|
Mpox In The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Mpox is endemic in western and central Africa, with the majority of cases occurring in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), where the disease is reportable. There, the more virulent Congo basin virus type has been affecting some of the world's poorest and socially excluded communities. Many cases occur sporadically or in small clusters, but large outbreaks also occur. Early cases The world's first case of human mpox was detected in a nine-month old child in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (then Zaire), two years after it reported its last case of smallpox. The onset of their rash was on 24 August. That year, the disease was identified in another four children, including three in Liberia who were playmates. At the time, evidence of the virus was found in non-human primates in Liberia and Sierre Leone. Active surveillance by the World Health Organization (WHO) between 1981 and 1986, identified 338 cases with a human-to-human transmission rate of 28%. Until 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
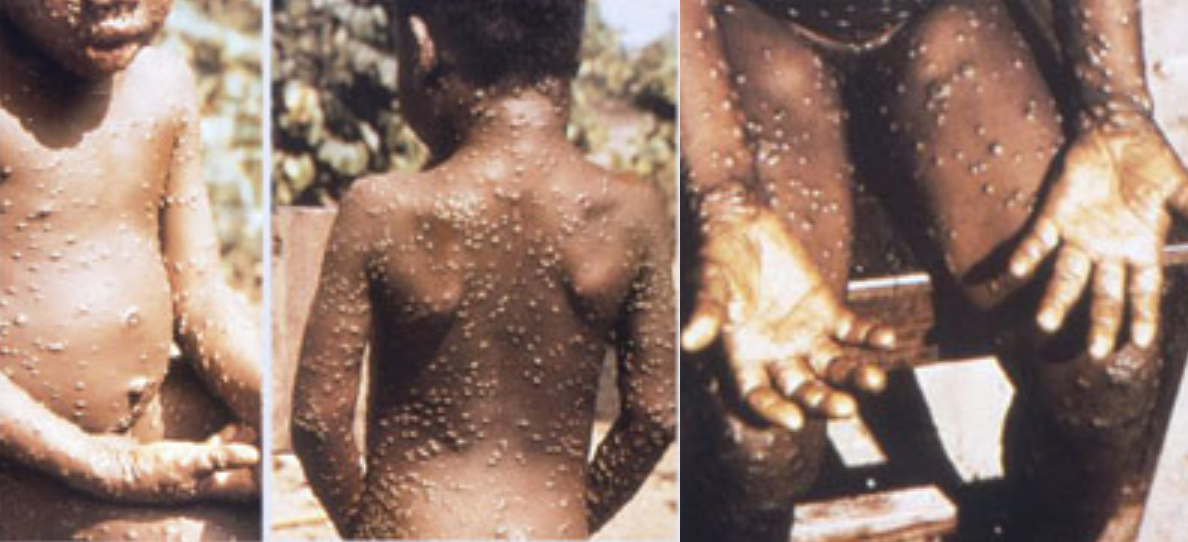
Mpox
Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) is an infectious viral disease that can occur in humans and some other animals. Symptoms include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The illness is usually mild and most of those infected will recover within a few weeks without treatment. The time from exposure to onset of symptoms ranges from five to twenty-one days and symptoms typically last from two to four weeks. Cases may be severe, especially in children, pregnant women or people with suppressed immune systems. The disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, a zoonotic virus in the genus ''Orthopoxvirus''. The variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, is also in this genus. Human-to-human transmission can occur through direct contact with infected skin or body fluids, including sexual contact. People remain infectious from the onset of symptoms until all the lesions have scabbed and healed. It may spread from infected animals by handl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkeypox Virus
''Monkeypox virus'' (MPV, MPXV, or hMPXV) is a species of double-stranded DNA virus that causes monkeypox in humans and other mammals. Monkeypox virus is a zoonotic virus belonging to the '' orthopoxvirus'' genus, making it closely related to the variola (VARV), cowpox (CPX), and vaccinia (VACV) viruses. MPV is oval-shaped with a lipoprotein outer membrane. The genome is approximately 190 kb. The variola and monkeypox virus are both orthopoxviruses, and so the smallpox vaccine is effective against monkeypox if given within 3–5 years before contracting the disease. The clinical presentation of Monkeypox is similar to smallpox, but with a milder rash and lower mortality rate. The virus is transmissible between animals and humans, by direct contact to the lesions or bodily fluids. Monkeypox was given its name after being isolated from monkeys, but the majority of the carriers of this virus are rodents. Variation in virulence of the virus has been observed in isolates from Centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host. In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to cause disease—is determined by its virulence factors. In the specific context of gene for gene systems, often in plants, virulence refers to a pathogen's ability to infect a resistant host. The noun ''virulence'' derives from the adjective ''virulent'', meaning disease severity. The word ''virulent'' derives from the Latin word ''virulentus'', meaning "a poisoned wound" or "full of poison." From an ecological standpoint, virulence is the loss of fitness induced by a parasite upon its host. Virulence can be understood in terms of proximate causes—those specific traits of the pathogen that help make the host ill—and ultimate causes—the evolutionary pressures that lead to virulent traits occurring in a pathogen strain. Virulent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Exclusion
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. It is used across disciplines including education, sociology, psychology, politics and economics. Social exclusion is the process in which individuals are blocked from (or denied full access to) various rights, opportunities and resources that are normally available to members of a different group, and which are fundamental to social integration and observance of human rights within that particular group (e.g., housing, employment, healthcare, civic engagement, democratic participation, and due process). Alienation or disenfranchisement resulting from social exclusion can be connected to a person's social class, race, skin color, religious affiliation, ethnic origin, educational status, childhood relationships, living standards, and or political opinions, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkeypox
Monkeypox (also called mpox by the WHO) is an infectious viral disease that can occur in humans and some other animals. Symptoms include fever, swollen lymph nodes, and a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over. The time from exposure to onset of symptoms ranges from five to twenty-one days. The duration of symptoms is typically two to four weeks. There may be mild symptoms, and it may occur without any symptoms being apparent. The classic presentation of fever and muscle pains, followed by swollen glands, with lesions all at the same stage, has not been found to be common to all outbreaks. Cases may be severe, especially in children, pregnant women or people with suppressed immune systems. The disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, a zoonotic virus in the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, is also in this genus. Of the two types in humans, cladeII (formerly West African clade) causes a less severe disease than the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |