|
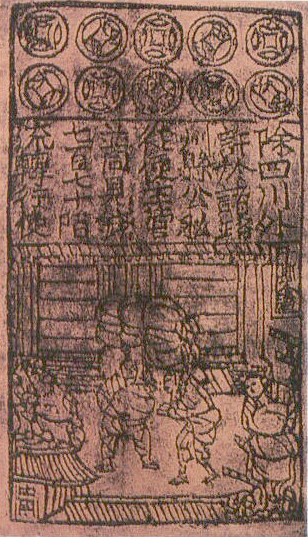
Momme (unit)
is both a Japanese unit of mass and former unit of currency. As a measurement, ''Momme'' is part of a table of Japanese units where during the Edo period it was equal to ryō (aka Tael). Since the Meiji era 1 momme has been reformed to equal exactly 3.75 grams in SI units. The latter term for Momme refers to when it was used as a unit of currency during the Edo period in the form of silver coins. As a term, the word "Momme" and its symbol "匁" are unique to Japan. The Chinese equivalent to ''Momme'' is ''qián'' (), which is also a generic word for "money". While the term ''Momme'' is no longer used for currency, it survives as a standard unit of measure used by pearl dealers to communicate with pearl producers and wholesalers. Origin The Japanese word ''Momme'' first appeared in a family book by the Ōuchi clan during the Bunmei era in 1484. In the English language the word first appears in the early 1700s per the Oxford English Dictionary, which first traces its usag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo), Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Edo society, Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of ''Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyō'' administering a ''Han system, han'' (feudal domain), although the country was still nominally organized as provinces of Japan, imperial provinces. Under the Tokugawa shogunate, Japan experienced rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first edition in 1884, traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, and provides ongoing descriptions of English language usage in its variations around the world. In 1857, work first began on the dictionary, though the first edition was not published until 1884. It began to be published in unbound Serial (literature), fascicles as work continued on the project, under the name of ''A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles; Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by The Philological Society''. In 1895, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' was first used unofficially on the covers of the series, and in 1928 the full dictionary was republished in 10 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (See: World economy.) In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). While international trade has existed throughout history (for example Uttarapatha, Silk Road, Amber Road, salt roads), its economic, social, and political importance has been on the rise in recent centuries. Carrying out trade at an international level is a complex process when compared to domestic trade. When trade takes place between two or more states, factors like currency, government policies, economy, judicial system, laws, and markets influence trade. To ease and justify the process of trade between countries of different economic standing in the modern era, some international economic organizations were formed, such as the World Trade Organization. These organizations work towards the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), Mole (unit), mole (mol), and candela (cd). An SI derived unit is a named combination of base units such as hertz (cycles per second), Newton (unit), newton (kg⋅m/s2), and tesla (unit), tesla (1 kg⋅s−2⋅A−1) and in the case of Celsius a shifted scale from Kelvin. Certain units have been Non-SI units mentioned in the SI#Units officially accepted for use with the SI, officially accepted for use with the SI. Some of these are decimalised, like the litre and electronvolt, and are considered "metric". Others, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Environment
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryō
The was a gold currency unit in the shakkanhō system in pre- Meiji Japan. It was eventually replaced with a system based on the '' yen''. Origins The ''ryō'' was originally a unit of weight from China, the ''tael.'' It came into use in Japan during the Kamakura period. By the Azuchi–Momoyama period it had become nearly uniform throughout Japan, about 4.4 ''monme'' as a unit of weight (about the same as 16.5 grams). During the Sengoku period, various local ''daimyō'' began to mint their own money. One of the best known and most prestigious of these private coins was the ''kōshūkin'' (甲州金, ''coin/gold of the Kōshū Province'') issued by warlord Takeda Shingen, who had substantial gold deposits within his territories. The value of the ''kōshūkin'' was based on its weight, with one ''kōshūkin'' equal to one ryō of gold, and thus stamped with its weight (about 15 grams). The exchange rate fluctuated. A ''ryō'' of gold was worth 3 kan (3000) copper coins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market. Traders generally negotiate through a medium of credit or exchange, such as money. Though some economists characterize barter (i.e. trading things without the use of money) as an early form of trade, money was invented before written history began. Consequently, any story of how money first developed is mostly based on conjecture and logical inference. Letters of credit, paper money, and non-physical money have greatly simplified and promoted trade as buying can be separated from selling, or earning. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade. In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labor, a predominant form of economic activity in which individuals and groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |