|
Moran Bluff
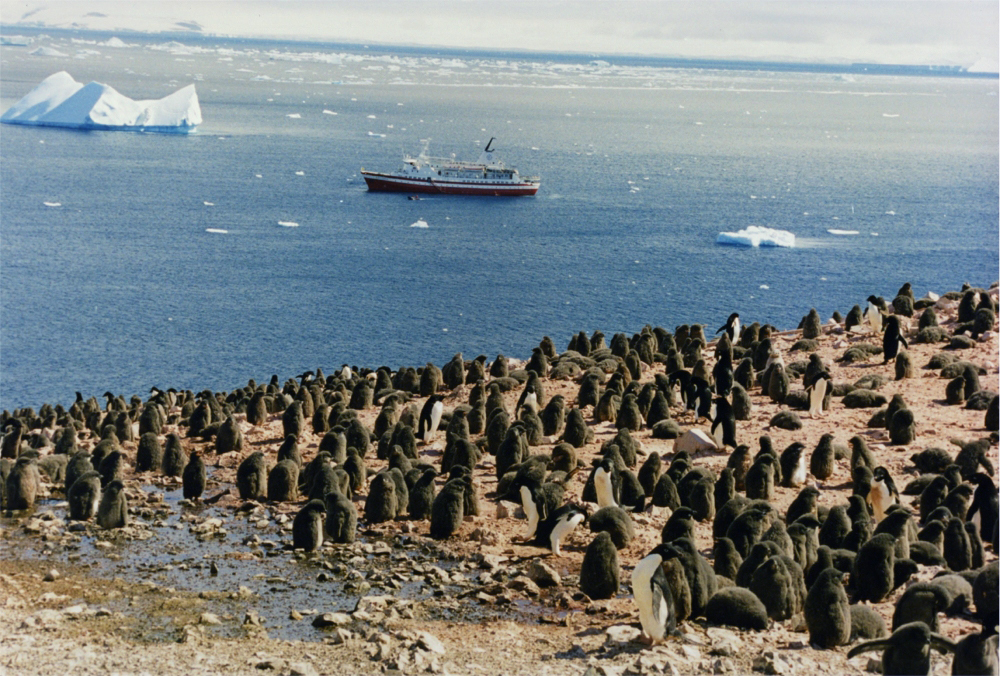
Shepard Island () is an island about long, lying west of Grant Island off the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The island is ice capped except at its northern, seaward side, and is almost wholly embedded in the Getz Ice Shelf. Location Shepard Island is in the north of the Getz Ice Shelf. Reynolds Strait is on its north side, separating it from Forrester Island. Grant Island is to the east. It is home to two Adélie penguin rookeries on its north shore. Features, from west to east, include Worley Point, Mount Petinos, Moran Bluff, Mathewson Point and Mount Colburn. Discovery and name Shepard Island was discovered by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) Expedition (1939–1941) and named for John Shepard Jr., a contributor to the expedition. Features Worley Point . A rock point, the site of an Adelie penguin rookery, forming the northwest corner of Shepard Island. Like Grant Island, eastward, Shepard Island is surrounded by the Getz Ice Shelf except on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
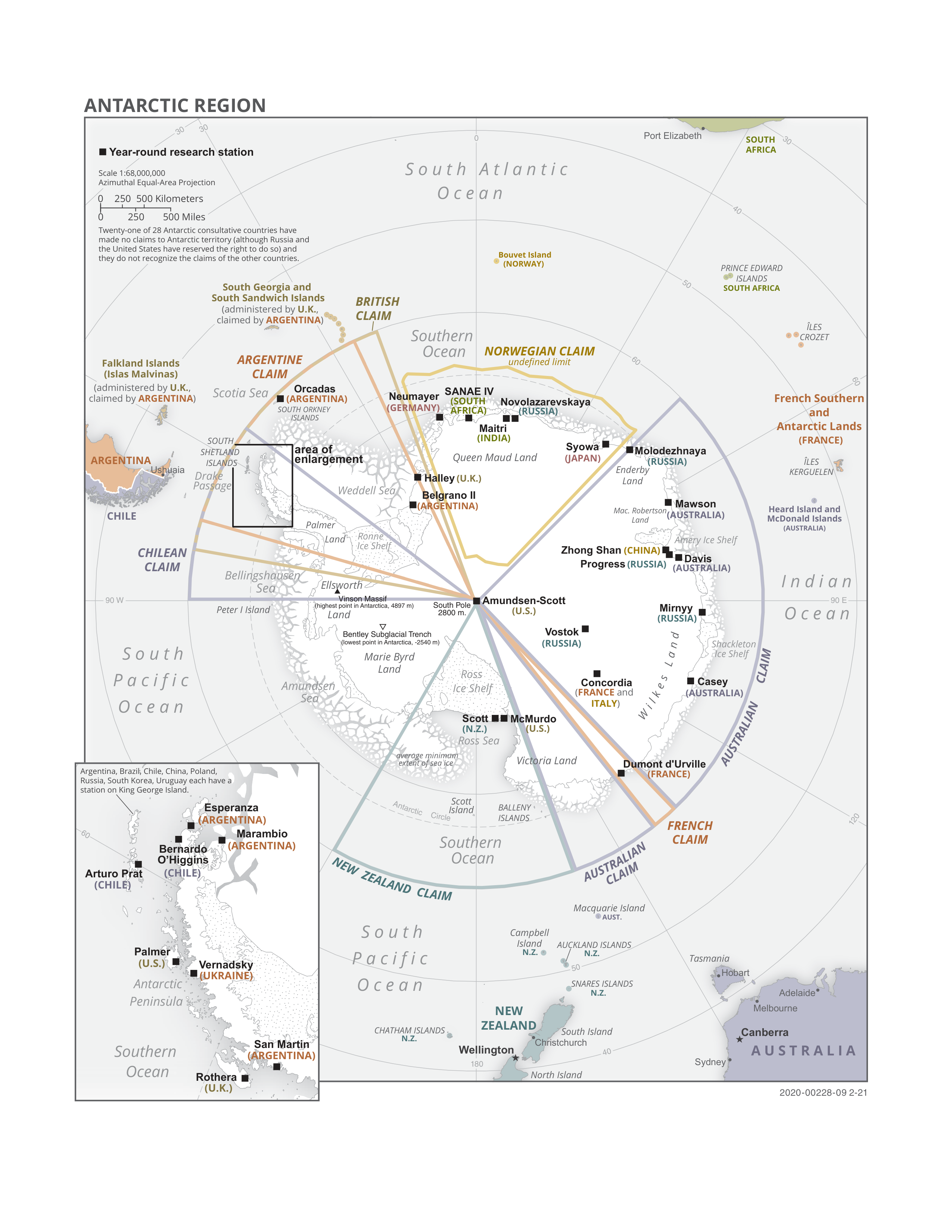
Antarctic Treaty System
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, designating the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning Military activity in the Antarctic, military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelf, ice shelves south of 60th parallel south, 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina. The main treaty was opened for signature on 1 December 1959, and officially coming into force, entered into force on 23 June 1961. The original signatories were the 12 countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcano, volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development. Islands are host to diverse plant and animal life. Oceanic islands have the sea as a natural barrier to the introduction of new species, causing the species that do reach the island to evolve in isolation. Continental islands share animal and plant life with the continent they split from. Depending on how long ago the continental is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant Island
Grant Island () is an ice-covered island, long and wide, lying east of the smaller Shepard Island off the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Like Shepard Island, Grant Island is surrounded by the Getz Ice Shelf on all but the north side. Location Grant Island is in the north, seaward edge of the Getz Ice Shelf. Reynolds Strait is on its north side, which is indented by Ledda Bay, and separates it from Forrester Island. Shepard Island is to the west. Features, from west to east, include Brookman Point, Mount Obiglio, Mount Hummel and McCarthy Point. Discovery and name Grant Island was discovered and charted by personnel aboard on February 4, 1962. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander E. G. Grant, Commanding Officer of USS ''Glacier'' at the time of discovery. Features and nearby features Brookman Point . The snow-covered northwest point of Grant Island. Discovered and first charted from the USS ''Glacier'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Byrd Land
Marie Byrd Land (MBL) is an unclaimed region of Antarctica. With an area of , it is the largest unclaimed territory on Earth. It was named after the wife of American naval officer Richard E. Byrd, who explored the region in the early 20th century. The territory lies in West Antarctica, east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean portion of the Antarctic or Southern Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon Byrd's exploration. Overview Because of its remoteness, even by Antarctic standards, most of Marie Byrd Land (the portion east of 150°W) has not been claimed by any sovereign state. It is by far the largest single unclaimed territory on Earth, with an area of , including Eights Coast, immediately east of Marie Byrd Land. In 1939, United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getz Ice Shelf
The Getz Ice Shelf () is an ice shelf over long and from wide, bordering the Hobbs Coast and Bakutis Coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, between the McDonald Heights and Martin Peninsula. Several large islands are partially or wholly embedded in the ice shelf. Location File:C74126s1 Ant.Dean Island Getz Ice Shelf.jpg, Western ice shelf Shepard to Carney islands File:C74112s5 Ant.Map Martin Peninsula context.jpg, Eastern ice shelf Carney Island to Martin Peninsula The Getz Ice Shelf extends along the north shore of Marie Byrd Land, from Hanessian Foreland and McDonald Heights in the west to Cape Herlacher on the Martin Peninsula to the east. The western section lies along the Hobbs Coast, while the section east of Dean Island lies along the full length of the Bakutis Coast. In the west the ice sheet is fed by glaciers that include, from west to east, Johnson Glacier, Venzke Glacier, Berry Glacier and DeVicq Glacier. Discovery and name The ice shelf westward of Siple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynolds Strait
Grant Island () is an ice-covered island, long and wide, lying east of the smaller Shepard Island off the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Like Shepard Island, Grant Island is surrounded by the Getz Ice Shelf on all but the north side. Location Grant Island is in the north, seaward edge of the Getz Ice Shelf. Reynolds Strait is on its north side, which is indented by Ledda Bay, and separates it from Forrester Island. Shepard Island is to the west. Features, from west to east, include Brookman Point, Mount Obiglio, Mount Hummel and McCarthy Point. Discovery and name Grant Island was discovered and charted by personnel aboard on February 4, 1962. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander E. G. Grant, Commanding Officer of USS ''Glacier'' at the time of discovery. Features and nearby features Brookman Point . The snow-covered northwest point of Grant Island. Discovered and first charted from the USS ''Glacier'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adélie Penguin
The Adélie penguin (''Pygoscelis adeliae'') is a species of penguin common along the entire coast of the Antarctic continent, which is the only place where it is found. It is the most widespread penguin species, and, along with the emperor penguin, is the most southerly distributed of all penguins. It is named after Adélie Land, in turn, named for Adèle Dumont d'Urville, who was married to French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville, who first discovered this penguin in 1840. Adélie penguins obtain their food by both predation and foraging, with a diet of mainly krill and fish. Taxonomy and systematics The first Adélie penguin specimens were collected by crew members of French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville on his expedition to Antarctica in the late 1830s and early 1840s. Jacques Bernard Hombron and Honoré Jacquinot, two French surgeons who doubled as naturalists on the journey, described the bird for science in 1841, giving it the scientific name ''Catarrhactes adeliæ''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Service
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. Research stations in Antarctica, scientific research and related Transport in Antarctica, logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |