|
Mobility (military)
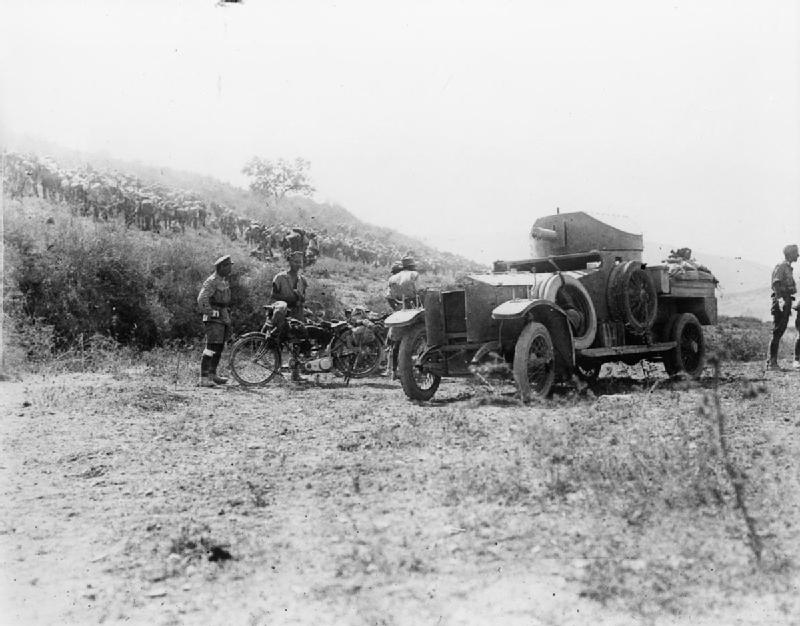
Mobility in military terms refers to the ability of a weapon system, combat unit or armed force to move toward a military objective. Combat forces with a higher mobility are able to move more quickly, and/or across more hostile terrain, than forces with lower mobility. Mobility is regarded as a vital component of the modern battlefield, as the ability to deliver weapon systems or combat units to their objective quickly can often mean the difference between victory and defeat. Armies around the world have massively increased their mobility over the last 100 years. In World War I, for example, most combat units could move on the battlefield only as fast as a soldier could walk. In the face of overwhelming firepower presented by machine guns and artillery, that resulted in stalemate and an inability to outmaneuver the enemy. By World War II, battlefield mobility had greatly improved with the development of the tank, and with tracked and other mechanized vehicles, to move forces to, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Terminology
Military terminology refers to the terminology, terms and language of military organizations, military personnel, personnel, and military doctrine. Much like other forms of corporate jargon, military terminology is distinguishable from colloquial language by its use of new or repurposed words and phrases typically only understandable by current and former members of the military or associated companies and agencies. Common understanding The operational pressure for uniform understanding has developed since the early 20th century with the importance of Joint warfare, joint operations between different services (army, navy, air force) of the same country. International alliances and operations, including peacekeeping, have added additional complexity. For example, the NATO alliance now maintains a large dictionary of common terms for use by member countries. Development work is also taking place between NATO and Russia on common terminology for extended air defence, in English, Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwerpunkt
''Blitzkrieg'(Lightning/Flash Warfare)'' is a word used to describe a combined arms surprise attack, using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with artillery, air assault, and close air support. The intent is to break through an opponent's lines of defense, dislocate the defenders, confuse the enemy by making it difficult to respond to the continuously changing front, and defeat them in a decisive : a battle of annihilation. During the interwar period, aircraft and tank technologies matured and were combined with the systematic application of the traditional German tactic of (maneuver warfare), involving the deep penetrations and the bypassing of enemy strong points to encircle and destroy opposing forces in a (cauldron battle/battle of encirclement). During the invasion of Poland, Western journalists adopted the term ''blitzkrieg'' to describe that form of armored warfare. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke Point
In military strategy, a choke point (or chokepoint), or sometimes bottleneck, is a geographical feature on land such as a valley, defile or bridge, or maritime passage through a critical waterway such as a strait, which an armed force is forced to pass through in order to reach its objective, sometimes on a substantially narrowed front and therefore greatly decreasing its combat effectiveness by making it harder to bring superior numbers to bear. A choke point can allow a numerically inferior defending force to use the terrain as a force multiplier to thwart or ambush a much larger opponent, as the attacker cannot advance any further without first securing passage through the choke point. Historical examples Some historical examples of the tactical use of choke points are King Leonidas I's defense of the Pass of Thermopylae during an invasion led by Xerxes I of Persia; the Battle of Stamford Bridge in which Harold Godwinson defeated Harald Hardrada; William Wallace' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
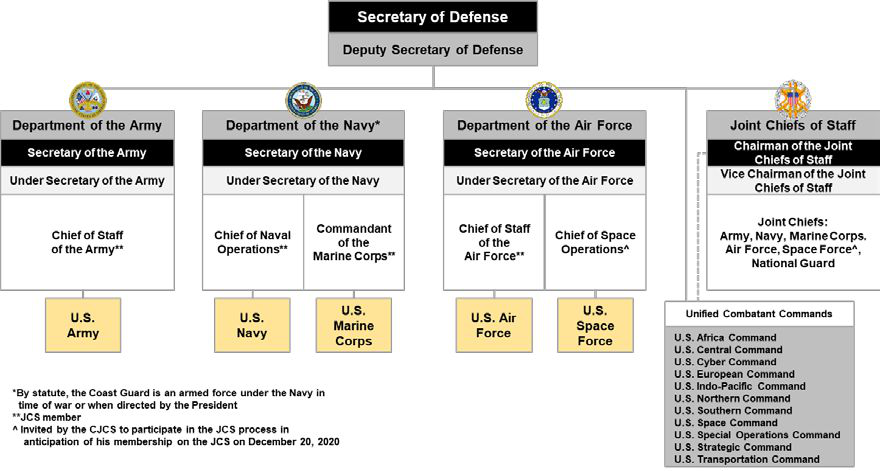
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battlefield
A battlefield, battleground, or field of battle is the location of a present or historic battle involving ground warfare. It is commonly understood to be limited to the point of contact between opposing forces, though battles may involve troops covering broad geographic areas. Although the term implies that battles are typically fought in a Plain, field – an open stretch of level ground – it applies to any type of terrain on which a battle is fought. The term can also have legal significance, and battlefields may have substantial historical and cultural value—the battlefield has been described as "a place where ideals and loyalties are put to the test".Veronica Fiorato, Anthea Boylston, Christopher Knüsel, ''Blood Red Roses: The Archaeology of a Mass Grave from the Battle of Towton AD 1461'' (2007), p. 3. Various acts and treaties restrict certain belligerent conduct to an identified battlefield. Other legal regimes promote the preservation of certain battlefields as si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark A
Mark may refer to: In the Bible * Mark the Evangelist (5–68), traditionally ascribed author of the Gospel of Mark * Gospel of Mark, one of the four canonical gospels and one of the three synoptic gospels Currencies * Mark (currency), a currency or unit of account in many nations * Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, the currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina * East German mark, the currency of the German Democratic Republic * Estonian mark, the currency of Estonia between 1918 and 1928 * Finnish markka (), the currency of Finland from 1860 until 28 February 2002 * Polish mark (), the currency of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Republic of Poland between 1917 and 1924 German * Deutsche Mark, the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until 2002 * German gold mark, the currency used in the German Empire from 1873 to 1914 * German Papiermark, the German currency from 4 August 1914 * German rentenmark, a currency issue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of Staff Of The United States Army
The chief of staff of the Army (CSA) is a statutory position in the United States Army held by a general officer. As the highest-ranking officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Army, the chief is the principal military advisor and a deputy to the secretary of the Army. In a separate capacity, the CSA is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff () and, thereby, a military advisor to the National Security Council, the secretary of defense, and the president of the United States. The CSA is typically the highest-ranking officer on active duty in the U.S. Army unless the chairman or the vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff are Army officers. The chief of staff of the Army is an administrative position based in the Pentagon. While the CSA does not have operational command authority over Army forces proper (which is within the purview of the combatant commanders who report to the secretary of defense), the CSA does exercise supervision of army units and organizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition, And Reconnaissance
ISTAR stands for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance. In its macroscopic sense, ISTAR is a practice that links several battlefield functions together to assist a combat force in employing its sensors and managing the information they gather. Information is collected on the battlefield through systematic observation by deployed soldiers and a variety of electronic sensors. ''Surveillance'', ''target acquisition'' and ''reconnaissance'' are methods of obtaining this information. The information is then passed to intelligence personnel for analysis, and then to the commander and their staff for the formulation of battle plans. Intelligence is processed information that is relevant and contributes to an understanding of the ground, and of enemy dispositions and intents. Intelligence failures can happen. ISR (Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance) ISR is the coordinated and integrated acquisition, processing and provision of timely, accurat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Transport
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Clément Ader built the "Ader Éole" in France and made an uncontrolled, powered hop in 1890. This was the first powered aircraft, although it did not achieve controlled flight. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896. A major leap followed with the construction of the ''Wright Flyer'', the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet engine which enabled aviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Unit
Military organization ( AE) or military organisation ( BE) is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. Formal military organization tends to use hierarchical forms (see Modern hierarchy for terminology and approximate troop strength per hierarchical unit). In some countries, paramilitary forces are included in a nation's armed forces, though not considered military. Armed forces that are not a part of military or paramilitary organizations, such as insurgent forces, often emulate military organizations, or use these structures. History The use of formalized ranks in a hierarchical structure came into widespread use with the Roman Army. The Roman Army was organized into legions, each comprising around 5000 soldiers and led by a legate. Each legion was further divided into centuries which were led by centurions. In modern times, executive control, management and administration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |