|
Mubarizun
The Mubarizun (, "duelists", or "champions") formed a special unit of the Rashidun army during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Mubarizun were a recognized part of the Muslim army with the purpose of engaging enemy champions in single combat. In Arab, Byzantine, and Sassanian warfare, battles usually began with duels between the champion warriors of the opposing armies.Nicolle, 1994, p. 36. The Muslim army would typically begin battle with its soldiers first equipping their armor, assembling their units to their positions and lastly dispatching the Mubarizun. Mubarizun fighters were instructed to refrain from pursuing any defeated enemy champions more than two-thirds of the way to the enemy lines to avoid the risk of being cut off. After the conclusion of the dueling phase, the army would launch its general advance. List of notable Mubarizun *Ali ibn Abi Talib *Hamza ibn Abd al-Muttalib * Dirar ibn al-Azwar *Al-Qa'qa' ibn Amr al-Tamimi * Asim ibn 'Amr al-Tamimi * Abd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Rahman Ibn Abu Bakr
ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn Abu Bakr (; –675),Siddiq-e-Akbar Hazrat Abu Bakr by prof. Masud ul Hassan Printed and published by A. Salam, Ferozsons Ltd 60, Shahrah-e-Quaid-e-Azam, Lahore was an Arab Muslim military commander in the service of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and the Rashidun caliphs Abu Bakr (), and Umar (). His mother was Umm Ruman and he was the full brother of Aisha. Unlike the rest of his family, including his father Abu Bakr and sister Aisha, he did not convert to Islam until the Treaty of Hudaybiyah in 628. Four generations of Abd al-Rahman's family had the distinction of being the companions (sahaba) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, namely Abd al-Rahman, his father Abu Bakr ''As-Siddiq'', his grandfather Uthman Abu Quhafa and his son Abu Atiq Muhammad. It was believed that no other family held this distinction. Biography While still a non-Muslim, Abd al-Rahman fought on the side of Quraish in the Battles of Badr and Uhud. In the Battle of Badr, he had an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Between Ali Ibn Abi Talib And Amr Ben Wad Near Medina
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict between multiple combatants with the intent to harm the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is resorted to either as a method of self-defense or to impose one's will upon others. An instance of combat can be a standalone confrontation or part of a wider conflict, and its scale can range from a fight between individuals to a war between organized groups. Combat may also be benign and recreational, as in the cases of combat sports and mock combat. Combat may comply with, or be in violation of, local or international laws regarding conflict. Examples of rules include the Geneva Conventions (covering the treatment of people in war), medieval chivalry, the Marquess of Queensberry Rules (covering boxing), and the individual rulesets of various combat sports. Hand-to-hand combat Hand-to-hand combat (melee) is combat at very close range, attacking the opponent with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qa'qa' Ibn Amr Al-Tamimi
Al-Qaʿqāʿ ibn ʿAmr ibn Mālik Al-Tamīmī () was an Arab Muslim commander and general in the Rashidun army who belonged to the tribe of Banu Tamim. He and his tribe converted to Islam possibly during the time of Ahnaf ibn Qais. He is known as a successful military commander who took part in two important victorious battles in the early Muslim Conquest, the Battle of Yarmouk against the Byzantine Empire (commanded by Khalid ibn al-Walid) and the Battle of al-Qadisiyyah against the Sassanian Empire which was led by Sa`d ibn Abi Waqqas. The Caliph Abu Bakr praised him as an equal to eleven thousand men so in return the caliph's successor, caliph Umar, only sent Qaʿqāʿ and a handful of bodyguards in the first wave of reinforcements to Al-Qadissiyah. Life Ridda wars Qa'qa ibn Amr At-tamimi converted along with his tribe, in the Year of the Delegations, 631 CE. But, for a brief period, he and other Tamim joined the force of the false prophetess Sajah bint al-Harith before she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From The Rashidun Caliphate
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
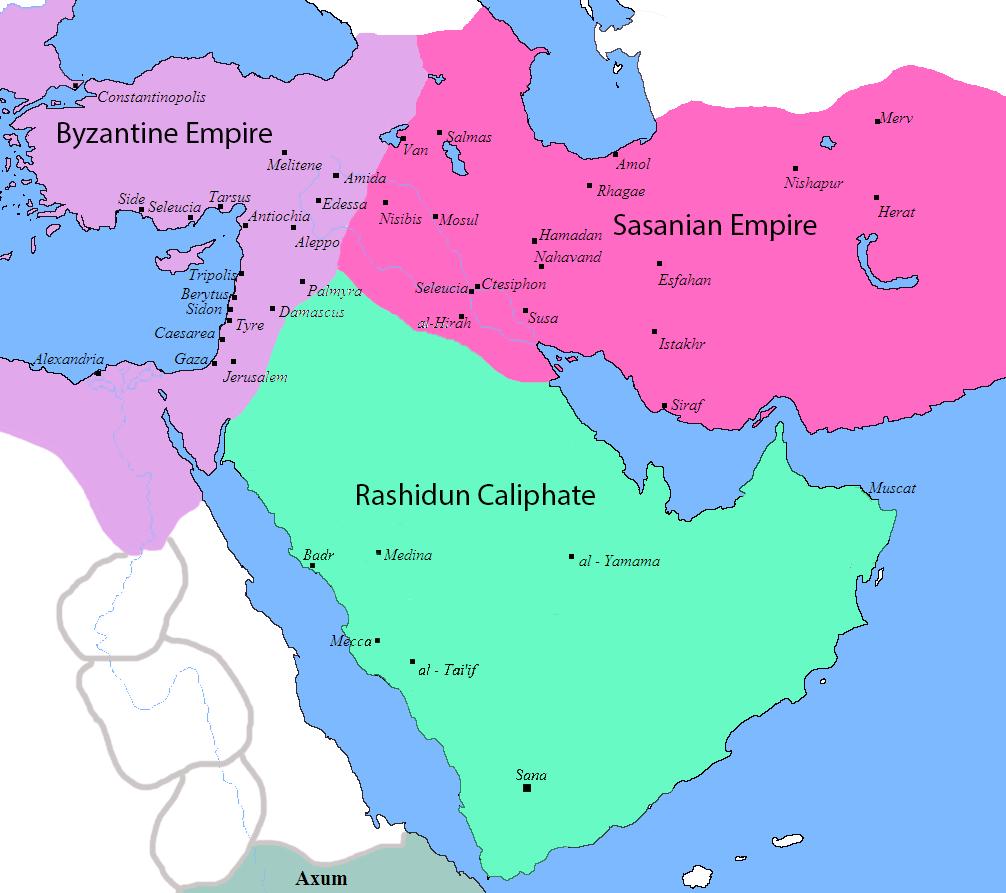
Muslim Conquest Of Syria
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and developed into the provincial region of Bilad al-Sham. Clashes between the Arabs and Byzantines on the southern Levantine borders of the Byzantine Empire had occurred during the lifetime of Muhammad, with the Battle of Muʿtah in 629 CE. However, the actual conquest did not begin until 634, two years after Muhammad's death. It was led by the first two Rashidun caliphs who succeeded Muhammad: Abu Bakr and Umar ibn al-Khattab. During this time, Khalid ibn al-Walid was the most important leader of the Rashidun army. It was the first time since the collapse of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in 539 BCE that the region was ruled again by Semitic-speaking people, after centuries of Persian (Achaemenid Empire), and then Roman-Greek (Macedonian Empire, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mard O Mard
''Mard ō mard'' (Middle Persian; literally "man to man") was an ancient Iranian tradition of single combat, the Sasanian Empire being most known for using it. During a battle, the Sasanian troops would use taunts and war cries to provoke the enemy into a single duel with a Sasanian champion. The tradition meant much to the Sasanians—in 421, during Bahram V's war against the Romans in 421–422, Ardazanes, a member of the " Immortals", was in a single duel killed by the Roman ''comes'' Areobindus, which contributed to Bahram V's acceptance of the defeat in the war and making peace with the Romans. In Sasanian art several ''mard o mard'' depictions are preserved in rock-reliefs in Naqsh-e Rostam and in a cameo of Shapur I and Valerian. Single combats have been narrated in ''Shahnameh'' ("The Book of Kings") of Ferdowsi, a notable example being those of the story of ''Davazdah Rokh Davāzdah Rokh () (Twelve combats) is a story in Shahnameh. This relatively long story (almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zubayr Ibn Al-Awwam
Al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam ibn Khuwaylid al-Asadi (; ) was an Arab Muslim commander in the service of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the caliphs Abu Bakr () and Umar () who played a leading role in the Ridda Wars, Ridda wars against rebel tribes in Arabia in 632–633 and later participated in early Muslim conquests of Muslim conquest of Persia, Sasanid Persia in 633–634, Muslim conquest of the Levant, Byzantine Syria in 634–638, and the Exarchate of Africa in 639–643. An early convert to Islam, Zubayr was a commander in the Battle of Badr in 624, in which the latter was instrumental in defeating the opponent forces of the Quraysh. He participated in almost all of the early Muslim battles and expeditions under Muhammad. In the Battle of the Trench, due to his military service, Muhammad bestowed the title ''Hawari Rasul Allah'' ('Disciple of Messenger of God') upon him. After Muhammad's demise, Zubayr was appointed as a commander, in the Ridda Wars, by caliph Abu Bakr. He was in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Bara' Ibn Malik
Al-Barāʾ ibn Mālik al-Anṣārī (; died ) was one of the Sahaba (companions of Muhammad), an Ansar belonging to the Banū al-Najjār branch of the Banu Khazraj. He was the brother of Anas ibn Malik. He was most known for his participations in the Ridda Wars against Musaylima and Muslim conquest of Persia. He died around 641-642 of wounds he received during his siege in Shushtar against the Sasanian Empire. Al-Barā has become a role model of conducting Jihad by later era Islamic communities. Biography Al-Bara' was from Banu Ghanm clan, a sub-branch of Banū al-Najjār branch belonging to the Banu Khazraj tribe. Al-Dhahabi recorded that his full Nisba (onomastics) lineage is Al-Barā son of Malik from the subclan of Al-Nadir ibn Damdam ibn Yazid ibn Haram ibn Jundub ibn 'Amr ibn Ghanam ibn 'Adi of the Banu Najjar. After Muhammad migrated to Medina, al-Baraa' worked as a camel chanter and lead of men's caravan of camels whenever Muhammad and his companions goes for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 632 until his death in 634. Abu Bakr was granted the honorific title ''al-Ṣiddīq'' (lit. the Veracious) by Muhammad, a designation that continues to be used by Sunni Muslims to this day. Born to Abu Quhafa and Umm al-Khayr of the Banu Taym, Abu Bakr was amongst the Early Muslims, earliest converts to Islam and propagated dawah to the Mushrikites. He was considered the first Da'i, Muslim missionary as several companions of the Prophet, companions of Muhammad converted through Abu Bakr. He accompanied Muhammad on his Hegira, migration to Medina and became one of his Haras (unit), bodyguards. Abu Bakr participated in all of List of expeditions of Muhammad, Muhammad's campaigns and served as the first in 631. In the absence of Muha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asim Ibn 'Amr Al-Tamimi
ʿĀṣim ibn ʿAmr ibn Mālik al-Usaydī al-Tamīmī () was a prominent member of Banu Tamim and military leader of Rashidun Caliphate during the rule of Abu Bakr Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ... and Umar. He played an active role during the Muslim conquest of Persia accompanying his older brother Al-Qa'qa' ibn Amr al-Tamimi. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Asim ibn Amr al-Tamimi 7th-century Arab people People of the Muslim conquest of Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirar Ibn Al-Azwar
Dhirarr ibn al-Azwar Al-Asadi () also spelled as Diraar or Dirarr (original name Diraar ibn Malik), was a skilled warrior since before the time of Islam who participated in the Early Muslim conquests and a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Dhiraar was known to his tribe as al-Azwar. Dhiraar was feared by the Byzantine army and was given the nickname ''The barechested Warrior'' or ''The barechested Champion'' for his tendency to fight without armor or upper garments. Diraar mostly known for killing three dozen enemy commanders and champions in the Battle of Ajnadayn, blocking the enemy retreat in the Battle of Yarmouk, and killing more than a hundred soldiers single handedly in the siege of Oxyrhynchus Bahnasa. Diraar was a member of the elite Rashidun cavalry unit and also a dueling specialist of the Rashidun Army operating mostly under the famous general Khalid ibn al-Walid, who trusted him in various tasks during Ridda wars, Muslim conquest of the Levant, Persia, No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
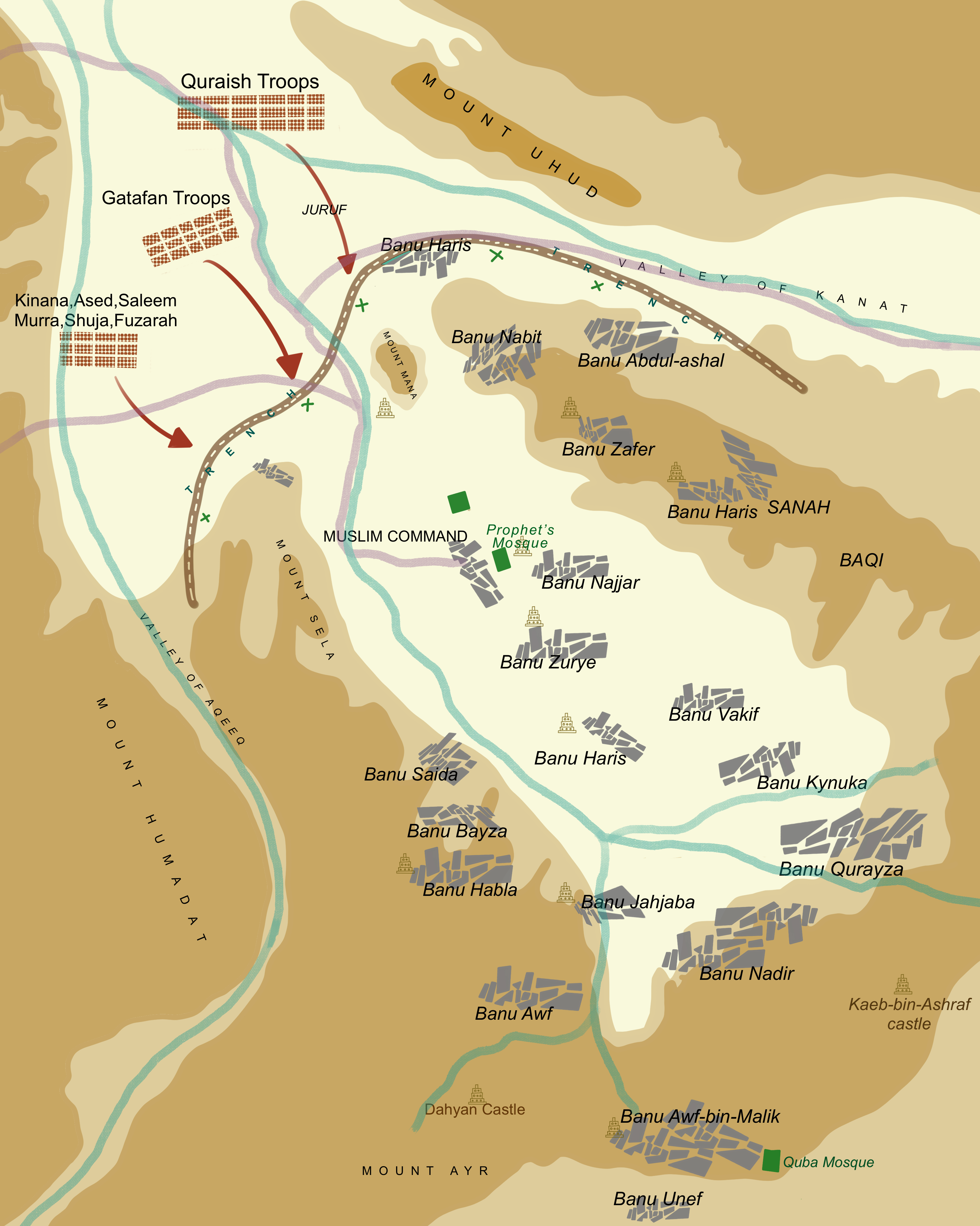
Rashidun Army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, granting them successive victories in their various campaigns. In its time, the Rashidun army was a very powerful and effective force. The three most successful generals of the army were Khalid ibn al-Walid, who Muslim conquest of Persia, conquered Persian Mesopotamia and the Muslim conquest of the Levant, Roman Levant, Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah, who also conquered parts of the Roman Levant, and Amr ibn al-As, who Muslim conquest of Egypt, conquered Roman Egypt. The army was a key component in the Rashidun Caliphate's territorial expansion and served as a medium for the early spread of Islam into the territories it conquered. Historical overview According to Tarikh at Tabari, the nucleus of the early caliphate forces were formed from the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |