|
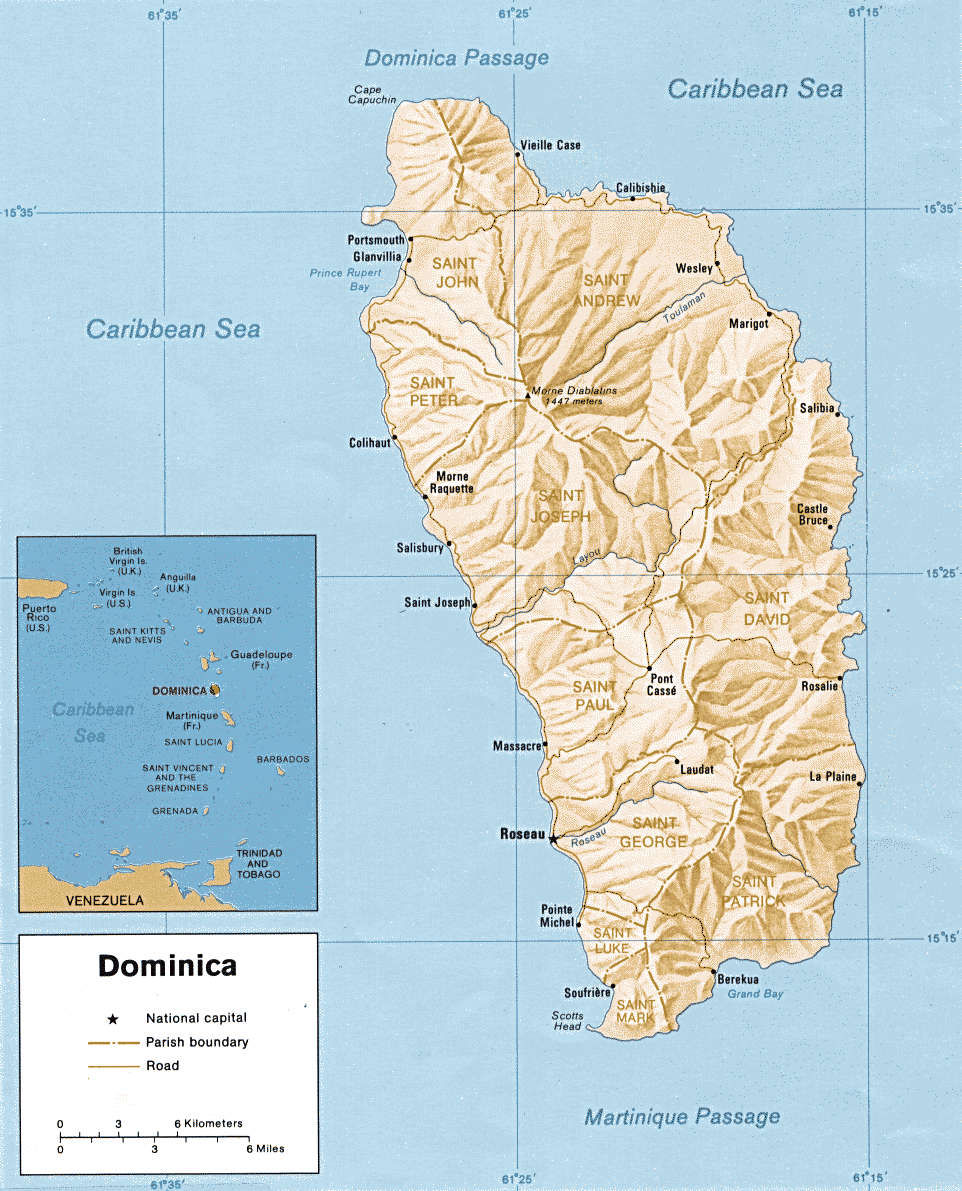
Morne Diablotins
Morne Diablotin is the highest mountain in Dominica, an island-nation in the Caribbean Lesser Antilles. It is the second highest mountain in the Lesser Antilles, after La Grande Soufrière in Guadeloupe. Morne Diablotin is located in the northern interior of the island, about north of Dominica's capital Roseau, Dominica, Roseau and about southeast of Portsmouth, Dominica, Portsmouth, the island's second-largest town. It is located within Morne Diablotin National Park. The mountain is volcano, volcanic, and last erupted c. 30,000 years ago. There are no known historical eruptions. The source of the Toulaman River lies in the mountain area. Morne Diablotin shares its name with the local term for the rare black-capped petrel (''Pterodroma hasitata''). See also * List of mountains of Dominica * List of volcanoes in Dominica References Mountains of Dominica Volcanoes of Dominica VEI-6 volcanoes Pleistocene stratovolcanoes Inactive volcanoes Highest points of countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Countries By Highest Point
The following sortable table lists land surface elevation extremes by country or dependent territory. Elevation, Topographic elevation is the vertical distance above the reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential Gravity, gravitational surface. Table National elevation ranges Of all countries, Lesotho has the world's highest low point at . Other countries with high low points include Rwanda and Andorra . Countries with very low high points include Maldives , Tuvalu, and the Marshall Islands . These island countries also have the smallest range between their lowest (sea level) and highest points, and are very sensitive to changes in sea level. The highest and lowest points in China constitute the greatest elevation range within any single country at . The elevation ranges are also great in Nepal , Pakistan , and India . Monaco's elevation range is among the greatest relative to surface area. Within its 2.02 km2 territory, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulaman River
The Toulaman River is a river in Dominica. Its source is in the Morne Diablotins Morne Diablotin is the highest mountain in Dominica, an island-nation in the Caribbean Lesser Antilles. It is the second highest mountain in the Lesser Antilles, after La Grande Soufrière in Guadeloupe. Morne Diablotin is located in the norther .... It empties into the sea on the northeastern coast, north of Marigot. See also * List of rivers of Dominica References Map of DominicaWater Resources Assessment of Dominica, Antigua and Barbuda, and St. Kitts and Nevis Rivers of Dominica {{Dominica-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inactive Volcanoes
Inactive is a TRPV channel in invertebrates Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum .... Inactive mutant flies show locomotor and hearing deficits. References Ion channels Nervous system {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Stratovolcanoes
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''Ice Age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold glacial periods and warmer interglacials, with the sea levels being up to lower th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEI-6 Volcanoes
The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) is a scale used to measure the size of explosive volcanic eruptions. It was devised by Christopher G. Newhall of the United States Geological Survey and Stephen Self in 1982. Volume of products, eruption cloud height, and qualitative observations (using terms ranging from "gentle" to "mega-colossal") are used to determine the explosivity value. The scale is open-ended with the largest eruptions in history given a magnitude of 8. A value of 0 is given for non-explosive eruptions, defined as less than of tephra ejected; and 8 representing a supervolcanic eruption that can eject (240 cubic miles) of tephra and have a cloud column height of over . The scale is logarithmic, with each interval on the scale representing a tenfold increase in observed ejecta criteria, with the exception of between VEI-0, VEI-1 and VEI-2. Classification With indices running from 0 to 8, the VEI associated with an eruption is dependent on how much volcanic materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Dominica
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Dominica
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Dominica ...
Dominica is an island-nation in the Caribbean that is part of the Lesser Antilles chain of islands. The island has active and extinct volcanoes. References {{Global Volcanism Program Dominica Volcanoes Dominica Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountains Of Dominica ...
Dominica is an island-nation in the Caribbean Lesser Antilles. The highest mountain peak on Dominica, at 4,747 ft, is Morne Diablotins, which is also the second highest mountain in the Lesser Antilles. See also * List of volcanoes in Dominica * Mountain peaks of the Caribbean References * External links {{DEFAULTSORT:Mountains Of Dominica, List Of Geography of Dominica Lists of landforms of Dominica Dominica Dominica geography-related lists Dominica Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day and Clarence Day, grandsons of Benjamin Day, and became a department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale University Press publishes approximately 300 new hardcover A hardcover, hard cover, or hardback (also known as hardbound, and sometimes as casebound (At p. 247.)) book is one bookbinding, bound with rigid protective covers (typically of binder's board or heavy paperboard covered with buckram or other clo ... and 150 new paperback books annually and has a backlist of about 5,000 books in print. Its books have won five National Book Awards, two National Book Critics Circle Awards and eight Pulitzer Prizes. The press maintains offices in New Haven, Connecticut and London, England. Yale is the only American university press with a full-scale publishing operation in Europe. It was a co-founder of the dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |