|
Mount Falconer
Mount Falconer () is a mountain, high, surmounting Lake Fryxell on the north wall of Taylor Valley, between Mount McLennan and Commonwealth Glacier in Antarctica. It was named by the Western Journey Party, led by Thomas Griffith Taylor, of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. Location Mount Falconer is in the southeast of the Asgard Range. The Commonwealth Glacier forms to its north and flows east and then south into the Taylor Valley. Lake Fryxell in the Taylor Valley is to the south of the mountain, and Canada Glacier flows southeast into Taylor Valley to the west of Mount Falconer. Mount McLennan is to the northwest. Features Named features include, from west to east: Perk Summit . A mountain peak, high, that is the highest elevation on the ridge between Mount McLennan and Mount Keohane. Named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) (1997) after Henry Perk, Chief Pilot, Kenn Borek Air, Ltd., Calgary, Canada, who has flown Twin O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount McLennan
Mount McLennan is a mountain south of the Howard Hills in the northeast part of the Scott Mountains, Enderby Land, Antarctica. It was plotted from air photos taken from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions aircraft in 1956 and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for K. McLennan, a member of the crew of the ''Discovery'' during the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition The British Australian (and) New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) was a research expedition into Antarctica between 1929 and 1931, involving two voyages over consecutive Austral summers. It was a British Commonwealth initiative, d ... of 1929–31. References Mountains of Enderby Land {{EnderbyLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria University Of Wellington Antarctic Expedition
The Antarctic Research Centre (ARC) is part of the School of Geography, Environment and Earth Sciences at Victoria University of Wellington. Its mission is to research " Antarctic climate history and processes, and their influence on the global climate system. The current director of the Antarctic Research Centre is Associate Professor Robert McKay. Directors * 1972–2007: Professor Peter Barrett * 2008–2016: Professor Tim Naish * 2017–2019: Professor Andrew Mackintosh * 2020–present: Professor Robert McKay History In December 1957, geology students Barrie McKelvey and Peter Webb along with biologist Ron Balham conducted an expedition to the then unexplored McMurdo Dry Valleys via the Royal New Zealand Navy Antarctic support ship HMNZS ''Endeavour''. This expedition formed the basic for the annual Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expeditions, which continue to the present day. Since this first expedition, over 400 staff and students have travelled to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huey Creek
Taylor Valley is an ice-free valley about long, once occupied by the receding Taylor Glacier. It lies north of the Kukri Hills between the Taylor Glacier and New Harbour in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Taylor Valley is the southernmost of the three large McMurdo Dry Valleys in the Transantarctic Mountains, located west of McMurdo Sound. Exploration and naming The Taylor Valley was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE, 1901–04). It was more fully explored by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09 (BrAE) and the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. It was named after the Taylor Glacier. Geology In the oblique aerial photo at right, the tan bands are sandstone layers from the Beacon Supergroup, a series of sedimentary rock layers formed at the bottom of a shallow sea between 250 million and 400 million years ago. Throughout that period, Earth's southern continents were locked into the supercontinent Gondwana. The dark band of rock that divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
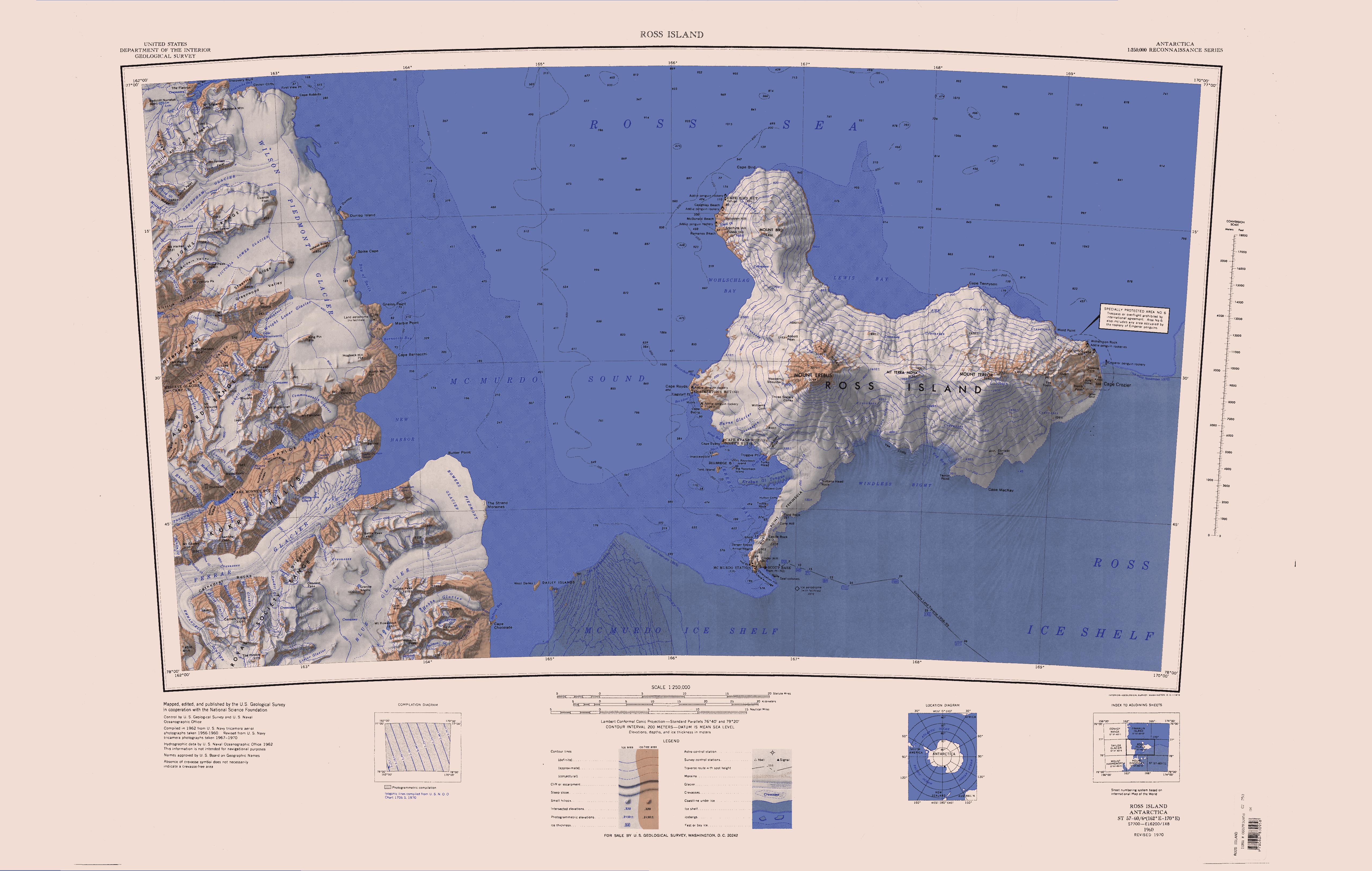
Cape Evans
Cape Evans () is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay. History The cape was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, who named it the " Skuary" after the birds. Scott's second expedition, the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, built its headquarters here, renaming the cape for Lieutenant Edward Evans, Royal Navy, second in command of the expedition. Scott's headquarters building still exists and is known as Scott's Hut. Historic sites and monuments Scott's Hut has been designated a Historic Site or Monument (HSM 16), following a proposal by New Zealand and the United Kingdom to the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting. A cross on Windvane Hill, Cape Evans, was erected by the Ross Sea Party, led by Captain Aeneas Mackintosh, of Sir Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition The Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beardmore Glacier
The Beardmore Glacier in Antarctica is one of the largest valley glaciers in the world, being long and having a width of . It descends about from the Antarctic Plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf and is bordered by the Commonwealth Range of the Queen Maud Mountains on the eastern side and the Queen Alexandra Range of the Central Transantarctic Mountains on the western. Its mouth is east of the Lennox-King Glacier. It is northwest of the Ramsey Glacier. Early exploration The glacier is one of the main passages through the Transantarctic Mountains to the great polar plateau beyond, and was one of the early routes to the South Pole despite its steep upward incline. The glacier was discovered and climbed by Ernest Shackleton during his Nimrod Expedition, ''Nimrod'' Expedition of 1908. Although Shackleton turned back at latitude 88° 23' S, just from the South Pole, he established the first proven route towards the pole and, in doing so, became the first person to set foot up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Falcon Scott
Captain Robert Falcon Scott (6 June 1868 – ) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer who led two expeditions to the Antarctic regions: the Discovery Expedition, ''Discovery'' expedition of 1901–04 and the Terra Nova Expedition, ''Terra Nova'' expedition of 1910–13. On the first expedition, he set a new southern record by marching to latitude 82°S and discovered the Antarctic Plateau, on which the South Pole is located. On the second venture, Scott led a party of five which reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912, less than five weeks after Amundsen's South Pole expedition. On the return journey from the Pole, a planned meeting with supporting dog teams from the base camp failed, despite Scott's written instructions, and at a distance of from their base camp at Hut Point and approximately from the next depot, Scott and his companions died. When Scott and his party's bodies were discovered, they had in their possession the first Antarctic fossils discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada Glacier
Canada Glacier is a small glacier flowing south-east into the northern side of Taylor Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is in the Ross Dependency. Its melting season is in the summer. Description The glacier receives less than 10 cm of snowfall annually, and is (technically) an ecosystem. Its seasonal melting feeds Lake Hoare to the west and Lake Fryxell to the east. At the north side of its head sit the Hothem Cliffs. History The glacier was discovered and named in the course of the Terra Nova Expedition (1910–1913), under Robert Scott. Charles S. Wright, a Canadian physicist, was a member of the party that explored the area. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of about 1 km2 on the eastern side of the glacier is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.131 because it contains some of the richest plant growth (bryophytes and algae) in the McMurdo Dry Valleys region. It is exceptionally import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
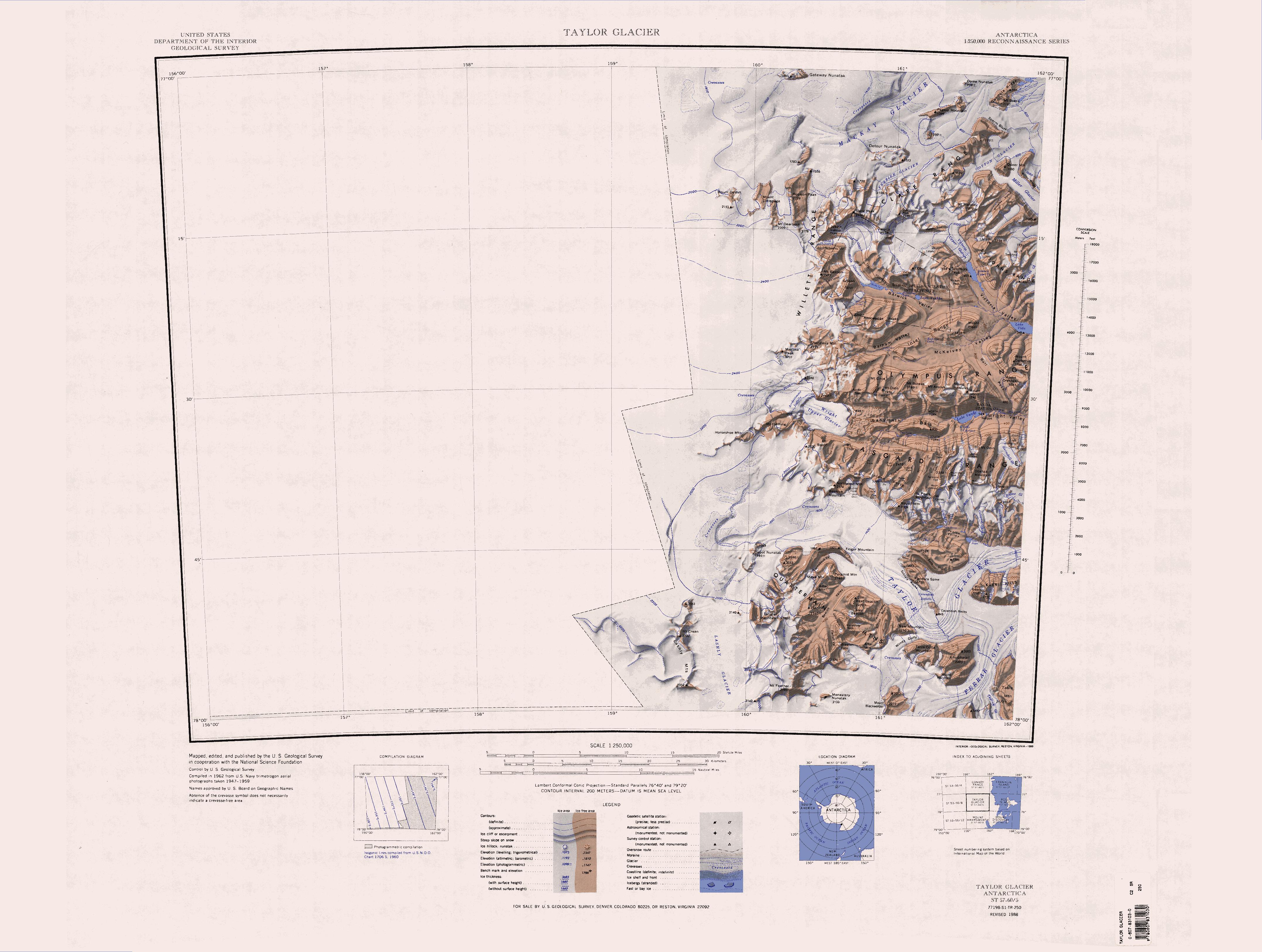
Asgard Range
The Asgard Range () is a mountain range in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It divides Wright Valley from Taylor Glacier and Taylor Valley. It is south of the Olympus Range and north of the Quartermain Mountains and the Kukri Hills. Name The Asgard Range was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) after Asgard, the home of the Norse gods. Location The Asgard Range extends in a west–east direction from Wright Upper Glacier, below the Antarctic Plateau, to Mount Newall above the Wilson Piedmont Glacier, which extends along the west coast of the Ross Sea. To the north, the Asgard Range is separated from the Olympus Range by the Wright Upper Glacier and the Wright Valley, from which the Wright Lower Glacier flows into the Wilson Piedmont Glacier. To the south, the Taylor Glacier and Taylor Valley separate the Asgard Range from the Quartermain Mountains and the Kukri Hills. Surrounding major glaciers and valleys * Wright Upper Glacie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |