and around Arabia. This period was marked by the change from the customs of the period of ''Jahiliyyah'' in pre-Islamic Arabia to an early Islamic system of governance, while also setting the defining principles of Fiqh, Islamic jurisprudence in accordance with Sharia and an Islamic theocracy. The two primary Arab tribes of Medina, the Banu Aws, Aws and the Banu Khazraj, Khazraj, had been battling each other for the control of Medina for more than a century before Hegira, Muhammad's arrival.Watt. al-Aus; Encyclopaedia of Islam With the pledges of al-Aqaba, which took place near Mina, Saudi Arabia, Mina, Muhammad was accepted as the common leader of Medina by the Aws and Khazraj and he addressed this by establishing the Constitution of Medina upon his arrival; a document which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Oriental Society
The American Oriental Society is a learned society that encourages basic research in the languages and literatures of the Near East and Asia. It was chartered under the laws of Massachusetts on September 7, 1842. It is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States and is the oldest devoted to a particular field of scholarship. The society encourages basic research in the languages and literatures of the Near East and Asia and covers subjects such as philology, literary criticism, textual criticism, paleography, epigraphy, linguistics, biography, archaeology, and the history of the intellectual and imaginative aspects of Eastern civilizations, especially of philosophy, religion, folklore and art. It is closely associated with Yale University, which is the site of its library. The society publishes a journal quarterly, the '' Journal of the American Oriental Society'', the most important American serial publication in the historical languages of Asia. Former presidents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By the seventh century, they had become wealthy merchants, dominating trade between the Indian Ocean, East Africa, and the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean. The tribe ran caravans to Gaza City, Gaza and Damascus in summer and to Yemen (region), Yemen in winter, while also mining and pursuing other enterprises on these routes. When Muhammad Muhammad's first revelation, began preaching Islam in Mecca, the Quraysh initially showed little concern. However, their opposition to his activities quickly grew as he increasingly challenged Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism, which was prevalent throughout pre-Islamic Arabia. As relations deteriorated, Muhammad and Early Muslims, his followers migrated to Medina (the journey known as the Hij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. Its concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, ethnicity, nation or state. These terms are similarly disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions. In the United States (US), Native American tribes are legally considered to have "domestic dependent nation" status within the territorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawah
' (, , "invitation", also spelt , , , or ) is the act of inviting people to Islam. The plural is () or (). Preachers who engage in dawah are known as da'i. Etymology literally means "issuing a summons" or "making an invitation". Grammatically, the word represents a gerund of a verb with the triconsonantal root ''d-ʕ-w'' () meaning variously "to summon" or "to invite". A Muslim who practices , either as a religious worker or in a volunteer community effort, is called a ' (, plural ' ). A , is a person who invites people to understand and accept Islam through dialogue and other techniques, who may be regarded as a missionary inviting people to the faith, prayer, and manner of Islamic life. Early Islam The term ''daʿwah'' ur'an. In '' sura'' (chapter) 30:25, for example, it denotes the call to the dead to rise on the Day of Judgment. When used in the Qur'an, it generally refers to Allah's invitation to live according to His will. Thus, when used in the first cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal (emblem)
A seal is a device for making an impression in Sealing wax, wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an Paper embossing, embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, or to prevent interference with a package or envelope by applying a seal which had to be broken to open the container (hence the modern English verb "to seal", which implies secure closing without an actual wax seal). The seal-making device is also referred to as the seal ''matrix'' or ''die''; the imprint it creates as the seal impression (or, more rarely, the ''sealing''). If the impression is made purely as a relief resulting from the greater pressure on the paper where the high parts of the matrix touch, the seal is known as a ''dry seal''; in other cases ink or another liquid or liquefied medium is used, in another color than the paper. In most traditional forms of dry seal the design on the seal matrix is in Intaglio (sculpture), intag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Hudaybiyyah
The Treaty of al-Hudaybiya () was an event that took place during the lifetime of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was a pivotal treaty between Muhammad, representing the state of Medina, and the tribe of the Quraysh in Mecca in March 628 (corresponding to Dhu al-Qi'dah, AH 6). The treaty helped to decrease tension between the two cities, affirmed peace for a period of 10 years, and authorised Muhammad's followers to return the following year in a peaceful pilgrimage, which was later known as the First Pilgrimage. However this treaty was broken in two years. According to Islamic sources, the treaty was broken by the Quraysh, which led Muhammad to march against Mecca in 630 with an army of 10,000 men. Background As a result of the rejection of his message and the persecution of his followers, the Islamic prophet Muhammad left his hometown of Mecca in 622 and migrated with his followers to the oasis town of Medina. There, he had more followers and founded a local power base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Pledge At Al-Aqabah
The second pledge at al-ʿAqabah () was an important event in Islam where 75 residents of the city of Medina pledged their loyalty to Muhammad as their leader in an oath of allegiance known as a '' bay'ah''. It preceded the Hijrah, or migration of Muhammad and his supporters from Mecca, where they were persecuted, to Medina, where Muhammad became ruler. The pledge occurred in 622 CE at a mountain pass (''al-ʿaqabah'') five kilometers from Mecca. Event Converts to Islam came from both non-Jewish tribes of Arabia The tribes of Arabia () have inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years and traditionally trace their ancestry to one of two forefathers: Adnan, whose descendants originate from Hejaz, West Arabia, Syrian Desert, North Arabia, East Ara ... present in Medina, such that by June of the subsequent year seventy-five Muslims came to Mecca for pilgrimage and to meet Muhammad. Meeting him secretly by night, the group made what was known as the Second Pledge of al-ʿ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 to 628, with an interruption of one year. Khosrow II was the son of Hormizd IV (reigned 579–590), and the grandson of Khosrow I (reigned 531–579). He was the last king of Iran to have a lengthy reign before the Muslim conquest of Iran, which began five years after his execution. He lost his throne, then recovered it with the help of the Byzantine emperor Maurice, and, a decade later, went on to emulate the feats of the Achaemenids, conquering the rich Roman provinces of the Middle East; much of his reign was spent in wars with the Byzantine Empire and struggling against usurpers such as Bahram Chobin and Vistahm. Khosrow II began a war against the Byzantines in 602, ostensibly to avenge the murder of his ally Maurice. Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
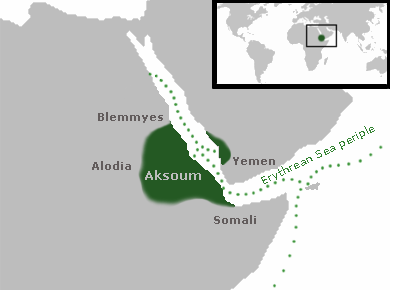
Negus
''Negus'' is the word for "king" in the Ethiopian Semitic languages and a Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles, title which was usually bestowed upon a regional ruler by the Ethiopian Emperor, Negusa Nagast, or "king of kings," in pre-1974 Ethiopia. The negus is referred to as Al-Najashi (النجاشي) in the Islamic tradition. History ''Negus'' is a noun derived from the Ge'ez Semitic root , meaning "to reign". The title Negus literally translated to Basileus (Greek language, Greek: βασιλεύς) in Ancient Greek, which was seen many times on Aksumite currency. The title has subsequently been used to translate the word "king" or "emperor" in Bible, Biblical and other literature. In more recent times, it was used as an honorific title bestowed on governors of the most important provinces (kingdoms): Gojjam, Begemder, Wello, Tigray Province, Tigray and the seaward kingdom, (where the variation Bahri Negasi (Sea King), was the title of the ruler of present-day central Eri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |