|
Mucoromycota
Mucoromycotina is a subphylum of uncertain placement in Fungi. It was considered part of the phylum Zygomycota, but recent phylogenetic studies have shown that it was polyphyletic and thus split into several groups, it is now thought to be a paraphyletic grouping. Mucoromycotina is currently composed of 3 orders, 61 genera, and 325 species. Some common characteristics seen throughout the species include: development of coenocytic mycelium, saprotrophic lifestyles, and filamentous. With the treatment of Tedersoo et al. 2018, Mucoromycotina is the only subphylum under Mucoromycota. It includes a diverse group of various molds, including the common bread molds ''Mucor'' and ''Rhizopus''. The other treatment of Mucoromycota is equivalent to current Mucoromyceta. History Zygomycete fungi were originally only ascribed to the phylum Zygomycota. Such classifications were based on physiological characteristics with little genetic support. A genetic study of Zygomycete fungi performed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucoromyceta
Mucoromyceta is a subkingdom of fungi which includes the divisions Calcarisporiellomycota, Glomeromycota, Mortierellomycota and Mucoromycota. This enormous group includes almost all molds. Sources published prior to Tedersoo et al. 2018 refer to this taxon as a phylum Mucoromycota, with three subphyla. In a 2016 study using this older treatement of "Mucoromycota" equivalent to current Mucoromyceta, the group appears as sister to Dikarya. Informally known as zygomycetes I, Mucoromyceta includes Mucoromycotina, Mortierellomycotina, and Glomeromycotina, and consists of mainly mycorrhizal fungi, root endophytes, and plant decomposers. Mucoromycotina and Glomeromycotina can form mycorrhiza-like relationships with nonvascular plants. Mucoromyceta contain multiple mycorrhizal lineages, root endophytes, and decomposers of plant-based carbon sources. Mucoromycotina species known as mycoparasites, or putative parasites of arthropods are like saprobes. When Mucoromyceta infect ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus Phyla
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi'' or ''Eumycete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former phylum, division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two Phylum, phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycotina, Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocyte, coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic. Etymology The name ''Zygomycota'' refers to the zygosporangium, zygosporangia characteristically formed by the members of this clade, in which resistant spherical Zygospore, spores are formed during sexual reproduction. ''Zygos'' is Greek language, Greek for "joining" or "a yoke", referring to the fusion of two hyphae, hyphal strands which produces t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kickxellomycotina
Kickxellomycotina is a fungus grouping in the subkingdom of Zoopagomyceta . The name was changed from "Harpellomycotina", because "Kickxellomycotina" had an older stem. It came from the genus '' Kickxella'', named after Jean Kickx. Orders include Asellariales, Kickxellales, Dimargaritales, and Harpellales. Taxonomy Taxonomy based on the work of Wijayawardene et al. 2019. Subphylum Kickxellomycotina Benny 2007 arpellomycotina Doweld 2014* Class Dimargaritomycetes Tedersoo et al. 2018 ** Order Ramicandelaberales Doweld 2014 *** Family Ramicandelaberaceae Doweld 2014 ** Order Dimargaritales Benjamin 1979 *** Family Spinaliaceae Doweld 2014 *** Family Dimargaritaceae Benjamin 1959 * Class Kickxellomycetes Tedersoo et al. 2018 ** Order Barbatosporales Doweld 2014 *** Family Barbatosporaceae Doweld 2014 ** Order Spiromycetales Doweld 2014 *** Family Spiromycetaceae Doweld 2014 ** Order Orphellales Valle et al. 2018 *** Family Orphellaceae Doweld 2014 ** Order Kic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
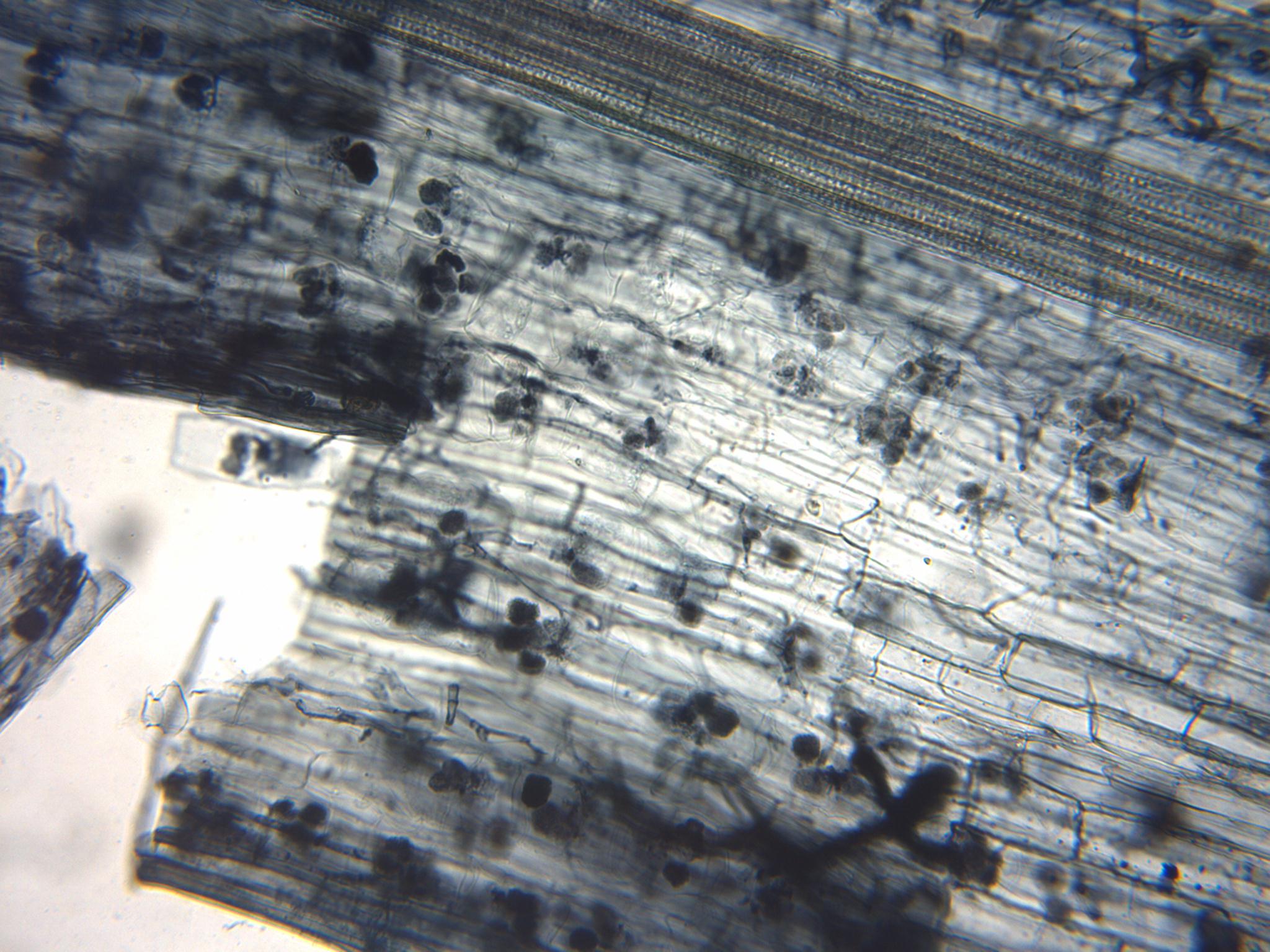
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of endomycorrhiza along with ericoid mycorrhiza and orchid mycorrhiza (not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza). They are characterized by the formation of unique tree-like structures, the arbuscules. In addition, globular storage structures called vesicles are often encountered. Arbuscular mycorrhizae are formed by fungi in the subphylum Glomeromycotina. This subphylum, along with the Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina, form the phylum Mucoromycota, a sister clade of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi. AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota (often referred to as glomeromycetes, as they include only one class, Glomeromycetes) are one of eight currently recognized division (mycology), divisions within the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas (AMs) with the thalli of bryophytes and the roots of vascular plant, vascular land plants. Not all species have been shown to form AMs, and one, ''Geosiphon pyriformis'', is known not to do so. Instead, it forms an endocytobiotic association with ''Nostoc'' cyanobacterium, cyanobacteria. The majority of evidence shows that the Glomeromycota are dependent on land plants (''Nostoc'' in the case of ''Geosiphon'') for carbon and energy, but there is recent circumstantial evidence that some species may be able to lead an independent existence. The arbuscular mycorrhizal species are terrestrial and widely distributed in soils worldwide where they form symbioses with the roots of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomophthoromycota
Entomophthoromycota is a division of kingdom fungi. In 2007, it was placed at the taxonomic rank of subphylum in the most recent revision of the entire fungus kingdom. In 2012, it was raised to the rank of phylum as "Entomophthoromycota" in a scientific paper by Richard A. Humber 2012. Divided into three classes and six families ( Ancylistaceae, Basidiobolaceae, Completoriaceae, Entomophthoraceae, Meristacraceae, and Neozygitaceae), it contains over 250 species that are mostly arthropod pathogens or soil- and litter-borne saprobes. Taxonomy Circumscribed by mycologist Richard Humber in 2012, it contains species formerly classified in the division Zygomycota. Humber's reorganization divides the division into three classes while retaining the previously defined family structure: Division Entomophthoromycota Humber 2012 ntomophthoromycotina Humber 2007:Class Neozygitomycetes Humber 2012 ::Order Neozygitales Humber 2012 :::Family Neozygitaceae Ben Ze’ev, Kenneth & Uzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectomycorrhizal
An ectomycorrhiza (from Greek ἐκτός ', "outside", μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; ectomycorrhizas or ectomycorrhizae, abbreviated EcM) is a form of symbiotic relationship that occurs between a fungal symbiont, or mycobiont, and the roots of various plant species. The mycobiont is often from the phyla Basidiomycota and Ascomycota, and more rarely from the Zygomycota. Ectomycorrhizas form on the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pine and rose families. Research on ectomycorrhizas is increasingly important in areas such as ecosystem management and restoration, forestry and agriculture. Unlike other mycorrhizal relationships, such as arbuscular mycorrhiza and ericoid mycorrhiza, ectomycorrhizal fungi do not penetrate their host's cell walls. Instead they form an entirely intercellular interface known as the Hartig net, consisting of highly branched hyphae forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is normally mutualistic. In particular species, or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus in the form of sugars or lipids, while the fungus supplies the plant with water and mineral nutrients, such as phosphorus, taken from the soil. Myco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprotrophic Nutrition
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (e.g. '' Mucor'') and with soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes. - "The word saprophyte and its derivatives, implying that a fungus is a plant, can be replaced by saprobe (σαπρός + βίος), which is without such implication." Saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( ''sapro-'' 'rotten material' + ''-phyte'' 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or of other plants. In fungi, the saprotrophic process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: agarics, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and '' Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |