|
Mount Takahe
Mount Takahe is a snow-covered shield volcano in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, from the Amundsen Sea. It is a mountain with parasitic vents and a caldera up to wide. Most of the volcano is formed by trachytic lava flows, but hyaloclastite is also found. Snow, ice, and glaciers cover most of Mount Takahe. With a volume of , it is a massive volcano; the parts of the edifice that are buried underneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet are probably even larger. It is part of the West Antarctic Rift System along with 18 other known volcanoes. The volcano was active in the Quaternary period. Radiometric dating has yielded ages of up to 300,000years for its rocks, and it reached its present height about 200,000years ago. Several tephra layers encountered in ice cores at Mount Waesche and Byrd Station have been attributed to Mount Takahe, although some of them were later linked to eruptions of Mount Berlin instead. The tephra layers were formed by explosive or phreatomagmatic eruptions. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Antarctica ...
This is a list of volcanoes in Antarctica. Table A 2017 study claimed to have found 138 volcanoes, of which 91 were previously unknown. Some volcanoes are entirely under the ice sheet. Unconfirmed volcanoes are not included in the table below. See also * Geology of Antarctica * Lists of volcanoes References Bibliography * Volcano World Web site {{Antarctica Antarctica Volcanoes A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which Paleoecology, paleoenvironmental or Archaeology, archaeological records can be placed. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
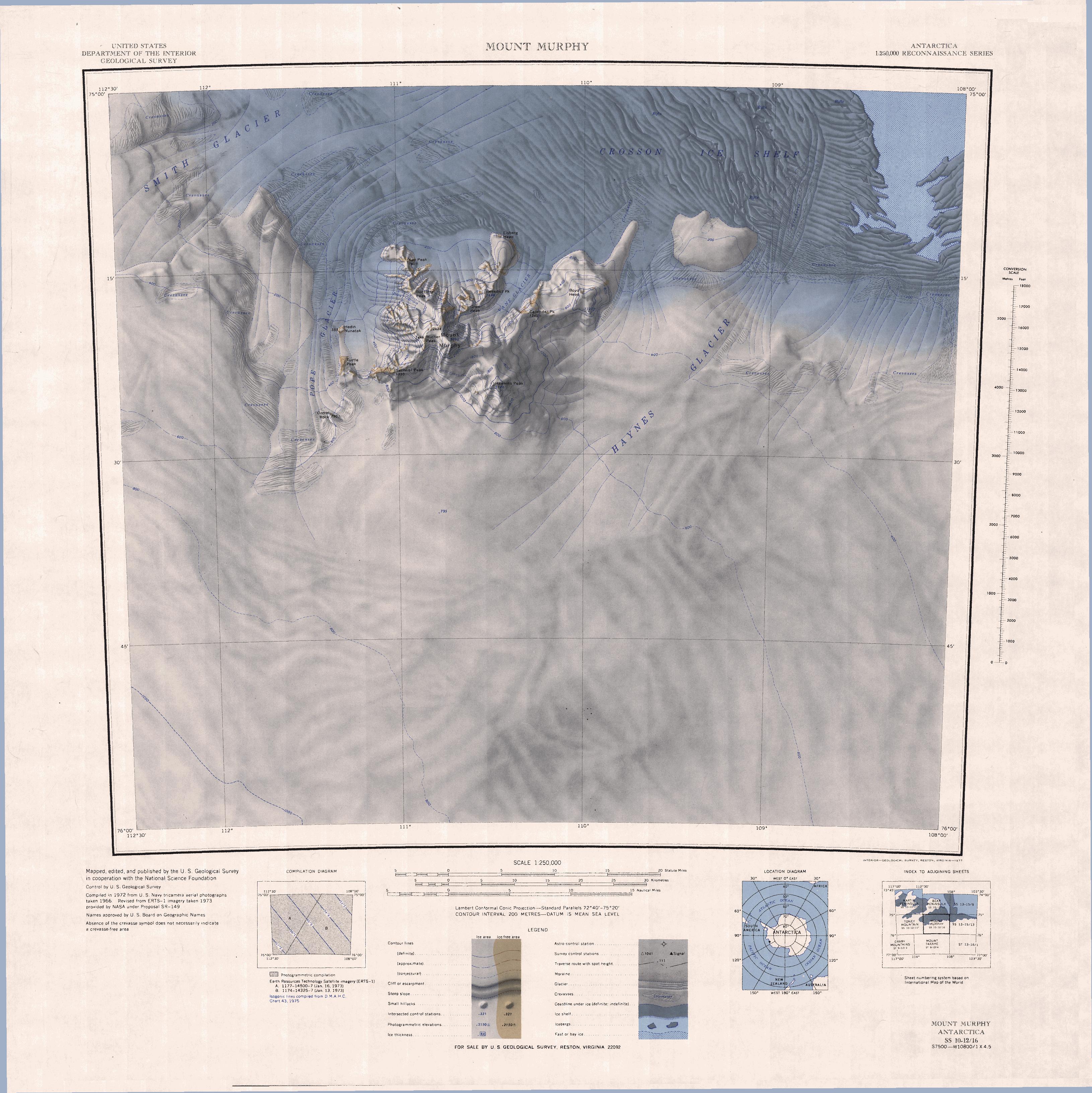
Mount Murphy
Mount Murphy () is a snow-covered mountain with steep, rocky slopes rising to https://worldribus.org/west-antarctica-ranges/ in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. It is directly south of Bear Peninsula and is bounded by Smith Glacier, Pope Glacier, and Haynes Glacier. Volcanic activity began in the Miocene with the eruption of basaltic and trachytic lava. Volcanism on the slopes of the volcano resumed much later during the Pleistocene, with a parasitic cone having been K–Ar dated to 0.9 million years old. Location The Mount Murphy massif lies on the south shore of the Crosson Ice Shelf, which extends into the Amundsen Sea on the Walgreen Coast of Marie Byrd Land. The Haynes Glacier flows into the ice shelf to its east, and the Pope Glacier flows into the ice shelf to the west. The Roos Glacier and Vane Glacier flow from the massif towards the ice shelf. Features, clockwise from the northwest, include Kay Peak, Buettner Peak, Grew Peak, Benedict Peak, Eisberg Head, Callender Peak, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear Peninsula
Bear Peninsula () is a peninsula about long and wide which is ice-covered except for several isolated rock bluffs and outcrops along its margins, lying east of Martin Peninsula on Walgreen Coast, Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Location The Bear Peninsula extends in a northeast direction from the Walgreen Coast of Marie Byrd Land between the Dotson Ice Shelf to the west and Smith Glacier and the Crosson Ice Shelf to the southeast. The north of the peninsula extends into the Amundsen Sea. The Thwaites Iceberg Tongue is to the northeast. Western features include, from south to north, Boschert Glacier, Hayden Peak, Gerrish Peaks, True Glacier, Hunt Bluff, Mount Bodziony, Zuniga Glacier, Jeffrey Head, Brush Glacier, Webster Pass, Rogers Spur and Sorenson Glacier. Northern features include, from west to east, Moore Dome, Koloc Point, Park Glacier, Harmon Bay, Gurnon Peninsula, Garwood Point and Hummer Point. Eastern features include, from north to south, Bunner Glacier, Hamilt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakutis Coast
The Getz Ice Shelf () is an ice shelf over long and from wide, bordering the Hobbs Coast and Bakutis Coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, between the McDonald Heights and Martin Peninsula. Several large islands are partially or wholly embedded in the ice shelf. Location File:C74126s1 Ant.Dean Island Getz Ice Shelf.jpg, Western ice shelf Shepard to Carney islands File:C74112s5 Ant.Map Martin Peninsula context.jpg, Eastern ice shelf Carney Island to Martin Peninsula The Getz Ice Shelf extends along the north shore of Marie Byrd Land, from Hanessian Foreland and McDonald Heights in the west to Cape Herlacher on the Martin Peninsula to the east. The western section lies along the Hobbs Coast, while the section east of Dean Island lies along the full length of the Bakutis Coast. In the west the ice sheet is fed by glaciers that include, from west to east, Johnson Glacier, Venzke Glacier, Berry Glacier and DeVicq Glacier. Discovery and name The ice shelf westward of Siple Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takahē
The South Island takahē (''Porphyrio hochstetteri'') is a Flightless bird, flightless swamphen indigenous to New Zealand and the largest living member of the Rail (bird), rail family. It is often known by the abbreviated name takahē, which it shares with the Holocene extinction, recently extinct North Island takahē. The two takahē species are also known as notornis. Takahē were hunted extensively by both early European settlers and Māori people, Māori, and takahē bones have been found in middens in the South Island. Fossil remains have also been found across the South Island. They were not named and described by Europeans until 1847, and then only from fossil bones. In 1850 a living bird was captured, and three more collected in the 19th century. After another bird was captured in 1898, and no more were to be found, the species was presumed extinct. Fifty years later, however, after a carefully planned search, South Island takahē were dramatically rediscovered in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene is an interglacial period within the ongoing Ice age, glacial cycles of the Quaternary, and is equivalent to Marine isotope stages, Marine Isotope Stage 1. The Holocene correlates with the last maximum axial tilt towards the Sun of the Earth#Axial tilt and seasons, Earth's obliquity. The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth, and impacts of the human species worldwide, including Recorded history, all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban culture, urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global significance for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone Hole
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar regions. The latter phenomenon is referred to as the #Ozone hole and its causes, ozone hole. There are also springtime polar tropospheric ozone depletion events in addition to these stratospheric events. The main causes of ozone depletion and the ozone hole are manufactured chemicals, especially manufactured halocarbon refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and foam-blowing agents (chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), HCFCs, Haloalkanes, halons), referred to as ''ozone-depleting substances'' (ODS). These compounds are transported into the stratosphere by Turbulence, turbulent mixing after being emitted from the surface, mixing much faster than the molecules can settle. Once in the stratosphere, they release atoms from the halogen group through photod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phreatomagmatic
Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) clasts.Heiken, G. & Wohletz, K. 1985. Volcanic Ash. University of California Press, Berkeley It is common for a large explosive eruption to have magmatic and phreatomagmatic components. Mechanisms Several competing theories exist as to the exact mechanism of ash formation. The most common is the theory of explosive thermal contraction of particles under rapid cooling from contact with water. In many cases the water is supplied by the sea, such as in the Surtsey eruption. In other cases the water may be present in a lake or caldera-lake, as at Santorini, where the phreatomagmatic component of the Minoan eruption was a result of both a lake and later the sea. There have also been examples of interaction between magma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a Viscosity, viscous magma such that expelled lava violently froths into volcanic ash when pressure is suddenly lowered at the vent. Sometimes a lava plug will block the conduit to the summit, and when this occurs, eruptions are more violent. Explosive eruptions can expel as much as per second of rocks, dust, gas and Pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic material, averaged over the duration of eruption, that travels at several hundred meters per second as high as into the atmosphere. This cloud may subsequently collapse, creating a fast-moving pyroclastic flow of hot volcanic matter. Physics Viscous magmas cool beneath the surface before they erupt. As they do this, bubbles exsolve from the magma. Because the magma is viscous, the bubbles remain trapped in the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Berlin
Mount Berlin is a glacier-covered volcano in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, from the Amundsen Sea. It is a roughly mountain with parasitic vents that consists of two coalesced volcanoes: Berlin proper with the Berlin Crater and Merrem Peak with a crater, away from Berlin. The summit of the volcano is above sea level. It has a volume of and rises from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. It is part of the Marie Byrd Land Volcanic Province. Trachyte is the dominant volcanic rock and occurs in the form of lava flows and pyroclastic rocks. The volcano began erupting during the Pliocene and was active into the late Pleistocene and the Holocene. Several tephra layers encountered in ice cores all over Antarctica – but in particular at Mount Moulton – have been linked to Mount Berlin, which is the most important source of such tephras in the region. The tephra layers were formed by explosive eruptions that generated high eruption columns. Presently, fumarolic activity occurs at Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |