|
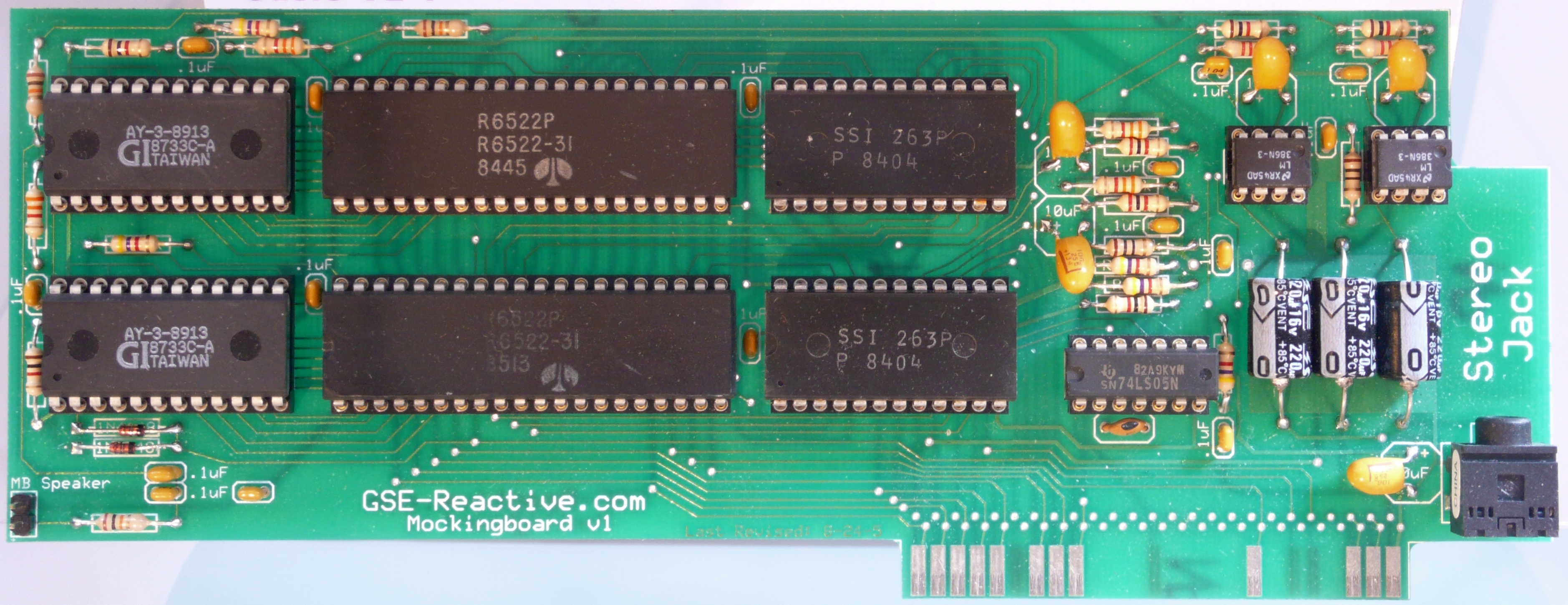
Mockingboard
The Mockingboard (a pun on "Mockingbird") is a sound card built by Sweet Micro Systems for the Apple II microcomputers. It improves on the Apple II's limited sound capabilities, as did other Apple II sound cards. In 1981, Sweet Micro Systems began designing products not only for creating music, but speech and general sound effects as well, culminating in the release of the Mockingboard in 1983. The Sound II was introduced at , and the Sound/Speech I at . The Mockingboard's hardware allowed programmers to create complex, high-quality sound without need for constant Central processing unit, CPU attention. The Mockingboard could be connected to the Apple's built-in speaker or to external Loudspeaker, speakers. However, as the quality of the built-in speaker was not high, the instruction manual recommended obtaining external speakers. The Mockingboard was available in various models for either the slot-based Apple II / Apple II Plus / Apple IIe systems or in one special model for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Card
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term ''sound card'' is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications. Sound functionality can also be integrated into the motherboard, using components similar to those found on plug-in cards. The integrated sound system is often still referred to as a ''sound card''. Sound processing hardware is also present on modern video cards with HDMI to output sound along with the video using that connector; previously they used a S/PDIF connection to the motherboard or sound card. Typical uses of sound cards or sound card functionality include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection. Sound cards are also used for computer-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Cards
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term ''sound card'' is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications. Sound functionality can also be integrated into the motherboard, using components similar to those found on plug-in cards. The integrated sound system is often still referred to as a ''sound card''. Sound processing hardware is also present on modern video cards with HDMI to output sound along with the video using that connector; previously they used a S/PDIF connection to the motherboard or sound card. Typical uses of sound cards or sound card functionality include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection. Sound cards are also used for computer-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II Sound Cards
Throughout its lengthy, multi-model lifespan, the Apple II series computers lacked any serious built-in sound capabilities. At the time of its release in 1977, this did not distinguish it from its contemporaries (ex. the TRS-80 and Commodore PET), but by 1982, it shared the market with several sound-equipped competitors such as the Commodore 64, whose MOS Technology SID, SID chip could produce sophisticated multi-timbral music and sound effects. All Apple II models (except the Apple IIGS, a significantly different, albeit backwards-compatible machine) possess a speaker, but it was limited to 1-bit output in the form of a simple voltage the user could switch on and off with software, creating clicks from the speaker each time the state was toggled. By turning the signal on and off rapidly, sounds with pitches could be produced. This approach places extreme constraints on software design, since it requires the CPU to be available to toggle the output at specific frequencies, and all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Street Music Writer
Bank Street Music Writer is an application for composing and playing music for the Atari 8-bit computers, Apple II, Commodore International, Commodore 64 and IBM PC. It was written by Glen Clancy - Biblio.com and published by Mindscape. The original Atari version, developed under the name "Note Processor", was released in 1985 and uses the computer's on-board sound chip to produce four-voice music recordings. The Commodore 64 version also uses that system's sound hardware, while the Apple (with ) and IBM PC versions require a Mindscape Music Board which was in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votrax
Votrax International, Inc. (originally the Vocal division of Federal Screw Works), or just Votrax, was a speech synthesis company located in the Detroit, Michigan area from 1971 to 1996. It began as a division of Federal Screw Works from 1971 to 1973. In 1974, it was given the ''Votrax'' name (taken from the name of its first commercial product, the model VS4 "Votrax") and moved to Troy, Michigan and, in 1980, split off of its parent company entirely and became Votrax International, Inc., which produced speech products up until 1984.Artic History  In 1984, the company restructured itself as a commercial phone/speech audio-response/auto-answering systems ...
In 1984, the company restructured itself as a commercial phone/speech audio-response/auto-answering systems ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
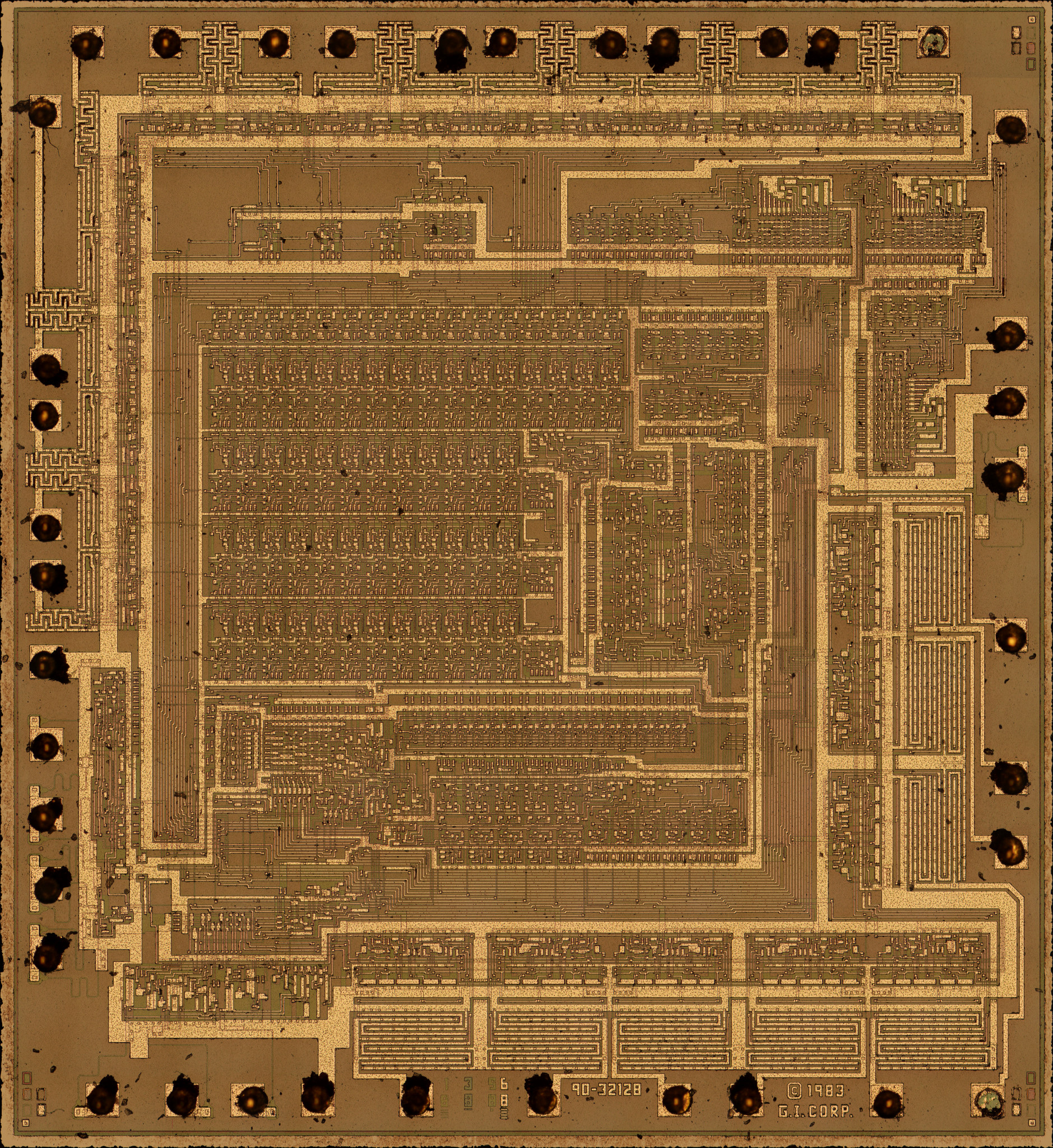
General Instrument AY-3-8910
The AY-3-8910 is a 3-voice programmable sound generator (PSG) designed by General Instrument (GI) in 1978, initially for use with their 16-bit computing, 16-bit General Instrument CP1600, CP1610 or one of the PIC microcontrollers, PIC1650 series of 8-bit computing, 8-bit microcomputers. The AY-3-8910 and its variants were used in many arcade games—Konami's ''Gyruss'' contains five—and Bally pinball machines as well as being the sound chip in the Intellivision and Vectrex video game consoles, and the Amstrad CPC, Oric-1, Colour Genie, Elektor TV Games Computer, MSX, Tiki 100 and later ZX Spectrum home computers. It was also used in the Mockingboard and Cricket sound cards for the Apple II and the Speech/Sound Cartridge for the TRS-80 Color Computer. After GI's spinoff of Microchip Technology in 1987, the chip was sold for a few years under the Microchip brand. It was also manufactured under license by Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha (with a selectable clock divider pin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phasor (sound Synthesizer)
Phasor is a stereo music, sound and speech synthesizer created by Applied Engineering for the Apple II family of computers. Consisting of a sound card and a set of related software, the Phasor system was designed to be compatible with most software written for other contemporary Apple II cards, including the Sweet Micro Systems Mockingboard, ALF's Apple Music Synthesizer, Echo+ An echo is a reflection of sound. Echo may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Echo (DC Comics), various different characters * Echo (Dollhouse), Echo (''Dollhouse''), the protagonist of the TV series ''Dollhouse' ... and Applied Engineering's earlier card Super Music Synthesizer. References ;NotesPhasor Manual External linksApplied Engineering 1986 Summer/Fall Catalog. Phasor appears on page 12 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
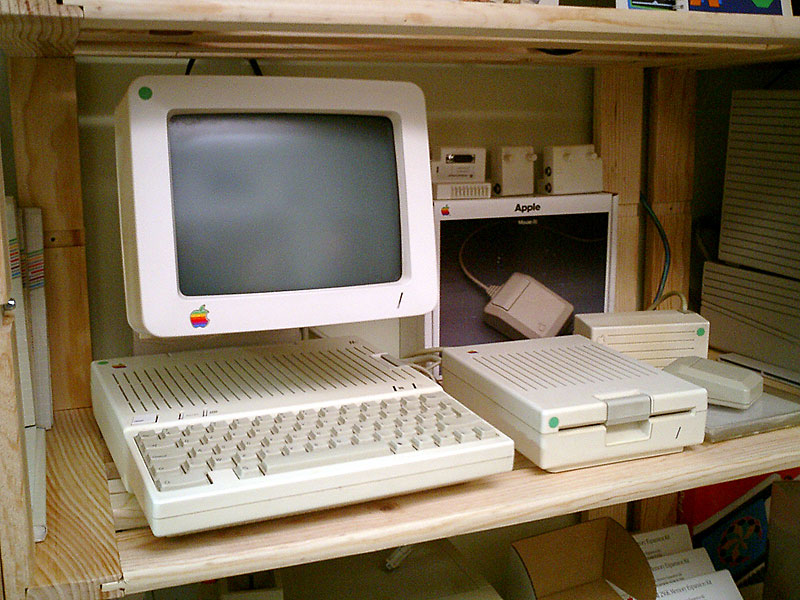
Apple IIc
The Apple IIc is a personal computer introduced by Apple Inc. shortly after the launch of the Macintosh 128K, original Macintosh in 1984. It is essentially a compact and portable version of the Apple IIe. The IIc has a built-in floppy disk drive and a keyboard, and was often sold with its matching monitor. The ''c'' in the name stands for ''compact'', referring to the fact it is a complete Apple II setup in a smaller notebook-sized housing. The computer is compatible with a wide range of Apple II software and peripherals. The Apple IIc has rear peripheral expansion ports integrated onto the main logic board instead of the expansion slots and direct motherboard access of earlier Apple II models. Apple intended the Apple IIc to require less technical expertise to use. The Apple IIc weighs . It was succeeded by the Apple IIc Plus in 1988. History The Apple IIc was released on April 24, 1984, during an Apple-held event called ''Apple II Forever''. With that motto, Apple proclaimed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal language text into speech; other systems render symbolic linguistic representations like phonetic transcriptions into speech. The reverse process is speech recognition. Synthesized speech can be created by concatenating pieces of recorded speech that are stored in a database. Systems differ in the size of the stored speech units; a system that stores phones or diphones provides the largest output range, but may lack clarity. For specific usage domains, the storage of entire words or sentences allows for high-quality output. Alternatively, a synthesizer can incorporate a model of the vocal tract and other human voice characteristics to create a completely "synthetic" voice output. The quality of a speech synthesizer is judged by its similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II Peripheral Cards
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are cultivated worldwide. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, '' Malus sieversii'', is still found. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Eurasia before they were introduced to North America by European colonists. Apples have cultural significance in many mythologies (including Norse and Greek) and religions (such as Christianity in Europe). Apples grown from seeds tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. For commercial purposes, including botanical evaluation, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after planting. Rootstocks are used to control the speed of growth and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPL3
The OPL (FM Operator Type-L) series is a family of sound chips developed by Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha. It consists of low-cost sound chips providing frequency modulation synthesis, FM synthesis for use in computing, music and video game applications. The OPL series of chips enabled the creation of affordable sound cards for IBM PC compatibles in the late 1980s such as the Ad Lib, Inc., AdLib and Sound Blaster, effectively becoming a de-facto standard until they were supplanted by "Wavetable synthesis#Background, wavetable synthesis" cards in the early-to-mid 1990s. Internal operation The internal operation of the chips is completely digital. Each FM-tone is generated by a digital oscillator using a form of direct digital synthesis. A low-frequency oscillator and an envelope generator drive an FM operator to produce floating-point output for the DAC. Decapsulation of the chips shows two look-up tables, one for calculating exponents and one for log-sine. This allows the FM operato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |