|
Mudrarakshasa
The Mudrarakshasa (मुद्राराक्षस, IAST: ''Mudrārākṣasa'', ) is a Sanskrit-language play by Vishakhadatta that narrates the ascent of the king Chandragupta Maurya ( BCE) to power in India. The play is an example of creative writing, but not entirely fictional. It is dated variously from the late 4th century to the 8th century CE. Characters *Chandragupta Maurya, one of the protagonists *Chanakya, one of the protagonists *Rakshasa, the main antagonist *Malayketu, the son of Parvataka and one of the henchmen * Parvatak, a greedy king who firstly supported Chandragupta but later changed his preference to Dhana Nanda * Vaidhorak * Durdhara, wife of Chandragupta Maurya *Bhadraketu *Chandandasa *Jeevsidhhi Adaptations There is a Tamil version based on the Sanskrit play and Keshavlal Dhruv translated the original into Gujarati as ''Mel ni Mudrika'' (1889). There is a Kannada version of the play ''Mudramanjusha'' written by Kempunarayana. The later e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya or Vishnugupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise, the ''Arthashastra'', a text dated to roughly between the fourth century BCE and the third century CE. As such, he is considered the pioneer of the field of political science and economics in India, and his work is thought of as an important precursor to classical economics.Waldauer, C., Zahka, W.J. and Pal, S. 1996Kauṭilya's Arthashastra: A neglected precursor to classical economics ''Indian Economic Review'', Vol. XXXI, No. 1, pp. 101–108. His works were lost near the end of the Gupta Empire in the sixth century CE and not rediscovered until the early 20th century. Around 321 BCE, Chanakya assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta in his rise to power and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakshasa (amatya)
Rakshasa is a character in the ancient Indian Sanskrit Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominalization, nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cul ...-language play ''Mudrarakshasa''. In the play, he holds the post of ''Amatya'' (prime minister) in the Nanda Empire, Nanda and Maurya Empire, Maurya courts of Magadha. Originally a minister of the Nanda king, he escapes during Chandragupta Maurya's conquest of the Nanda empire. He then makes several attempts to overthrow Chandragupta, but each time, he is outsmarted by Chandragupta's advisor Chanakya. Finally, he agrees to give up the resistance, and accepts the post of ''amatya'' in the Maurya court. ''Mudrarakshasa'' biography Rakshasa appears in Vishakhadatta's play Mudrarakshasa. In the ''Mudrarakshasa'', Chanakya feels insulted by the Nanda Empire, Nanda king, and overt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empire that reached its peak under the reign of his grandson, Asoka, from 268 BCE to 231 BCE. The nature of the political formation that existed in Chandragupta's time is not certain. The Mauryan empire was a loose-knit empire. Quote: "The geography of the Mauryan Empire resembled a spider with a small dense body and long spindly legs. The highest echelons of imperial society lived in the inner circle composed of the ruler, his immediate family, other relatives, and close allies, who formed a dynastic core. Outside the core, empire travelled stringy routes dotted with armed cities. Outside the palace, in the capital cities, the highest ranks in the imperial elite were held by military commanders whose active loyalty and success in war determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishakhadatta
Vishakhadatta ( sa, विशाखदत्त) was an Indian Sanskrit poet and playwright. Although Vishakhadatta furnishes the names of his father and grandfather as ''Maharaja'' Bhaskaradatta and ''Maharaja'' Vateshvaradatta in his political drama '' Mudrārākṣasa'', we know little else about him. Only two of his plays, the '' Mudrārākṣasa'' and the '' Devichandraguptam'' are known to us. His period is not certain but he probably flourished in or after the 6th century CE. Some scholars such as A. S. Altekar, K. P. Jayaswal and Sten Konow theorized that Vishakhadatta was a contemporary of Chandragupta II, and lived in late 4th century to early 5th century. But this view has been challenged by other scholars, including Moriz Winternitz and R. C. Majumdar. Mudrarakshasa '' Mudrārākṣasa'' ("Rákshasa's Ring") is Vishakhadatta’s only surviving play, although there exist fragments of another work ascribed to him. Vishakhadatta has stressed upon historical facts in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Classical Drama
The term Indian classical drama refers to the tradition of dramatic literature and performance in ancient India. The roots of drama in the Indian subcontinent can be traced back to the Rigveda (1200-1500 BCE), which contains a number of hymns in the form of dialogues, or even scenes, as well as hymns that make use of other literary forms such as animal fables However, Indian drama begins its classical stage in the 3rd-4th century BCE with the composition of the Natya Shastra, Nātyaśāstra (''lit. The Science of Drama''). Indian classical drama is regarded as the highest achievement of Sanskrit literature. The Buddhist playwright, poet and philosopher Asvaghosa, who composed the ''Buddhacarita'', is considered to have been one of the first Sanskrit dramatists along with Bhāsa, who likely lived in the 2nd century BCE, and is famous for writing two of the only surviving tragedies in Sanskrit drama. Despite its name, a classical Sanskrit drama uses both Sanskrit and Prakrit lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanakya (TV Series)
''Chanakya'' is a 47-part drama epic Indian television historical drama written and directed by Dr. Chandraprakash Dwivedi that was originally telecasted on DD National from 8 September 1991 to 9 August 1992. Produced by Prakash Dwivedi, the series is a fictionalized account of the life and times of 4th century BCE Indian economist, strategist and political theorist Chanakya (also known as Vishnugupta) and is based on events occurring between 340 BCE and 321/20 BCE, starting with Chanakya's boyhood and culminating in the coronation of Chandragupta Maurya. Chandraprakash Dwivedi played the title role of Chanakya. Plot The series is divided into three acts :- * The early life of Vishnugupta in the kingdom of Magadha and the circumstances leading to his self-imposed exile, particularly the persecution (and subsequent death) of his father at the hands of Dhanananda, King of Magadha. * The invasion of northwestern India by Alexander, his death, the rebellion led by native Indian kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porus The Elder
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only mentioned in Greek sources. Credited to have been a legendary warrior with exceptional skills, Porus unsuccessfully fought against Alexander the Great in the Battle of the Hydaspes (326 BC).Fuller, pg 198 In the aftermath, an impressed Alexander not only reinstated him as his satrap but also granted him dominion over lands to the south-east extending until the Hyphasis ( Beas).p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. SpenceArrian Anabasis of Alexander, V.29.2 Porus reportedly died sometime between 321 and 315 BC. Sources The only contemporary information available on Porus and his kingdom is from Greek sources, whereas Indian sources do not mention him. These Greek sources differ considerably among themselves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keshavlal Dhruv
Dewan Bahadur Keshavlal Harshadrai Dhruv (17 October 1859 – 13 March 1938), also spelt as Keshavlal Harshad Dhruva and known by his pen name Vanmali, was a research scholar, philologist, critic, editor of Middle and Old Gujarati works, and translator of Sanskrit classic poetry and plays from India. He was a professor of Gujarati and taught at Gujarat College. He headed several literary organizations. Life Keshavlal was born on 17 October 1859 in Bahiyel near Dehgam in Gujarat, India. He completed matriculation in 1876 and Bachelor of Arts in 1882. He taught at Premchand Raichand Training College in Ahmedabad for a brief period. Later he joined Ranchhodlal Chotalal High School and was appointed a Headmaster in 1908. He retired from there in 1915 and joined Gujarat College as the professor of Gujarati language and literature. He retired from there in 1934. He headed Gujarat Vidya Sabha from 1920 to 1938. His essay on philology at the first Gujarati Sahitya Parishad, held in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
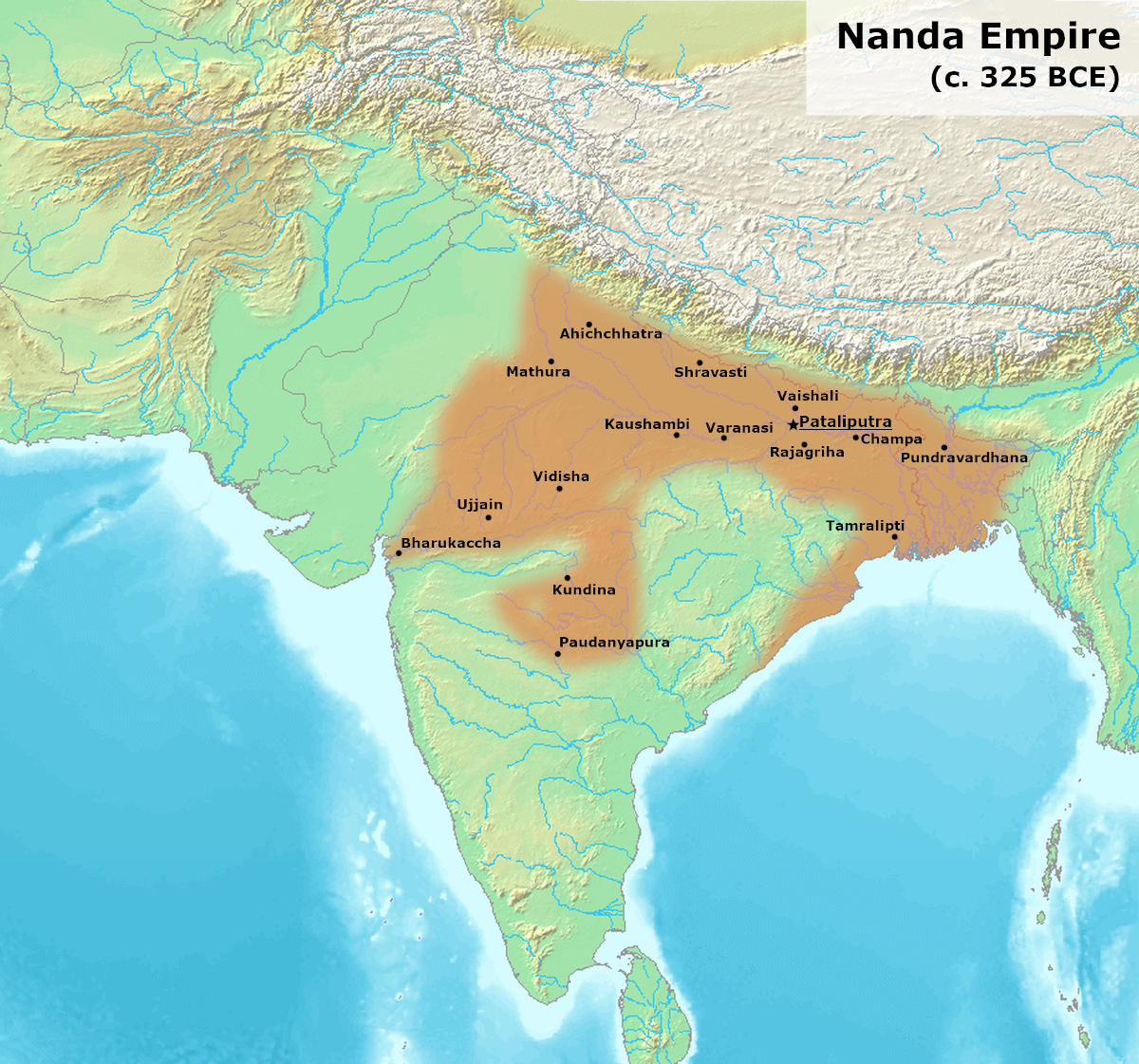
Pataliputra
Pataliputra ( IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the confluence of two rivers, the Son and the Ganges. He shifted his capital from Rajgriha to Patliputra due to the latter's central location in the empire. It became the capital of major powers in ancient India, such as the Shishunaga Empire (c. 413–345 BCE), Nanda Empire (c. 460 or 420–325 BCE), the Maurya Empire (c. 320–180 BCE), the Gupta Empire (c. 320–550 CE), and the Pala Empire (c. 750–1200 CE). During the Maurya period (see below), it became one of the largest cities in the world. As per the Greek diplomat, traveler and historian Megasthenes, during the Mauryan Empire (c. 320–180 BCE) it was among the first cities in the world to have a highly efficient form of local self government. Afterwards, Sher Shah S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motilal Banarsidass
Motilal Banarsidass Publishing House (MLBD) is an Indian academic publishing house, founded in Delhi, India in 1903. It publishes and distributes serials, monographs, and scholarly publications on Asian religions, Buddhology, Indology, Eastern philosophy, history, culture, arts, architecture, archaeology, language, literature, linguistics, musicology, mysticism, yoga, tantra, occult, medicine, astronomy, and astrology. Amongst its publications are the 100 volumes of the Mahapuranas; the 50 volumes of the '' Sacred Books of the East'', edited by Max Müller; ''Bibliotheca Buddhica'' (30 volumes in 32 pts); Ramcharitmanas with Hindi and English translations; the Manusmriti in 10 volumes and the Sanskrit lexicon; and the 7 volumes of ''Encyclopedia of Indian Philosophies''. It also brings out books based on research and study conducted at organizations such as the Indian Council of Historical Research (ICHR), Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA), and Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plays Adapted Into Films
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Depictions Of Indian Men
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |