|
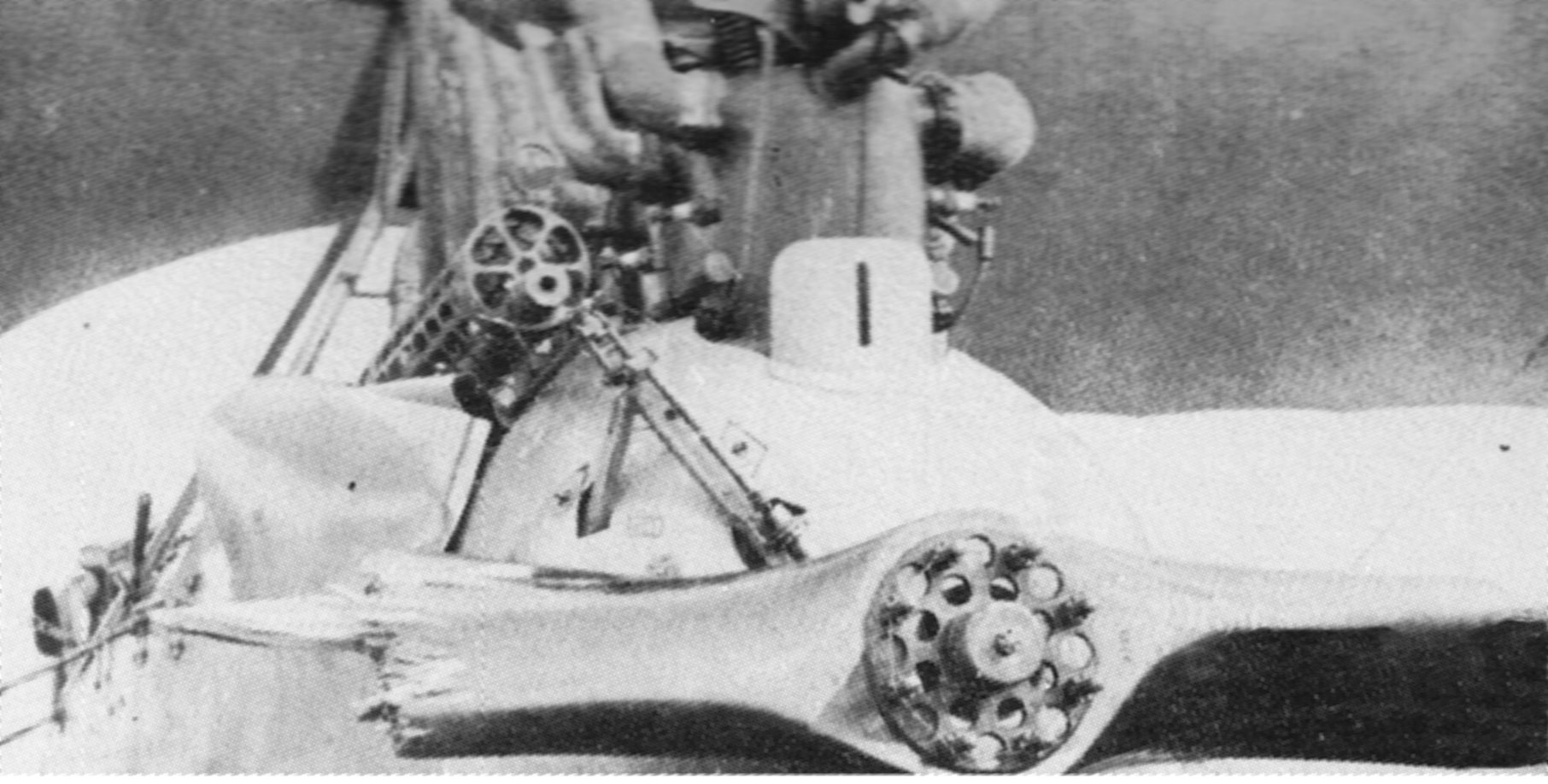
Morane-Saulnier Type L
The Morane-Saulnier L, or Morane-Saulnier Type L, or officially MoS-3, was a French parasol wing one or two-seat scout aeroplane of the First World War. The Type L became one of the first successful fighter aircraft when it was fitted with a single machine gun that fired through the arc of the propeller, which was protected by armoured deflector wedges. Its immediate effectiveness in this role launched an arms race in fighter development, and the Type L was swiftly rendered obsolete. The original Type L used wing warping for lateral control, but a later version designated Type LA was fitted with ailerons.Taylor 1989, p. 684. Built by Morane-Saulnier, large numbers of the Type L were ordered by the French '' Aviation Militaire'' at the outbreak of the war. In total about 600 Type Ls were built and, in addition to the French air force, they served with the Royal Flying Corps, Royal Naval Air Service and the Imperial Russian Air Service. The type was also produced under licence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Air Service
The Imperial Russian Air Service () was an air force founded in 1912 for Russian Empire, Imperial Russia."''12 августа 1912 года приказом по военному ведомству вопросы воздухоплавания и авиации были изъяты из ведения Главного инженерного управления и переданы специально созданному органу: в воздухоплавательную часть Генерального штаба. Эта дата считается днём образования военной авиации России''"12 августа 1912 года // "Щит и меч", No. 29 (1333) от 9 августа 2012 года, стр.8 The Air Service operated for five years and only saw combat in World War I before being reorganized and renamed in 1917 following the Russian Revolution. With the onset of the Russian Civil War, some former IRAS pilots joined Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabellum MG14
The Parabellum MG 14 was a 7.92 mm caliber World War I machine gun built by Deutsche Waffen und Munitionsfabriken. It was a redesign of the Maschinengewehr 08 machine gun (itself an adaptation of the Maxim gun) system intended for use on aircraft and zeppelins. Design Like the earlier Vickers machine gun, it used a toggle action that broke upwards rather than downwards, the opposite way to the MG 08, making for a much more compact receiver. The fusee spring was replaced with an internal spring design, the breech block was completely different and the spent cartridges dropped out the bottom of the receiver, rather than being ejected forward through a hole under the breech from the receiver. There appear to be no action or receiver parts interchangeable with the MG 08. The MG 08's belt-style ammunition feed was enclosed in a drum, the recoil casing was lightened and the cooling jacket was modified for air- instead of water-cooling. The rate of fire was 700 rounds/minute. The bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Wintgens
''Leutnant'' Kurt Wintgens (1 August 1894 – 25 September 1916) was a German World War I fighter ace. He was the first fighter pilot to score an aerial victory with a synchronized machine gun. Wintgens was the recipient of the Iron Cross and the Pour le Mérite (Blue Max). Background Wintgens was born into a military family in Neustadt in Oberschlesien. His military service commenced when he joined the Telegraphen-Bataillon Nr. 2 in Frankfurt/ Oder as a ''Fahnenjunker'' (cadet officer) in 1913. Involvement in First World War Though still in military school when the war began in 1914, Wintgens was sent to the Eastern Front as a leutnant and won the Iron Cross, 2nd Class. On transferring to the German Air Service, Wintgens flew first as an observer, apparently alternating with telegraph duty. However, in early 1915 he entered pilot training at the Fokker school in Schwerin, where ''Leutnant'' Otto Parschau had already been brought in by the Fokker factory to prepare an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotchkiss M1909 Benet–Mercie Machine Gun
Hotchkiss may refer to: Places Canada * Hotchkiss, Alberta * Hotchkiss, Calgary United States * Hotchkiss, Colorado * Hotchkiss, Virginia * Hotchkiss, West Virginia Business and industry * Automobiles Hotchkiss, a French automobile manufacturer * Hotchkiss et Cie, a French armaments manufacturer * Hotchkiss Ordnance Company, an English armaments manufacturer Military * Hotchkiss H35, a French tank of World War II * Hotchkiss gun ** Hotchkiss machine gun, including a list of variants * Hotchkiss M201, a French light transport vehicle Other uses * Hotchkiss (surname) * Hotchkiss drive, a form of automobile power transmission and suspension. * Hotchkiss Bicycle Railroad in Smithville, Burlington County, New Jersey, U.S. * Hotchkiss School The Hotchkiss School is a private college-preparatory day and boarding school in Lakeville, Connecticut. It educates approximately 600 students in grades 9–12, plus postgraduates. Founded in 1891, it was one of the first Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization Gear
A synchronization gear (also known as a gun synchronizer or interrupter gear) was a device enabling a single-engine tractor configuration aircraft to fire its forward-firing armament through the arc of its spinning Propeller (aeronautics), propeller without bullets striking the blades. This allowed the aircraft, rather than the gun, to be aimed at the target. There were many practical problems, mostly arising from the inherently imprecise nature of an automatic gun's firing, the great (and varying) velocity of the blades of a spinning propeller, and the very high speed at which any gear synchronizing the two had to operate. In practice, all known gears worked on the principle of actively triggering each shot, in the manner of a semi-automatic weapon. Design and experimentation with gun synchronization had been underway in French Third Republic, France and German Empire, Germany in 1913–1914, following the ideas of August Euler, who seems to have been the first to suggest mounti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Saulnier (aircraft Manufacturer)
Raymond Victor Gabriel Jules Saulnier (Paris 27 September 1881 – Chécy 4 March 1964) was a French aeronautical engineer. He was a graduate of the École Centrale Paris, and first collaborated with Louis Blériot on the Blériot XI used for the Channel crossing. In 1911, he founded the Morane-Saulnier company with the Morane brothers, where he designed many aircraft and for which he filed numerous patents. He also designed the aircraft in which Roland Garros made the first crossing of the Mediterranean on 23 September 1913. He was chief editor of an aviation periodical, and wrote «Etude, centrage(sic) et classification des Aéroplanes», which was considered an authoritative work on aircraft. He personally managed Morane-Saulnier until 1961. In 1962, the company filed for bankruptcy before being integrated firstly into Sud-Aviation, of which it became a subsidiary, then into SOCATA (Société de Construction d'Avions de Tourisme et Affaires). He had the first idea of a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escadrille 23
''Escadrille 23'' of the French Air Force was formed at Brie on 4 August 1914. History Escadrille 23 was equipped with Morane-Saulniers and forwarded to ''VI Armee'' of the French Army in September, and transferred to ''IV Armee'' in October 1914. Later that month, it moved to the Somme. It would operate from there until 6 August 1915. It then returned to the ''VI Armee'' for a short spell before being posted to ''IV Armee'' on 21 August 1915.Franks, Bailey 1992, p. 90. On 20 September 1915, the unit re-equipped with Nieuports and became ''Escadrille N23''. Its performance earned it a citation in orders on 5 November 1916. It was credited with victories over 17 enemy aircraft and four observation balloons. On 3 February 1917, the ''escadrille'' was posted to ''VII Armee''; it soon moved to support ''II Armee''. On 19 March 1918, the ''escadrille'' earned the fourragere of the ''Croix de Guerre'' by being cited again, for downing another 23 enemy airplanes. The unit subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Garros (aviator)
Eugène Adrien Roland Georges Garros (; 6 October 1888 – 5 October 1918) was a French aviation pioneer and fighter pilot. Garros began a career in aviation in 1909 and performed many early feats such as the first-ever airplane crossing of the Mediterranean Sea in 1913. He joined the French Army, French army and became one of the earliest fighter pilots during World War I. Garros was shot down and died on 5 October 1918. In 1928, the Stade Roland Garros, Roland Garros tennis stadium was named in his memory; the French Open tennis tournament officially takes the name of Roland Garros, which is held in this stadium. Biography Roland Garros was born in Saint-Denis, Réunion, and studied at the Lycée Janson de Sailly and HEC Paris. At the age of 12, he caught pneumonia, and was sent to Cannes to recover. He took up cycling to restore his health, and went on to win an inter-school championship in the sport. He was also keen on football, rugby and tennis.Lefèvre-Garros, 2001, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviator
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as drone operators, flight attendants, mechanics and ground crew, are not classified as aviators. In recognition of the pilots' qualifications and responsibilities, most militaries and many airlines worldwide award aviator badges to their pilots. Definition The first recorded use of the term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in French) was in 1887, as a variation of ''aviation'', from the Latin ''avis'' (meaning ''bird''), coined in 1863 by in ''Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne'' ("Aviation or Air Navigation"). The term ''aviatrix'' (''aviatrice'' in French), now archaic, was formerly used for a female pilot. The term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |