|
Mount Kanaga
Kanaga Volcano, or Mount Kanaga, is a stratovolcano at the northern tip of Kanaga Island in the Aleutian Islands, Alaska.Alaska Volcano Observatory, Volcano Information -- Kanaga Retrieved Dec. 16, 2022. It is situated within a , which forms the arcuate Kanaton Ridge south and east of Kanaga. A occupies part of the SE caldera floor. The summit of Kanaga has a crater with fumarolic activity. It is located about 25 km (16&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanaga Island
Kanaga Island (; ) is a part of the Andreanof Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. The island measures long and between wide with an area of , making it the 42nd largest island in the United States. The island's most notable feature is Mount Kanaga, a volcano which last erupted in 1995. Gallery References "Kanaga Island" ''Encyclopædia Britannica The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...''. Retrieved July 7, 2005. Andreanof Islands Islands of Alaska Islands of Unorganized Borough, Alaska {{AleutiansWestAK-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Volcano Observatory
The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) is a joint program of the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Geophysical Institute of the University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAFGI), and the State of Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys (ADGGS). AVO was formed in 1988, and uses federal, state, and university resources to monitor and study Alaska's volcanology, hazardous volcanoes, to predict and record eruptive activity, and to mitigate volcanic hazards to life and property. The Observatory website allows users to monitor active volcanoes, with seismographs and webcameras that update regularly. AVO monitors more than 20 volcanoes in Cook Inlet, which is close to Alaskan population centers, and the Aleutian Arc due to the hazard that plumes of ash pose to aviation. AVO operates out of two locations. One is at the U.S. Geological Survey office on the campus of Alaska Pacific University in Anchorage. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Unorganized Borough, Alaska
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calderas Of Alaska
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
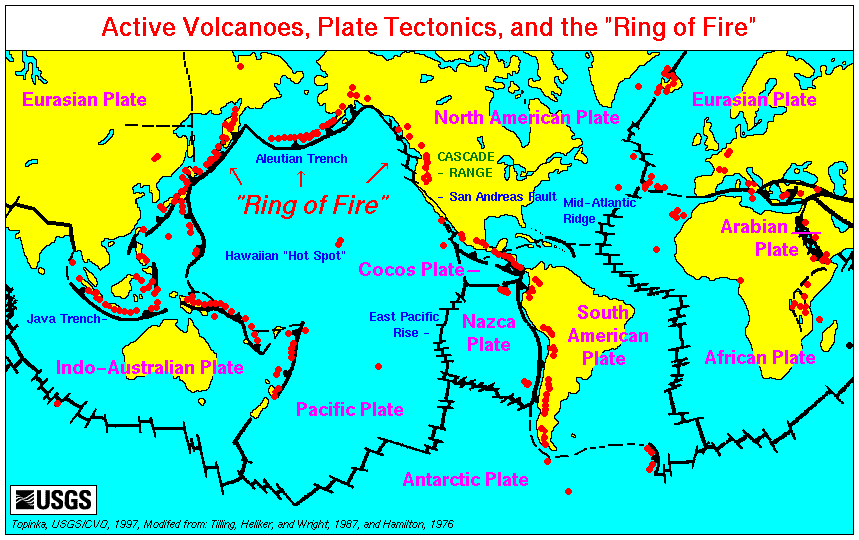
Volcanic Crater Lakes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of The Aleutian Islands
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the Crust (geology), crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Volcanoes
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcanoes Of The United States
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a typically conical volcano built up by many alternating layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and explosive eruptions. Some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and solidifies before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high to intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but can travel as far as 8 km (5 mi). The term ''composite volcano'' is used because strata are usually mixed and uneven instead of neat layers. They are among the most common types of volcanoes; more than 700 stratovolcanoes have erupted lava during the Holocene Epoch (the last 11,700 years), and many older, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In The United States Of America
This article contains a list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories. Alaska American Samoa Arizona California Colorado Hawaii Idaho Illinois Louisiana Michigan Mississippi Missouri Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico North Carolina Northern Mariana Islands Oregon Texas Utah Virginia Washington Wyoming See also *Geothermal energy in the United States *List of Cascade volcanoes * List of large volume volcanic eruptions in the Basin and Range Province *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of volcanoes in Mexico *List of volcanoes in Russia *List of volcanic craters in Alaska * List of volcanic craters in Arizona * List of lava flows in Arizona *List of Yellowstone geothermal features * National Volcano Early Warning and Monitoring System * United States Geological Survey National Volcanic Threat Assessment References External links 2018 Update to the U.S. Geological Survey Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Alaska Volcanoes Kanaga
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |