|
Mount Cherry-Garrard
Mount Cherry-Garrard () is a peak at the seaward end of the divide between Simpson Glacier and Fendley Glacier, on the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The topographical feature was first charted by the Northern Party, led by Victor Campbell, of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. They named the feature for Apsley Cherry-Garrard, Assistant Zoologist on the expedition. The mountain lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams Cape Williams () is an ice-covered cape in Antarctica. It is the termination of Buell Peninsula at the east side of the terminus of Lillie Glacier at the lower ends of George Glacier and Zykov Glacier. The peninsula is 15 nautical miles (28 ... and Cape Adare. References * Mountains of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennell Coast
Pennell Coast is that portion of the coast of Antarctica between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. To the west of Cape Williams lies Oates Coast, and to the east and south of Cape Adare lies Borchgrevink Coast. Named by New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) in 1961 after Lieutenant Harry Pennell, Royal Navy, commander of the Terra Nova, the expedition ship of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. Pennell engaged in oceanographic work in the Ross Sea during this period. In February 1911 he sailed along this coast in exploration and an endeavor to land the Northern Party led by Lieutenant Victor Campbell. The name is also used more loosely to refer to both the coast itself and the hinterland extending south to the watershed of the Southern Cross Mountains Southern Cross Mountains is the name applied to the group of Antarctic mountain ranges lying between the Mariner and Priestley Glaciers in Victoria Land. Seaward parts of this area were first viewed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (topography)
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson Glacier
Simpson Glacier () is a glacier, 6 miles (10 km) long, in the Admiralty Mountains. It flows northward to the coast between Nelson Cliff and Mount Cherry-Garrard where it forms the Simpson Glacier Tongue. The latter feature was named by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, after Sir George Simpson, meteorologist of the expedition. The glacier described was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS), 1960–63,a and was so named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established ... (US-ACAN) because (with Fendley Glacier to the east) it nourishes the Simpson Glacier Tongue. Admiralty Mountains Glaciers of Pennell Coast {{PennellCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fendley Glacier
Fendley Glacier () is a glacier, long, flowing northeast from the Admiralty Mountains to enter the sea between Mount Cherry-Garrard and the Atkinson Cliffs, on the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. This geographical feature was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Tech. Sergeant Iman A. Fendley, United States Air Force, who perished in the crash of a C-124 Globemaster aircraft in this vicinity in 1958. The glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams Cape Williams () is an ice-covered cape in Antarctica. It is the termination of Buell Peninsula at the east side of the terminus of Lillie Glacier at the lower ends of George Glacier and Zykov Glacier. The peninsula is 15 nautical miles (28 ... and Cape Adare. References Glaciers of Pennell Coast {{PennellCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Campbell (Royal Navy Officer)
Victor Lindsey Arbuthnot Campbell (20 August 1875 – 19 November 1956) was an English Royal Navy officer and Antarctic explorer. Career ''Terra Nova'' expedition In 1910, he was first officer on the ''Terra Nova'' expedition by Robert Falcon Scott. After arriving in Antarctica in January 1911, his role was to lead an eastern party of six men to explore and carry out scientific work in King Edward VII Land, to the east of the Barrier. On 26 January 1911, Campbell's party left in the and headed east. After failing to find a suitable landing site on the King Edward VII Land shore, Campbell decided to sail to Victoria Land. On its return westward, ''Terra Nova'' encountered Roald Amundsen's expedition camped in the Bay of Whales, an inlet in the Barrier. After returning to Cape Evans and informing Scott of Amundsen's location, Campbell's party were renamed the "Northern Party" and set off again, sailing northwards and put ashore at Robertson's Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13
The ''Terra Nova'' Expedition, officially the British Antarctic Expedition, was an expedition to Antarctica which took place between 1910 and 1913. Led by Captain Robert Falcon Scott, the expedition had various scientific and geographical objectives. Scott wished to continue the scientific work that he had begun when leading the ''Discovery'' Expedition from 1901 to 1904, and wanted to be the first to reach the geographic South Pole. He and four companions attained the pole on 17 January 1912, where they found that a Norwegian team led by Roald Amundsen had preceded them by 34 days. Scott's party of five died on the return journey from the pole; some of their bodies, journals, and photographs were found by a search party eight months later. The expedition, named after its supply ship, was a private venture financed by public contributions and a government grant. It had further backing from the Admiralty, which released experienced seamen to the expedition, and from the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
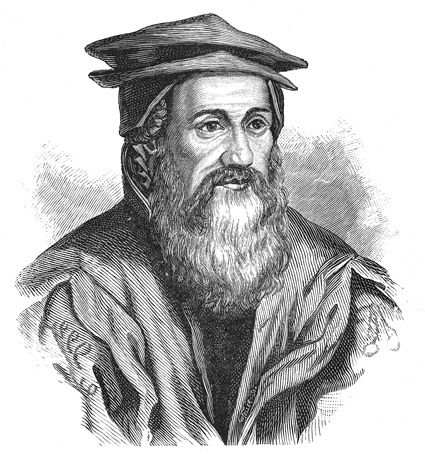
Apsley Cherry-Garrard
Apsley George Benet Cherry-Garrard (2 January 1886 – 18 May 1959) was an English explorer of Antarctica. He was a member of the ''Terra Nova'' expedition and is acclaimed for his 1922 account of this expedition, ''The Worst Journey in the World''. Early life Born in Bedford, as Apsley George Benet Cherry, the eldest child of Apsley Cherry of Denford Park and his wife, Evelyn Edith (née Sharpin), daughter of Henry Wilson Sharpin of Bedford. He was educated at Winchester College and at Christ Church, Oxford where he read classics and modern history. While at Oxford, he rowed in the 1908 Christ Church crew which won the Grand Challenge Cup at the Henley Royal Regatta. His surname was changed to Cherry-Garrard by the terms of his great-aunt's will, through which his father inherited the Lamer Park estate near Wheathampstead, Hertfordshire. Apsley inherited the estate on his father's death in 1907. Cherry-Garrard had always been enamoured of the stories of his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Williams
Cape Williams () is an ice-covered cape in Antarctica. It is the termination of Buell Peninsula at the east side of the terminus of Lillie Glacier at the lower ends of George Glacier and Zykov Glacier. The peninsula is 15 nautical miles (28 km) long and is situated at the extremity of the Pennell Coast portion of Victoria Land Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. I ..., lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. It was discovered in February 1911 when the Terra Nova of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, explored the area westward of Cape North, and it was named for William Williams, Chief Engine-room Artificer on the Terra Nova. Headlands of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Adare
Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Description Marking the north end of Borchgrevink Coast and the west end of Pennell Coast, the cape separates the Ross Sea to the east from the Southern Ocean to the west, and is backed by the high Admiralty Mountains. Cape Adare was an important landing site and base camp during early Antarctic exploration. Off the coast to the northeast are the Adare Seamounts and the Adare Trough. History Captain James Ross discovered Cape Adare in January 1841 and named it after his friend the Viscount Adare (the title is derived from Adare, Ireland). In January 1895, Norwegian explorers Henrik Bull and Carsten Borchgrevink from the ship ''Antarctic'' landed at Cape Adare as the first documented landing on Antarctica, collecting geological specimens. Borchgrevink returned to the cape leading his own ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |