|
Monument Scientific Moises Bertoni
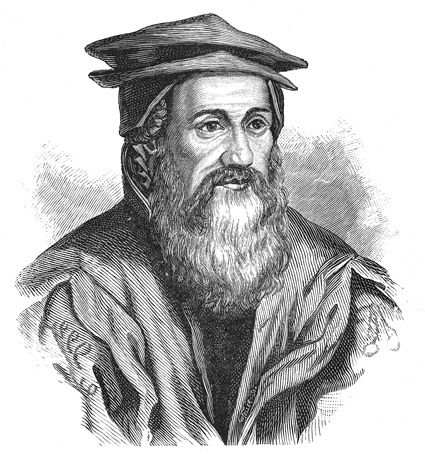
The Scientific Monument Moises Bertoni is located in the District of Presidente Franco District, Presidente Franco, Department of Alto Paraná Department, Alto Paraná, Paraguay riverside Rio Paraná, Paraná, approximately 26 km of the city of Presidente Franco and was recognized on April 13, 1955, has an area of 199 hectares. This monument was the home of wise Swiss Moisés Santiago Bertoni, Moses Santiago Bertoni (born 1857 Lottigna, Ticino, Switzerland, died 1929 Foz do Iguaçu, Foz de Iguazu, Paraguay), which eventually settled in this area while still young, and provided invaluable services to the people and Paraguayan Government. He became Minister of Agriculture, of Paraguay. He died at this site in 1929. His house It is home to the history and life of a Swiss man who investigated and learned about the culture of the Guarani people, Guaraní probably more than any other European time. Moisés Santiago Bertoni, Moses Bertoni was a real idealist and passionate botani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidente Franco District
Presidente Franco (also simply known as Franco) is a district and city of the Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay. Aside from being the oldest city in Alto Paraná Department, it is a place of rich exports of fruits and vegetables. Also, Presidente Franco is well known for Saltos del Monday, a 45 m tall and 120 m wide waterfall, Eastern Paraguay. It is a border port city in Paraguay, located in the eastern sector of the country, along the Paraná River, Alto Paraná Department. Etymology City located at the junction of rivers Paraná and Monday, neighbor of Puerto Iguazú, in Argentina, is called the "City of the Three Borders", since there converge the territories of the countries of Paraguay, Brazil and Argentina. Its name is in honor of Manuel Franco, president of Paraguay in 1918. Weather The average annual temperature is 21 °C, the highest reaches 38 °C and the minimum 0 °C. The highest annual amount of the country in rainfall occurs in the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
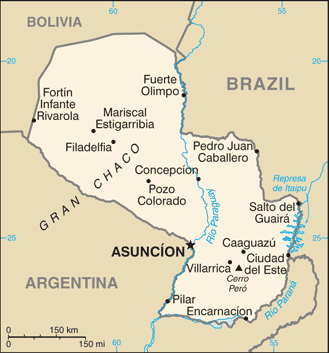
Protected Areas Of Paraguay
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourism In Paraguay
Tourism in Paraguay employs 9,500 people, according to data from 2010. Paraguay was the least visited country of South America after Guyana and Suriname, with only 610,000 international tourists for the period 2013–2014. Typical meals like sopa paraguaya, asado al asador, home made oven cooked chicken, sweets, and marmalades are an attraction for tourists. In rural areas, tourists can see crops of sugarcane, maize, cassava, snuff, coffee, peanut, rice, sorghum, tung, and spurge, as well as other fruits of the Paraguayan land, such as the avocado, handle, papaya, and pineapple. Rural tourism provides insight into the native culture of the peoples of Amazonian origin and highlights their maternal relationship to the land. Foreign tourism The count of foreign tourists in 2011 decreased by 12% from the previous year. The number of visitors entered was 520,926, while in 2010 it was of 465,264. In 2015, the number of foreign tourists exceeded 1.2 million. Arrivals by country Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Paraguay
The history of Paraguay begins with the interaction between the early Spanish colonists and the indigenous people. The agricultural Guaraní lived in eastern Paraguay and neighboring countries and the nomadic Guaycuruan tribes lived in western Paraguay. The first Spanish explorers reached Paraguay in 1524. As Paraguay lacked mineral wealth and was isolated and land-locked, it was relatively unimportant to the Spanish. The small number of Spanish men resident in Paraguay intermarried with native women, resulting in a mestizo population. Most of the Guaraní (often called "Indians" or "Indios" in older documents) adopted the Roman Catholic religion of the Spaniards, but continued to speak the Guaraní language which along with Spanish is spoken by most people in Paraguay. In the 17th and 18th century the Jesuits established missions among the Guaraní which were called reductions. The Jesuits succeeded in spreading Christianity and giving the Guaraní some degree of protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moises Bertoni Foundation
The Moises Bertoni Foundation was established in January 1988 in memory of Moisés Santiago Bertoni, as an environmental foundation and conservation, aiming to contribute to the protection and sustainable development of natural resources in Paraguay Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th .... The Foundation is a nonprofit organization that specializes in sustainable development and manages the Mbaracayu Natural Forest Reserve, the largest continuous remnant of the Interior Atlantic Forest in Paraguay. The foundation focuses on promoting environmental, social, and economic development, in an effort to overcome the dominant paradigm of conservation as something separate from human activity. On 29 July 2005, the ABC announced that in August 2005 Yan Speranza would become the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciudad Del Este
Ciudad del Este (, Spanish for Eastern City; often shortered as CDE) is the second-largest city in Paraguay and capital of the Alto Paraná Department, situated on the Paraná River. It is located 327 km from Asunción, the capital, and is adjacent to the border with Brazil, to which it is connected by the Friendship Bridge on the Paraná River. It is the largest city within the Triple Frontier region, which borders Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil and Puerto Iguazú, Argentina. The Itaipú Dam, one of the largest hydroelectric power plants in the world, is near Ciudad del Este, as is the Iguazu Falls. Ciudad del Este is a commercial city, and is one of the largest free-trade zones in the world. Its tax-free status attracts many Brazilians and Argentines to the city. Ciudad del Este has consulates for Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Peru, Uruguay, Spain, France, Germany, Italy, Slovakia, Syria, Turkey, and Taiwan. The city is home to Club Atlético 3 de Febrero, whose home groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltos Del Monday
The Municipal Park Monday and its main attraction – approximately tall and wide waterfall named Saltos del Monday – are located in the Presidente Franco District, Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay, located around 25°33'40.6"S latitude and 54°38'00.1"W longitude, occupying an area of . Weather The average annual temperature is 21 °C, the highest reaches 38 °C and the minimum 0 °C. The highest annual amount of the country in rainfall occurs in the region of Alto Paraná. Animals and Plants The Municipal Park Monday includes a natural reserve of nine hectares covered by a thick vegetation, rich with diverse species of flora and fauna and is one of the last remaining blocks of the Alto Paraná Atlantic forests west from the Paraná River. Hydrography The Monday River empties into the Paraná River, has a variable flow depending on the seasons of rain. Tourism In Presidente Franco District, nature gives the region a show over the waters, the imposing Mond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryocopus Galeatus
The helmeted woodpecker (''Celeus galeatus'') is a species of bird in the family Picidae. It has been recorded from far northeastern Argentina, southeastern Brazil, and eastern Paraguay. Its habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. It is threatened by habitat loss. Taxonomy Coenraad Jacob Temminck described the helmeted woodpecker in 1822. Its specific epithet is from the Latin word ''galea'', meaning "helmet". It was reclassified as ''Hylatomus galeatus'' by some authorities. Upon sequencing the mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, two studies published in 2015 found that it lay genetically with the latter genus and proposed the name ''Celeus galeatus''. The placement of the helmeted woodpecker in the genus ''Celeus'' was accepted by the International Ornithologists' Union. Its genetic position indicates that it has evolved to mimic the lineated woodpecker (''Dryocopus lineatus''), whose range it shares, by adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate ( Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araucaria Angustifolia
''Araucaria angustifolia'', the Paraná pine, Brazilian pine or candelabra tree (, or ), is a critically endangered species in the conifer genus '' Araucaria''. Although the common names in various languages refer to the species as a "pine", it does not belong in the genus ''Pinus''. Origin and taxonomy The genus ''Araucaria'' was part of terrestrial flora since the Triassic and found its apogee in Gondwana. Today, it is restricted to the Southern Hemisphere and has 19 species. Distribution Covering an original area of , it has now lost an estimated 97% of its habitat to logging, agriculture, and silviculture. It is native to southern Brazil (also found in high-altitude areas of southern Minas Gerais, in central Rio de Janeiro and in the east and south of São Paulo, but more typically in the states of Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul). According to a study made by Brazilian researcher Reinhard Maack, the original area of occurrence represented 36.67% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |