|
Moshoryne
Moshoryne ( uk, Мошорине) is a village in central Ukraine, Kropyvnytskyi Raion, Kirovohrad Oblast, in Subottsi rural hromada. It has a population of Geography The Beshka River flows through the territory of the village History The village was founded by Serbian immigrants in the middle of the 18th century, probably from the Serbian village of Moshoryn, and they named the local river Beshka, probably after the village of Beshka in Serbia, where the immigrants could have come from. In 1772 there were 121 houses. As of 1886 3359 people lived here. Here were 536 farm households, an Orthodox church, a school, and 9 benches. During the Holodomor of 1932–1933, at least 26 villagers died. According to the recollections of a local resident, Olena Yermolenko (1913-2002): "Every day in 1933, on my way home from work, I saw people lying by the road from the collective farm Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subottsi Rural Hromada
Subottsi rural hromada is a hromada A hromada ( uk, територіальна громада, lit=territorial community, translit=terytorialna hromada) is a basic unit of administrative division in Ukraine, similar to a municipality. It was established by the Government of Ukra ... of Ukraine, located in Kropyvnytskyi Raion, Kirovohrad Oblast. Its administrative center is the village Subottsi. It has an area of , and a population of 11,832 people. The hromada contains 23 villages: Subottsi, Bohdanivka, Kostyantynivka, Trepivka, Barvinivka, Vasyne, Volodymyrivka, Hlyboka Balka, Dilyno-Kamianka, Kopani, Kokhanivka, Kucherivka, Milova Balka, Moshoryne, Novovodyane, Novopolyana, Novoromanivka, Novotrepivka, Sablyne, Spaso-Mozharivka, and Topylo. References Kropyvnytskyi Raion Hromadas of Kirovohrad Oblast {{Kirovohrad-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beshka (river)
Beshka ( uk, Бешка) is a river in Kirovohrad Oblast, Ukraine. It is a tributary of the Inhulets. The name of the river comes from Turkish or , a word meaning "five", or in a religious context, "God given plurality", with the suffix , literally "rock". The town Pyatykhatky has a similar origin in Turkish cultural influence. It begins near the village of Sokil'nyky, flows to the southeast through the villages of Volodymyrivka, Moshoryne, Svitlopil, the town of Nova Praha Nova Praha ( uk, Нова Прага; russian: Новая Прага) is an urban-type settlement in Oleksandriia Raion of Kirovohrad Oblast in Ukraine. It is located on the banks of the Beshka, a right tributary of the Inhulets in the basin of ... and flows into the Inhulets within the village of Novy Starodub. References {{Reflist Rivers of Kirovohrad Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
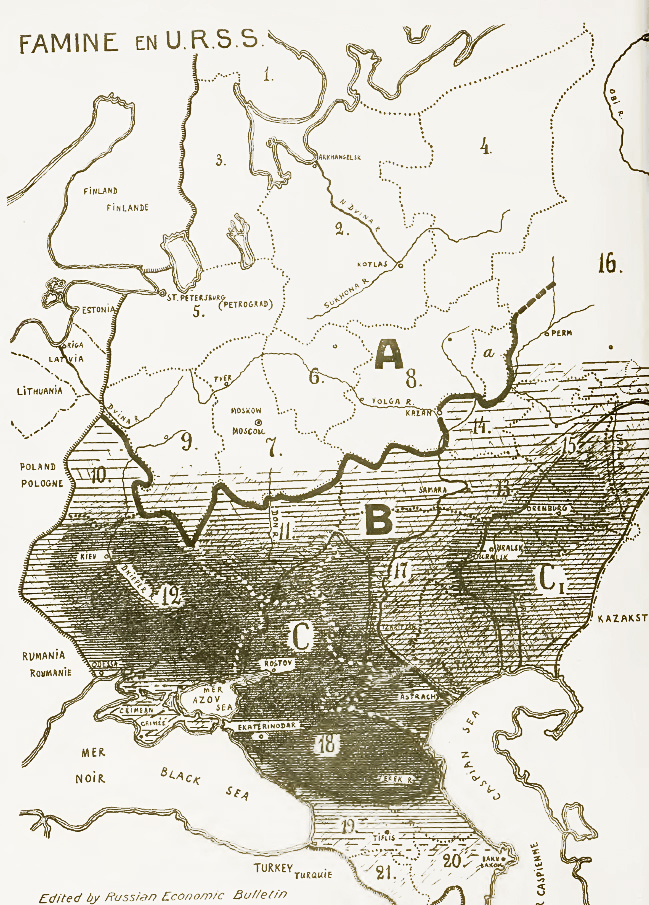
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Kropyvnytskyi Raion
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the State Political Directorate, GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in charge of the Soviet Union, Soviet network of Correctional labour camp, forced labour camps which were set up by order of Vladimir Lenin, reaching its peak during Joseph Stalin's rule from the 1930s to the early 1950s. English-language speakers also use the word ''gulag'' in reference to each of the forced-labor camps that existed in the Soviet Union, including the camps that existed in the History of the Soviet Union (1927–1953), post-Lenin era. The Gulag is recognized as a major instrument of political repression in the Soviet Union. The camps housed a wide range of convicts, from petty criminals to political prisoners, a large number of whom were convicted by simplified procedures, such as NKVD troikas or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulak
Kulak (; russian: кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈlak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned over of land towards the end of the Russian Empire. In the early Soviet Union, particularly in Soviet Russia and Azerbaijan, ''kulak'' became a vague reference to property ownership among peasants who were considered hesitant allies of the Bolshevik Revolution. In Ukraine during 1930–1931, there also existed a term of pidkurkulnyk (almost wealthy peasant); these were considered "sub-kulaks". ''Kulak'' originally referred to former peasants in the Russian Empire who became wealthier during the Stolypin reform of 1906 to 1914, which aimed to reduce radicalism amongst the peasantry and produce profit-minded, politically conservative farmers. During the Russian Revolution, ''kulak'' was used to chastise peasants who withheld grain from the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolkhoz
A kolkhoz ( rus, колхо́з, a=ru-kolkhoz.ogg, p=kɐlˈxos) was a form of collective farm in the Soviet Union. Kolkhozes existed along with state farms or sovkhoz., a contraction of советское хозяйство, soviet ownership or state ownership, sovetskoye khozaystvo. Russian plural: ''sovkhozy''; anglicized plural: ''sovkhozes''. These were the two components of the socialized farm sector that began to emerge in Soviet agriculture after the October Revolution of 1917, as an antithesis both to the feudal structure of impoverished serfdom and aristocratic landlords and to individual or family farming. The 1920s were characterized by spontaneous emergence of collective farms, under influence of traveling propaganda workers. Initially, a collective farm resembled an updated version of the traditional Russian " commune", the generic "farming association" (''zemledel’cheskaya artel’''), the Association for Joint Cultivation of Land (TOZ), and finally the ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Serbia (historical Province)
New Serbia, or Novoserbia, , or , ; russian: Новая Сербия, , or , ; sr, Нова Србија / , or / ; Slavo-Serbian: Нова Сербія, ''Nova Serbiya'', or Ново-Сербія, ''Novo-Serbiya''; ro, Noua Serbie was a military frontier of Imperial Russia from 1752 to 1764 subordinated directly to the Senat and Military Collegium. The founder of New Serbia was Jovan Horvat. Horvat was a leader of a group which rejected a post-riot compromise reached after the demilitarization of their section of the Military Frontier. The rejected compromise envisaged transfer of those who want to remain warriors to the Banat Military Frontier while those who would remain in the region would get provincial status with preservation of religious autonomy. Contrary to serfs, Eastern Orthodox Serbs enjoyed substantial levels of autonomy (in exchange for fight against the Ottoman Empire) granted in multiple documents starting with Statuta Valachorum, but which was gradually ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |