|
Mouse Moth
The mouse moth (''Amphipyra tragopoginis'') is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is a widespread species with a Holarctic distribution. Distribution Europe (except the extreme north, and not occurring in the south of Spain, Sicily, or the Balkans); also in Armenia, Asia Minor, Syria, Iran, Western Siberia, Kashmir (extending thence into Punjab). Recently introduced in Canada and North America. This is a rather drab but distinctive species. The forewings are uniform dark brown with three blackish spots arranged in a triangle. The hindwings are buffish, darker towards the margins. The wingspan is 32–40 mm. The common name derives from the species' habit of scuttling away on foot when disturbed rather than flying. Despite this, it can fly strongly and is attracted to light, sugar and nectar-rich flowers. In the British Isles, the adult is active from July to September. Description Forewing dull brown, dusted with paler scales, varying from pale to blackish brown; su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Alexander Clerck
Carl Alexander Clerck (1709 – 22 July 1765) was a Sweden, Swedish entomologist and arachnology, arachnologist. Clerck came from a family in the petty Swedish nobility, nobility and entered the University of Uppsala in 1726. Little is known of his studies; although a contemporary of Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, it is unknown whether he had any contact with him during his time in Uppsala. His limited means forced him to leave university early and enter into government service, later ending up working in the administration of the City of Stockholm. His interest in natural history appears to have come at a more mature age, influenced by a lecture of Linnaeus he attended in Stockholm in 1739. In the following years he collected and categorized many spiders, published together with more general observations on the morphology and behaviour of spiders, in his ''Svenska Spindlar'' ("Swedish spiders", 1757, also known by its Latin subtitle, ''Aranei Suecici''). He also started the publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
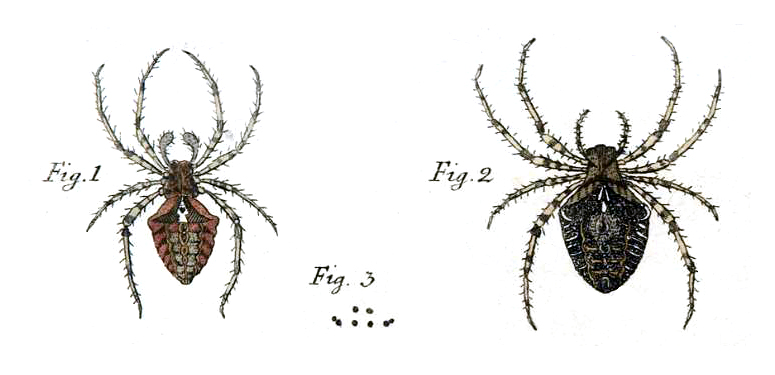
Buckler W The Larvæ Of The British Butterflies And Moths PlateCIII
A buckler (French ''bouclier'' 'shield', from Old French ''bocle, boucle'' 'boss') is a small shield, up to 45 cm (up to 18 in) in diameter, gripped in the fist with a central handle behind the boss. It became more common as a companion weapon in hand-to-hand combat during the Medieval and Renaissance periods. Its size made it poor protection against missile weapons (e.g., arrows) but useful in deflecting the blow of an opponent's weapons, binding their arms, hindering their movements, or punching them. The seminal study of the topic has been undertaken by Herbert Schmidt and has devised the following typology: * Type I: round * Type II: rectangular or trapezoidal * Type III: oval or teardrop shaped with the cross-section of the buckler further refining these types: * Type a: flat * Type b: concave * Type c: convex * Type d: wavy The combination of the two classifiers determines the buckler type. Thus a Type Ia buckler is a round flat buckler; a Type IId buckler is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragaria
''Fragaria'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, commonly known as strawberries for their edible fruits. There are more than 20 described species and many Hybrid plant, hybrids and cultivars. The most common strawberries grown commercially are cultivars of the strawberry, garden strawberry, a hybrid known as ''Fragaria'' × ''ananassa''. Strawberries have a taste that varies by cultivar, and ranges from quite sweet to rather tart. Strawberries are an important commercial fruit crop, widely grown in all temperate regions of the world. Description Strawberries are not Berry (botany), berries in the botanical sense.Esau, K. 1977. ''Anatomy of seed plants''. John Wiley and Sons, New York. The fleshy and edible part of the "fruit" is a receptacle (botany), receptacle, and the parts that are sometimes mistakenly called "seeds" are achenes and therefore the true botanical fruits. Etymology The genus name derives from ("strawberry") and , a suffix used to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
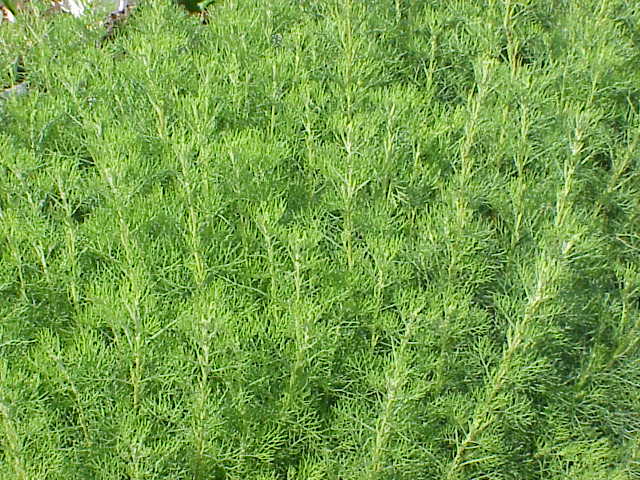
Foeniculum
''Foeniculum '' is a genus of flowering plants in the carrot family. It includes the commonly cultivated fennel, ''Foeniculum vulgare.'' ;Species *'' Foeniculum scoparium'' Quézel - North Africa *'' Foeniculum subinodorum'' Maire, Weiller & Wilczek - North Africa *''Foeniculum vulgare'' Mill. - Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ..., cultivated and naturalized in many regions References {{Authority control Apioideae Taxa named by Philip Miller Apioideae genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilobium
''Epilobium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Onagraceae, containing about 197 species. The genus has a worldwide distribution. It is most prevalent in the subarctic, temperate and subantarctic regions, whereas in the subtropics and tropics ''Epilobium'' species are restricted to the cool montane biomes, such as the New Guinea Highlands. The taxonomy of the genus has varied between different botanists, but the modern trend is to include the previously recognised genera ''Boisduvalia'', '' Chamaenerion'' (previously ''Chamerion''), ''Pyrogennema'' and ''Zauschneria'' within ''Epilobium'' according to Peter H. Raven, who has extensively studied the willowherbs and merges the other segregate genera into ''Epilobium''. Fringed willowherb (''Epilobium ciliatum'') is likely a cryptic species complex; apparently these plants also commonly hybridize with their congeners. Most species are known by the common name willowherbs for their willow-like leaves. Those that were on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crataegus
''Crataegus'' (), commonly called hawthorn, quickthorn, thornapple, Voss, E. G. 1985. ''Michigan Flora: A guide to the identification and occurrence of the native and naturalized seed-plants of the state. Part II: Dicots (Saururaceae–Cornaceae)''. Cranbrook Institute of Science and University of Michigan Herbarium, Ann Arbor, Michigan. May-tree,Graves, Robert. ''The White Goddess: A Historical Grammar of Poetic Myth'', 1948, amended and enlarged 1966, New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. whitethorn, Mayflower or hawberry, is a genus of several hundred species of shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere in Europe, Asia, North Africa and North America. The name "hawthorn" was originally applied to the species native to northern Europe, especially the common hawthorn ''C. monogyna'', and the unmodified name is often so used in Britain and Ireland. The name is now also applied to the entire genus and to the related Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercis Canadensis
''Cercis canadensis'', the eastern redbud, is a large deciduous shrub or small tree, native to eastern North America from southern Michigan south to central Mexico, west to New Mexico. Species thrive as far west as California and as far north as southern Ontario. It is the state tree of Oklahoma. The prevalence of the so-called "Columbus strain" has seen the residents of Columbus, Wisconsin, embrace the plant in their city's identity. Known as the "Redbud City," the town hosts "Redbud Day" annually the Saturday before Mother's Day, organizing a variety of themed events to recognize the tree. Description The eastern redbud typically grows to tall with an spread. It generally has a short, often twisted trunk and spreading branches. A 10-year-old tree will generally be around tall. The bark is dark in color, smooth, later scaly with ridges somewhat apparent, sometimes with maroon patches. The twigs are slender and zigzag, nearly black in color, spotted with lighter lenticels. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanula
''Campanula'' () is the type genus of the Campanulaceae family (biology), family of flowering plants. ''Campanula'' are commonly known as bellflowers and take both their common and scientific names from the bell-shaped flowers—''campanula'' is Latin for "little bell". The genus includes over 500 species and several subspecies, distributed across the temperate and subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with centers of diversity in the Mediterranean region, Balkans, Caucasus and mountains of western Asia. The range also extends into mountains in tropical regions of Asia and Africa. The species include annual plant, annual, biennial plant, biennial and perennial plant, perennial plants, and vary in habit from dwarf arctic and alpine species under 5 cm high, to large Temperateness, temperate grassland and woodland species growing to tall. Description image:Campanula flower parts text.jpg, upright=1.35, thumbThe leaf, leaves are alternate and often vary in shape on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisia (genus)
''Artemisia'' ( ) is a large, diverse genus of plants belonging to the daisy family, Asteraceae, with almost 500 species. Common names for various species in the genus include mugwort, wormwood, and sagebrush. Some botanists split the genus into several genera, but DNA analysis does not support the maintenance of the genera ''Crossostephium'', ''Filifolium'', ''Neopallasia'', ''Seriphidium'', and ''Sphaeromeria''; three other segregate genera—''Stilnolepis'', ''Elachanthemum'', and ''Kaschgaria''—are maintained by this evidence. Occasionally, some of the species are called sages, causing confusion with the ''Salvia'' sages in the family Lamiaceae. ''Artemisia'' comprises hardy herbaceous plants and shrubs, which are known for the powerful chemical constituents in their essential oils. ''Artemisia'' species grow in temperate climates of both hemispheres, usually in dry or semiarid habitats. Notable species include '' A. vulgaris'' (common mugwort), '' A. triden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquilegia
''Aquilegia'', commonly known as columbines, is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae (buttercups). The genus includes between 80 and 400 taxa (described species and subspecies) with natural Species distribution, ranges across the Northern Hemisphere. Natural and Introduced species, introduced populations of ''Aquilegia'' exist on all continents but Antarctica. Known for their high physical variability and ease of Hybridization in perennial plants, hybridization, columbines are popular garden plants and have been used to create many Cultivar, cultivated varieties. ''Aquilegia'' typically possess stiff stems and leaves divide into multiple Leaflet (botany), leaflets. Columbines often have colorful flowers with five sepals and five petals. The petals generally feature nectar spurs which differ in lengths between species. In North America, morphological variations in spurs evolved to suit different pollinators. Some species and varieties of columbines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocynum
''Apocynum'', commonly known as dogbane or Indian hemp, is a small genus of the flowering plant family Apocynaceae. Its name comes from Ancient Greek , from ''apo-'' "away" and ''kyōn'' "dog", referring to dogbane ('' Cionura erecta''), which was used to poison dogs. The genus is native to North America, temperate Asia, and southeastern Europe. ''Apocynum'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species, including the queen butterfly and the mouse moth. Uses ''Apocynum cannabinum'' is used as a source of fiber by Native Americans. '' Apocynum venetum'' () is used as an herbal tea in China. Dogbane contains cymarin, a cardiotonic agent formerly used to treat cardiac arrhythmia in humans. Species Almost 300 names have been proposed in the genus for species, subspecies, and forms. , only the following five species and hybrids are currently recognized, with several subspecies and varieties accepted for '' A. androsaemifolium'' and '' A. venetum'' (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthriscus
''Anthriscus'' (chervils) is a common plant genus of the family Apiaceae, growing in Europe and temperate parts of Asia. It comprises 15 species. The genus grows in meadows and verges on slightly wet porous soils. One species, '' Anthriscus cerefolium'' is cultivated and used in the kitchen to flavor foods. ''Anthriscus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the mouse moth (recorded on cow parsley). The hollow stem is erect and branched, ending in compound umbels of small white or greenish flowers. The leaves are bipinnate or tripinnate. Species of ''Anthriscus'' * '' Anthriscus africana'' Hook. f. (Africa) * '' Anthriscus caucalis'' M. Bieb. - Bur chervil (native to Africa and Eurasia, introduced elsewhere) * '' Anthriscus cerefolium'' (L.) Hoffm. - Garden chervil, French parsley (native to Eurasia, introduced elsewhere) * '' Anthriscus fumarioides'' (Waldst. & Kit.) Spreng. (Albania, Greece, Italy, Yugoslavia) * '' Anthriscus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |