|
Morozov Design Bureau
Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau (), often simply called Morozov Design Bureau or abbreviated KMDB, is a state-owned Ukrainian company in Kharkiv which designs armoured vehicles, including the T-80UD and T-84 main battle tanks, as well as military prime movers. It was responsible for designing and creating many important Soviet-era armoured fighting vehicles, including the BT tank series, with its most famous designs being the T-34, T-54, and T-64 tanks. It is closely associated with the Malyshev Factory. History KMDB started as the Tank Design Team of the Kharkiv Locomotive Factory ''Komintern'' (KhPZ, now Malyshev Factory) in 1927, in Kharkiv, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, and was responsible for the T-12 and T-24 light tanks. In the 1930s, the design team was designated as the independent T2K Tank Design Bureau, and began work on the BT tank series. In 1936 the plant was re-designated "Plant No. 183", and the design bureau "KB-190". The plant also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a business entity created or owned by a national or local government, either through an executive order or legislation. SOEs aim to generate profit for the government, prevent private sector monopolies, provide goods at lower prices, implement government policies, or serve remote areas where private businesses are scarce. The government typically holds full or majority ownership and oversees operations. SOEs have a distinct legal structure, with financial and developmental goals, like making services more accessible while earning profit (such as a state railway). They can be considered as government-affiliated entities designed to meet commercial and state capitalist objectives. Terminology The terminology around the term state-owned enterprise is murky. All three words in the term are challenged and subject to interpretation. First, it is debatable what the term "state" implies (e.g., it is unclear whether municipally owned corporations and ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Fighting Vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (British English) or armored fighting vehicle (American English) (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by vehicle armour, armour, generally combining operational mobility with Offensive (military), offensive and defense (military), defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or Continuous track, tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armored car (military), armoured cars, assault guns, Self-propelled artillery, self-propelled artilleries, infantry fighting vehicles (IFV), and armoured personnel carriers (APC). Armoured fighting vehicles are classified according to their characteristics and intended role on the battlefield. The classifications are not absolute; two countries may classify the same vehicle differently, and the criteria change over time. For example, relatively lightly armed armoured personnel carriers were largely superseded by infantry fighting vehicles with much heavier armament in a similar role. Successful designs are often ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoye Sormovo Factory No
Krasnoye may refer to: * Krasnoye, Krasnensky District, Belgorod Oblast, rural locality and the administrative center of Krasnensky District of Belgorod Oblast, Russia * Krasnoye, Krasninsky District, Smolensk Oblast, rural locality in the Krasninsky District of Smolensk Oblast, Russia * Krasnoye, Trubchevsky District, Bryansk Oblast, rural locality in Trubchevsky District, Bryansk Oblast, Russia * Krasnoye-na-Volge, urban locality in Krasnoselsky District of Kostroma Oblast, Russia * Krasnoye (crater), a crater on Mars * Krasnoye Sormovo Factory No. 112, one of the oldest shipbuilding factories in Russia, located in the Sormovsky City District of Nizhny Novgorod See also * Krasny (other) * Krasnoye Selo (inhabited locality) * Lake Krasnoye (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalingrad Tractor Plant
The Volgograd Tractor Plant (, ''Volgogradski traktorni zavod'', or , ''VgTZ''), formerly the ''Dzerzhinskiy'' Tractor Factory or the Stalingrad Tractor Plant, is a heavy equipment factory located in Volgograd, Russia. It was once one of the largest tractor manufacturing enterprises in the USSR. It was a site of fierce fighting during World War II's Battle of Stalingrad. During its lifetime, VgTZ has supplied more than 2.5 million tractors to the farming industry, making a huge contribution to the mechanization of agriculture. VgTZ tractors operate in 32 countries throughout Southeast Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, and Latin America. Also used for the production of military vehicles, VgTZ is inextricably linked with the history of Soviet tank building. The plant continues to operate on a small scale, but much of it is now derelict or has been demolished. History Until 1961, the plant was called the Stalingrad Tractor Plant named for F. Dzerzhinsky (, ''Stalingradski tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
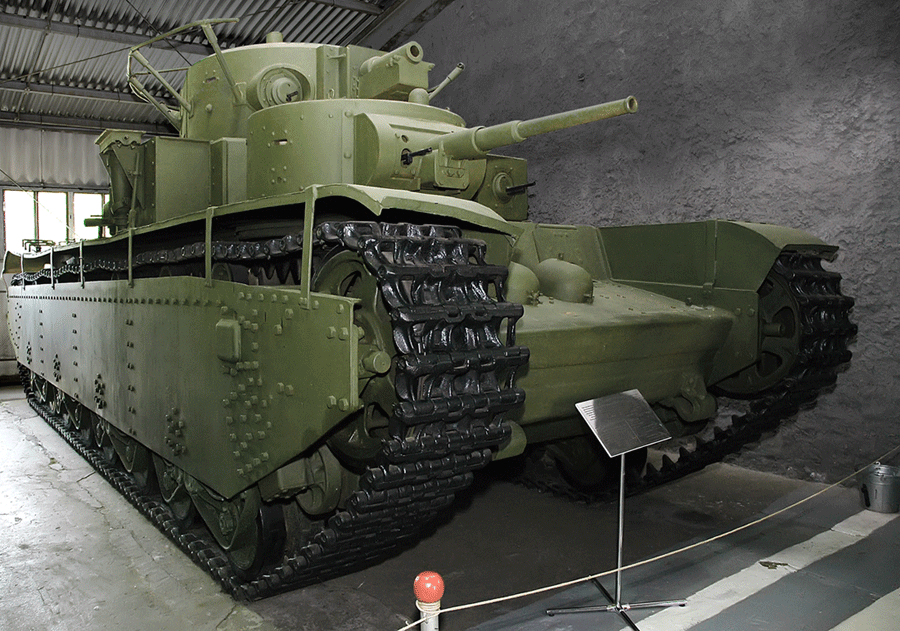
T-35
The T-35 was a Soviet multi- turreted heavy tank of the interwar period and early Second World War that saw limited service with the Red Army. Often called a land battleship, it was the only five-turreted heavy tank in the world to reach production, but proved to be slow and mechanically unreliable. Most of the T-35 tanks still operational at the time of Operation Barbarossa were lost due to mechanical failure rather than enemy action. It was designed to complement the contemporary T-28 medium tank; however, very few were built. Outwardly, it was large; but internally, the spaces were cramped with the fighting compartments separated from each other. Some of the turrets obscured the entrance hatches. Production history The T-35 was developed by the OKMO design bureau of the Bolshevik Factory, which began work on a heavy tank in 1930. Two teams developed separate designs. The team headed by German engineer Grotte worked on the 100-ton four-turreted TG-5 tank, armed with a 107& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-24 Tank
The T-24 was a Soviet medium tank built in 1931. Only twenty four were built, and none saw combat. This was the first tank produced at the KhPZ factory in Kharkov, which was later responsible for the very successful BT series, T-34 and T-54 Soviet tanks. The T-24's suspension was used successfully in the Soviet Union's first purpose-built artillery tractors. The T-24's main armament was a 45 mm gun. It had a ball-mount 7.62 mm DT machine gun in the hull, another in the turret, and a third in a secondary turret atop the main turret. The tank was well-armoured for its time, but the engine and transmission had problems. Production history A tank design bureau was established at the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) in Kharkov, Soviet Ukraine, in 1928. The first tank project of the factory was the T-12 (or T-1-12). This was a larger version of the T-18, with a more powerful engine (the T-18 was based on the Renault FT). The idea of the T-24 tank was so great, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Ukraine
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. Under the Soviet one-party model, the Ukrainian SSR was governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union through its republican branch, the Communist Party of Ukraine. The first iterations of the Ukrainian SSR were established during the Russian Revolution, particularly after the Bolshevik Revolution. The outbreak of the Ukrainian–Soviet War in the former Russian Empire saw the Bolsheviks defeat the independent Ukrainian People's Republic, during the conflict against which they founded the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets, which was governed by the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), in December 1917; it was later succeeded by the Ukrainian Soviet Republic in 1918. Simultaneously with the Russian Civil War, the Ukrainian War of Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malyshev Factory
The Malyshev Factory (; abbreviated ), formerly the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (, ), is a state-owned manufacturer of heavy equipment in Kharkiv, Ukraine. It was named after the Soviet politician Vyacheslav Malyshev. The factory is part of the state concern, Ukroboronprom. It produces diesel engines, farm machinery, coal mining, sugar refining, and wind farm equipment, but is best known for its production of Soviet tanks, including the BT tank series of fast tanks, the famous T-34 of the Second World War, the Cold War T-64 and T-80, and their modern Ukrainian successor, the T-84. The factory is closely associated with the Morozov Design Bureau (KMDB), designer of military armoured fighting vehicles and the Kharkiv Engine Design Bureau (KEDB) for engines. In 1958, it developed the Kharkovchanka, an off-road vehicle which reached the South Pole the following year. At its height during the Soviet era, the factory employed 60,000 of Kharkiv's 1.5 million inhabitants. , 5,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-64
The T-64 is a Soviet tank manufactured in Kharkiv, and designed by Alexander Morozov. The tank was introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank divisions, while the T-62 supported infantry in motor rifle divisions. It introduced advanced features including composite armour, a compact engine and transmission, and a smoothbore 125-mm gun equipped with an autoloader to allow the crew to be reduced to three so the tank could be smaller and lighter. In spite of being armed and armoured like a heavy tank, the T-64 weighed only . These features made the T-64 expensive to build, significantly more so than previous generations of Soviet tanks. This was especially true of the power plant, which was time-consuming to build and cost twice as much as more conventional designs. Several proposals were made to improve the T-64 with new engines, but chief designer Alexander Alexandrovich Morozov's political power in Moscow kept t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |