|
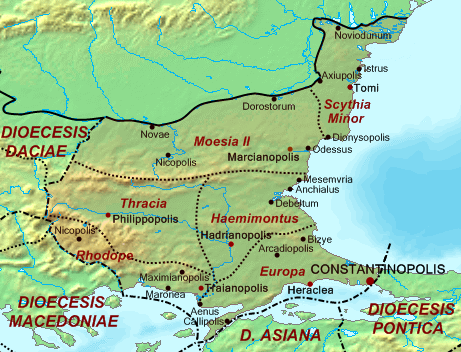
Moesia Secunda
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region of Moesia was inhabited chiefly by Thracian, Illyrian, and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, the Latin name of a Thracian tribe who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moesia be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracia Outcut From Roman Provinces Of Illyricum, Macedonia, Dacia, Moesia, Pannonia And Thracia
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the Roman Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
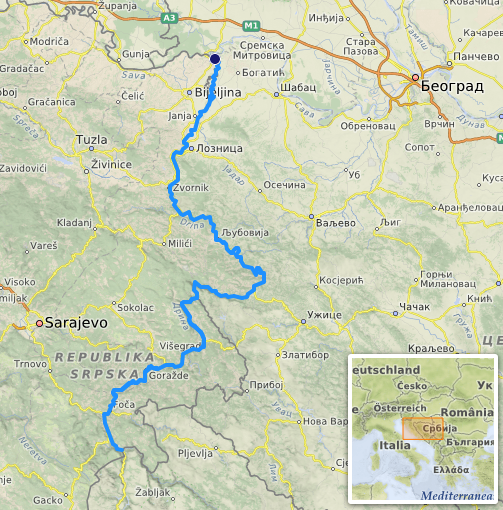
Drinus
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long river in the Balkans, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps which belongs to the Danube River drainage basin. Its name is derived from the Ancient Rome, Roman name of the river () which in turn is derived from Greek language, Greek (Ancient Greek: ) which is derived from the native name of Illyrian language, Illyrian origin. But, this etymology is not sure.Illyrian languages are poorly documented (only ~50 glosses, mostly personal/place names). - No surviving texts exist, unlike Thracian (which has ~200 inscriptions and loanwords in Greek). - Scholars often label any pre-Slavic Balkan hydronym as "Illyrian" by default, even without proof.We don’t know if Drinus was Illyrian, Thracian, or another lost Paleo-Balkan language. - The safest claim: Drina derives from a ancient Indo-European roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a Roman consul, consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority. In the Roman Republic, military command, or ''imperium'', could be exercised constitutionally only by a consul. Only two consuls served at a time, each elected to a one-year term. They could not normally serve two terms in a row; if a military campaign was in progress at the end of a consul's term, the consul in command might have his command Prorogatio, prorogued, allowing him to continue in command. This custom allowed for continuity of command despite the high turnover of consuls. In the Roman Empire, proconsul was a title held by a civil governor and did not imply military command. In modern times, various officials with notable delegated authority have been referred to as proconsuls. Studies of leadership typically divide leaders into policymakers and subordinate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Scribonius Curio (consul 76 BC)
Gaius Scribonius Curio (c. 124 – 53 BC) was a Roman statesman, soldier and a famous orator. He was nicknamed Burbuleius (after an actor) for the way he moved his body while speaking. Curio was noted as a public orator and for the purity of his Latin language. Career He was probably born between 125 and 123 BC. In 90 BC, during the Social War, Curio was a tribune of the plebs. From 87 BC until 81 BC he served as a legate under Lucius Cornelius Sulla; First in Greece and Asia during Sulla's campaigns against king Mithridates of Pontus then against the Cinna- Marius faction during Sulla's civil war. During the First Mithridatic War he besieged the Athenian tyrant Aristion, who had taken position on the Acropolis, during the Siege of Athens. In 76 BC, he was elected consul, along with Gnaeus Octavius. After his consulship he was allocated Macedonia as his proconsular command. He successfully fought the Dardani and the Moesians, for which the Senate granted him a triumph. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of information about the Getae are Greek and Roman chroniclers, who write that the Getae were closely related to the neighbouring Thracians to the south and Dacians to the north. Cassius Dio writes that the Getae are the same people as the Dacians, Getae being the Greek name for the Dacians. Modern scholars continue to debate the details of these relationships. The Getae first appear in historical records as fierce opponents of the Scythian campaign of Darius I, Persian invasion in 513 BC, as described by the early Greek historian Herodotus. They faded out of historical records during the Roman Empire, when many appear to have become Romans, and others north of the Danube were gradually overwhelmed by other peoples moving from the north and east tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burebista
Burebista () was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, and modern day Romania and Moldova. In the 7th and 6thcenturies BC it became home to the Thracian peoples, including the Getae and the Dacians. From the 4thcentury to the middle of the 2ndcentury BC the Dacian peoples were influenced by La Tène Celts who brought new technologies with them into Dacia. Sometime in the 2ndcentury BC, the Dacians expelled the Celts from their lands. Dacians often warred with neighbouring tribes, but the relative isolation of the Dacian peoples in the Carpathian Mountains allowed them to survive and even to thrive. By the 1stcentury BC the Dacians had become the dominant power. From 61 BC onwards Burebista pursued a series of conquests that expanded the Dacian kingdom. The tribes of the Boii and Taurisci we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any group of people organized for governance, such as the board of a corporation, the government of a country, or the government of a country subdivision. A polity may have various forms, such as a republic administered by an elected representative, the realm of a hereditary monarch, and others. The preeminent polities today are Westphalian sovereignty, Westphalian states and nation-states, commonly referred to as countries. Overview In geopolitics, a polity can manifest in different forms such as a State (polity), state, an empire, an international organization, a political organization or another identifiable, resource-manipulating organizational structure. A polity like a state does not need to be a Sovereignty, sovereign unit. The preeminent polities tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Conquest Of Dacia
Trajan's Dacian Wars (101–102, 105–106) were two military campaigns fought between the Roman Empire and Dacia during Emperor Trajan's rule. The conflicts were triggered by the constant Dacian threat on the Danubian province of Moesia and also by the increasing need for resources of the economy of the Empire. Background Throughout the 1st century, Roman policy dictated that threats from neighbouring nations and provinces were to be contained promptly. Dacia had been on the Roman agenda since before the days of Caesar when the Dacians defeated a Roman army at the Battle of Histria. Domitian's Dacian War had re-established peace with Dacia in 89 AD. However, the Dacian king Decebalus used the Roman annual subsidy of 8 million sestercesJones (1992), p150. and craftsmen in trades devoted to both peace and war, and war machines intended to defend the empire's borders to fortify his own defences instead. Despite some co-operation on the diplomatic front with Domitian, Decebalu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesi
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; , ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the Timok River to the south of the Danube. The Moesi do not appear in ancient sources before Augustus's death in 14 CE and are mentioned only by three authors dealing with the Roman warfare in the region and the ethnonymic situation between mid-1st century BC and mid-1st century CE: Ovid, Strabo and Livy. Recent research suggests that a Paleo-Balkan people known as the ''Moesi'' never actually existed but the name was transplanted from Asia Minor Mysians to the Balkans by the Romans as an alternative name for the people who lived in the later province of Moesia Superior as Dardani communities. This decision in Roman literature is linked to the appropriation of the name ''Dardani'' in official Roman ideological discourse as Trojan ancestors of the Romans and the creation of a fictive name for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thraco-Illyrian
The term Thraco-Illyrian refers to a hypothesis according to which the Daco-Thracian and Illyrian languages comprise a distinct branch of Indo-European. Thraco-Illyrian is also used as a term merely implying a Thracian- Illyrian interference, mixture or sprachbund, or as a shorthand way of saying that it is not determined whether a subject is to be considered as pertaining to Thracian or Illyrian. Downgraded to a geo-linguistic concept, these languages are referred to as Paleo-Balkan. The linguistical hypothesis was especially current in the early 20th century, but after the 1960s it was seriously called into question. New publications argued that no strong evidence for Thraco-Illyrian exists, and that the two language-areas show more differences than correspondences ( Vladimir Georgiev, Ivan Duridanov, Eric Hamp, ''et al.''). It has also been pointed out that the onomastic studies carried out in the 20th century were conducted through pan-Thracian and pan-Illyrian theoretica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrians
The Illyrians (, ; ) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Ancient Greece, Greeks. The territory the Illyrians inhabited came to be known as Illyria to later Greek and Roman Republic, Roman authors, who identified a territory that corresponds to most of Albania, Montenegro, Kosovo, much of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, western and central Serbia and some parts of Slovenia between the Adriatic Sea in the west, the Drava river in the north, the Great Morava, Morava river in the east and the Ceraunian Mountains in the south. The first account of Illyrian people dates back to the 6th century BC, in the works of the ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus. The name "Illyrians", as applied by the ancient Greeks to their northern neighbors, may have referred to a broad, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |