|
Molecular Symmetry
In chemistry, molecular symmetry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical property, chemical properties, such as whether or not it has a molecular dipole moment, dipole moment, as well as its allowed spectroscopy, spectroscopic transitions. To do this it is necessary to use group theory. This involves classifying the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Symmetry is useful in the study of molecular orbitals, with applications to the Hückel method, to ligand field theory, and to the Woodward–Hoffmann rules. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy and inorganic chemistry discuss symmetry. Another framework on a larger scale is the use of crystal sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde Symmetry Elements
Formaldehyde ( , ) (Preferred IUPAC name, systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that Polymerization, polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as aqueous solutions (formalin), which consists mainly of the hydrate CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). As a precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds, in 2006 the global production of formaldehyde was estimated at 12 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Formaldehyde also occurs naturally. It is derived from the degradation of serine, dimethylglycine, and lipids. Demethylases act by converting N-methyl groups to formaldehyde. Formaldehyde is classified as a group 1 carcinogen and can cause respiratory and skin irritation upon exposure. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal System
In crystallography, a crystal system is a set of point groups (a group of geometric symmetries with at least one fixed point). A lattice system is a set of Bravais lattices (an infinite array of discrete points). Space groups (symmetry groups of a configuration in space) are classified into crystal systems according to their point groups, and into lattice systems according to their Bravais lattices. Crystal systems that have space groups assigned to a common lattice system are combined into a crystal family. The seven crystal systems are ''triclinic'', ''monoclinic'', ''orthorhombic'', ''tetragonal'', ''trigonal'', ''hexagonal'', and ''cubic''. Informally, two crystals are in the same crystal system if they have similar symmetries (though there are many exceptions). Classifications Crystals can be classified in three ways: lattice systems, crystal systems and crystal families. The various classifications are often confused: in particular the trigonal crystal system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a ''center of rotation''. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientation (geometry), orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis, rotation around a axis. The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or ''autorotation''). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal ''spin axis'' can be called a ''pole''; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or ''orbit''), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Element
In chemistry and crystallography, a symmetry element is a point, line, or plane about which symmetry operations can take place. In particular, a symmetry element can be a mirror plane, an axis of rotation (either proper and improper), or a center of inversion. For an object such as a molecule or a crystal, a symmetry element corresponds to a set of symmetry operations, which are the rigid transformations employing the symmetry element that leave the object unchanged. The set containing these operations form one of the symmetry groups of the object. The elements of this symmetry group should not be confused with the "symmetry element" itself. Loosely, a symmetry element is the geometric set of fixed points of a symmetry operation. For example, for rotation about an axis, the points on the axis do not move and in a reflection the points that remain unchanged make up a plane of symmetry. Identity The identity symmetry element is found in all objects and is denoted ''E''. It cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
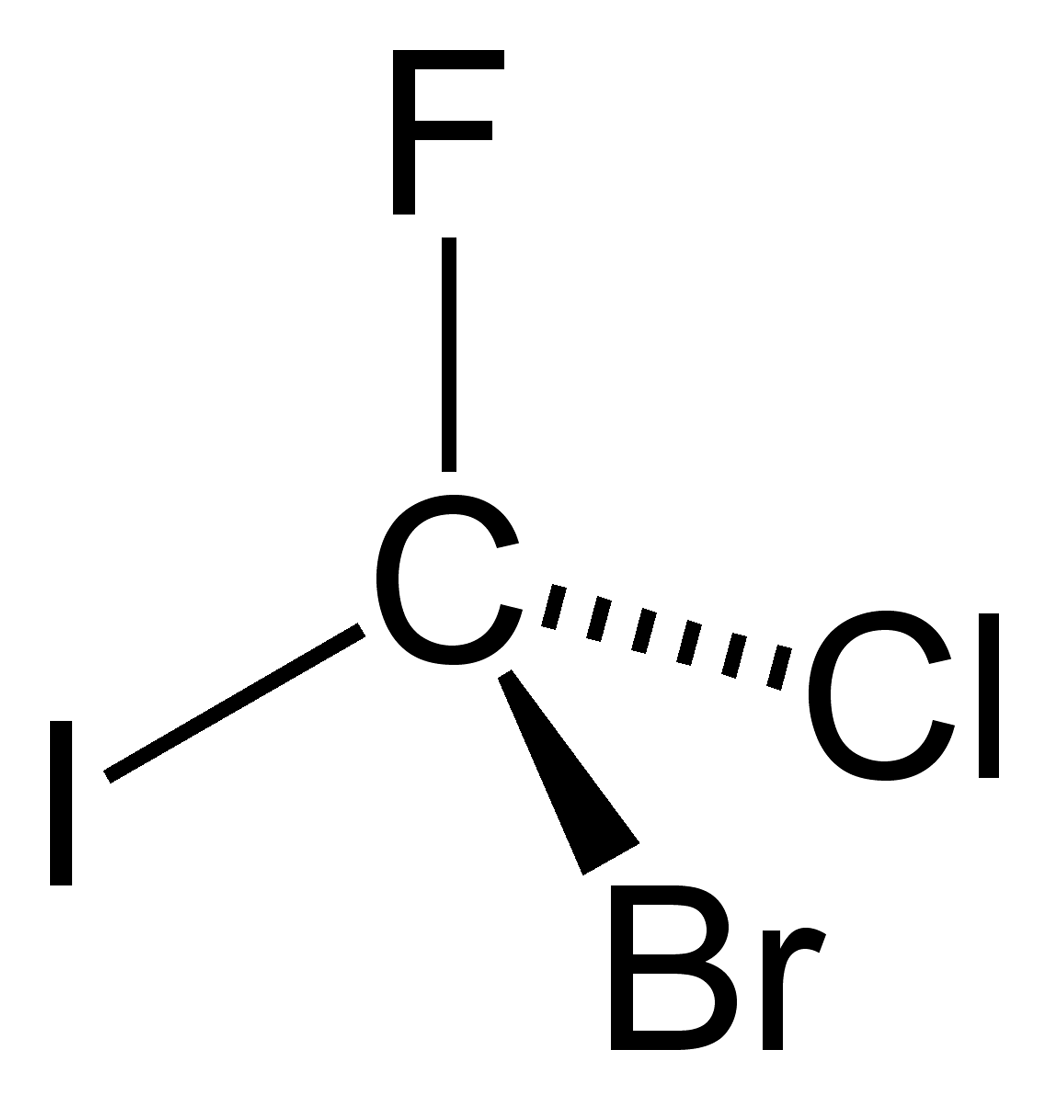
Chiral Sym CCXYXY
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superposed (not to be confused with superimposed) onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called '' enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, ''enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superposable mirror ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral Sym CHHXX
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be wikt:superpose, superposed (not to be confused with wikt:superimpose, superimposed) onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called ''enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, ''enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral Sym CCCXYXY
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superposed (not to be confused with superimposed) onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called '' enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, ''enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superposable mirror ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotation (geometry), rotations, translation (geometry), translations, and some Conformational isomerism, conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physics, physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activity, optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic mixture, racem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |